Question
Please Help complete the TODO's CompletedTwoProbeChainHT.java the other codes are completed Main.java public class Main { /** * entry point for testing * * @param
Please Help complete the TODO's CompletedTwoProbeChainHT.java the other codes are completed
Main.java
public class Main { /** * entry point for testing * * @param args the command line arguments */ public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("TwoProbeChainHT: "); //Uncomment as needed. //testIntegers(new CompletedTwoProbeChainHT
st.put(38334343, 92); assert(!st.isEmpty()) : "symbol table is empty after inserting elemetns"; assert(st.size() == 11) : "does not contain correct number of elements"; assert(st.contains(-42341145)) : "added key -42341145 does not exist"; assert(st.contains(0)) : "added key 0 does not exist" ; assert(st.contains(38334343)) : "added key 38334343 does not exist"; assert(!st.contains(-62341145)) : "contains unknown key -62341145"; assert(!st.contains(-1)) : "contains unknown key -1"; assert(!st.contains(58334343)) : "contains unknown key -58334343"; Set
//delete key not there size = st.size(); st.delete(49); assert(st.get(49) == null) : "returned non-null for key that was deleted"; assert(st.size() == size) : "size changed"; assert(!st.contains(49)) : "a missing key is contained after it was deleted"; //delete key there (48, 42) size = st.size(); st.delete(48); assert(st.get(48) == null) : "returned non-null for key that was deleted"; assert(st.size() == size - 1) : "size did not update"; assert(!st.contains(48)) : "a deleted key is still contained"; System.out.println(" DONE "); } /** * Test string operations on symbol table implementation. No JUnit; ugly. * * @param st An object implementing a symbol table. */ public static void testStrings(SymbolTable
/ote: the following code does not check if keys is maintained properl- it should. System.out.println(" Testing put()... "); //add new key int size = st.size(); st.put("TEST", 42); assert(st.size() == size + 1) : "size did not update."; assert(st.contains("TEST")) : "does not contain new key"; assert(st.get("TEST") == 42) : "does not return correct value"; //update existing key size = st.size(); st.put("AAAA", 2); assert(st.size() == size) : "size changed"; assert(st.contains("AAAA")) : "does not contain updated key"; assert(st.get("AAAA") == 2) : "does not return updated value"; System.out.println(" Testing get... "); //get key not there size = st.size(); Integer ret = st.get("TEST2"); assert(ret == null) : "returned non-null for key that doesn't exist"; assert(st.size() == size) : "size changed"; assert(!st.contains("TEST2")) : "a key that doesn't exist appeared after get'ing it"; //get key there ("DAFDW", 52) size = st.size(); ret = st.get("DAFDW"); assert(ret == 52) : "returned incorrect value for key"; assert(st.size() == size) : "size changed"; assert(st.contains("DAFDW")) : "key vanished after get'ing it"; System.out.println(" Testing delete... "); //delete key not there size = st.size(); st.delete("
System.out.println(" DONE "); } }
ProbingHT.java
public interface ProbingHT
SymbolTable.java
public interface SymbolTable
CompletedLinearProbingHT.java
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue;
public class CompletedLinearProbingHT
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 997; private int size; private int capacity; private Key[] keys; private Value[] values;
public CompletedLinearProbingHT() { this(DEFAULT_CAPACITY); }
public CompletedLinearProbingHT(int capacity) { this.capacity = capacity; keys = (Key[]) new Object[capacity]; values = (Value[]) new Object[capacity]; }
@Override public int hash(Key key, int i) { // Basic hash function from the slides: hash(k, i) = ((k * hashCode() & 0x7fffffff) + i) % M return (key.hashCode() & 0x7fffffff) % capacity + i; }
@Override public void put(Key key, Value val) { if (key == null) { return; }
int i; for (i = hash(key, 0); keys[i] != null; i = hash(key, ++i)) { if (keys[i].equals(key)) { values[i] = val; return; } }
keys[i] = key; values[i] = val; size++; }
@Override public Value get(Key key) { if (key == null) { return null; }
for (int i = hash(key, 0); keys[i] != null; i = hash(key, ++i)) { if (keys[i].equals(key)) { return values[i]; } }
return null; }
@Override public void delete(Key key) { if (key == null) { return; }
int i = hash(key, 0); while (keys[i] != null) { if (keys[i].equals(key)) { // Shift all keys and values after the deleted element to the left by 1 for (int j = i; j
// Set the last element to null keys[size - 1] = null; values[size - 1] = null; size--; return; } i = hash(key, ++i); } }
@Override public boolean contains(Key key) { return get(key) != null; }
@Override public boolean isEmpty() { return size == 0; }
@Override public int size() { return size; }
@Override public Iterable @Override public int getM() { return capacity; } @Override public Object getTableEntry(int i) { return keys[i] + " : " + values[i]; } } CompletedQuadProbingHT.java public class CompletedQuadProbingHT public CompletedQuadProbingHT() { super(); } @Override public int hash(Key key, int i) { return (key.hashCode()); } } CompletedTwoProbeChainHT.java import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; public class CompletedTwoProbeChainHT //any constructors must be made public @Override public int hash(Key key) { //TODO return 0; } @Override public int hash2(Key key) { //TODO return 0; } @Override public void put(Key key, Value val) { //TODO } @Override public Value get(Key key) { //TODO return null; } @Override public void delete(Key key) { //TODO } @Override public boolean contains(Key key) { //TODO return false; } @Override public boolean isEmpty() { //TODO return false; } @Override public int size() { //TODO return 0; } @Override public Iterable //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // THESE METHODS ARE ONLY FOR GRADING AND COME FROM THE TWOPROBECHAINHT INTERFACE. @Override public int getM() { //TODO. We suggest something like: //return M; return 0; } @Override public int getChainSize(int i) { //TODO. We suggest something like: //return entries[i].size(); return 0; } } CODE OUTPUT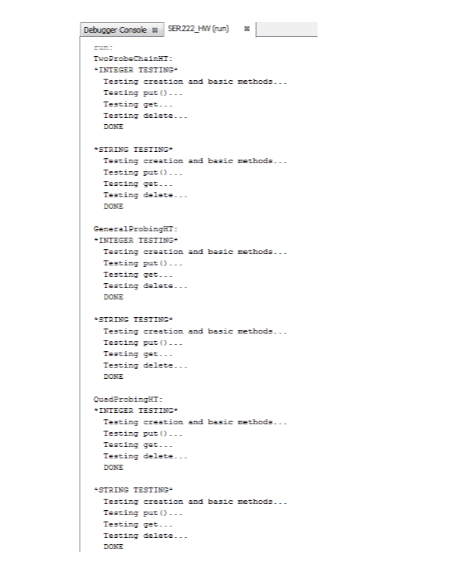
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


