PLEASE HELP, I have been trying forever to get the answers to these couple questions and no luck. Begging for help, will always rate you
PT2
PT3
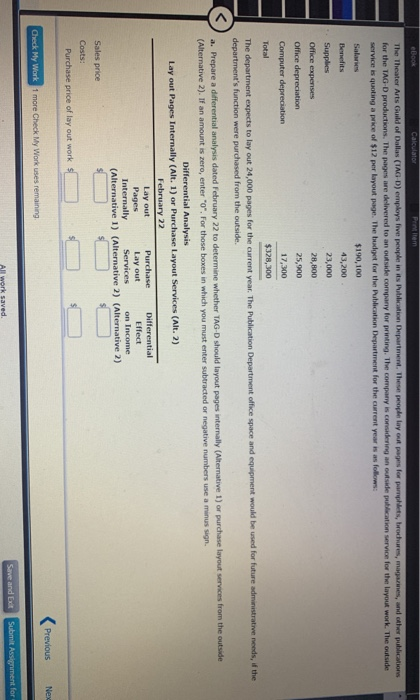
PT4
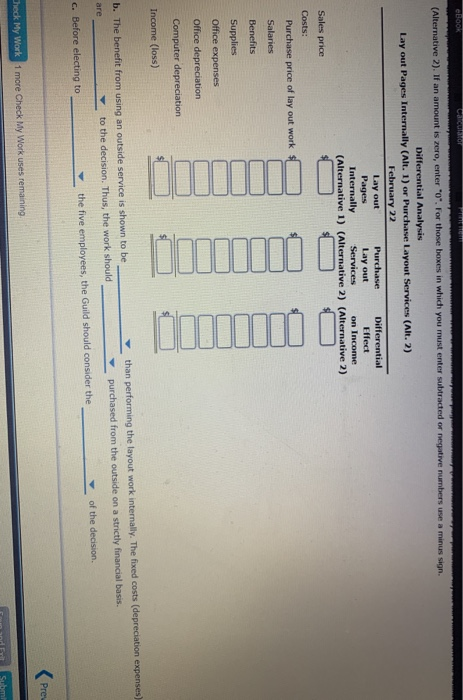
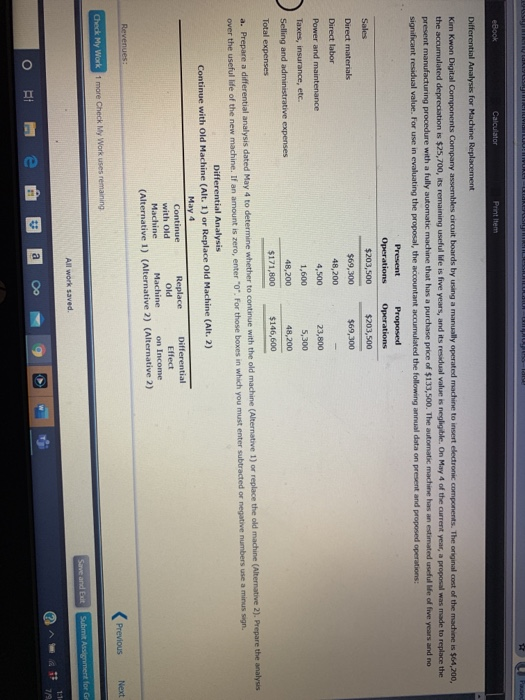
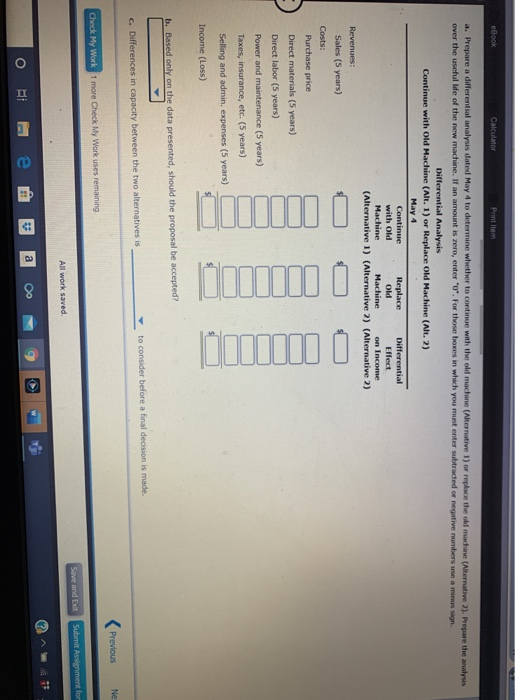
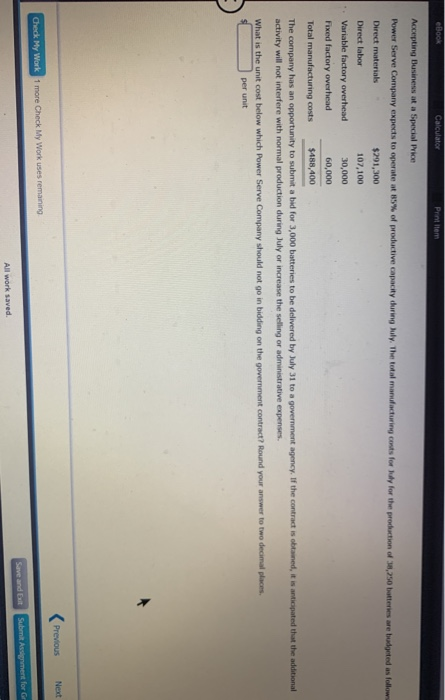
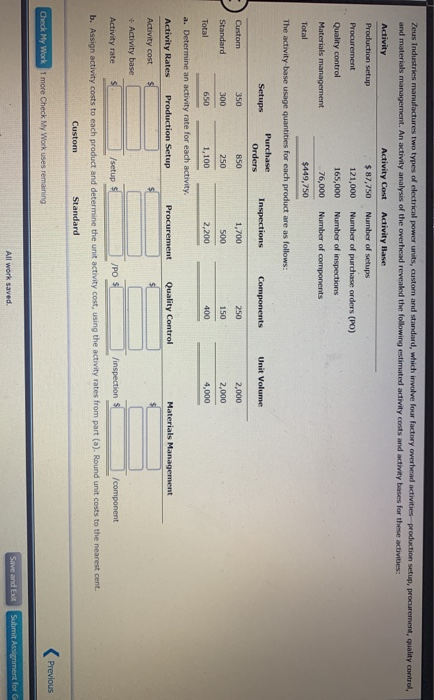
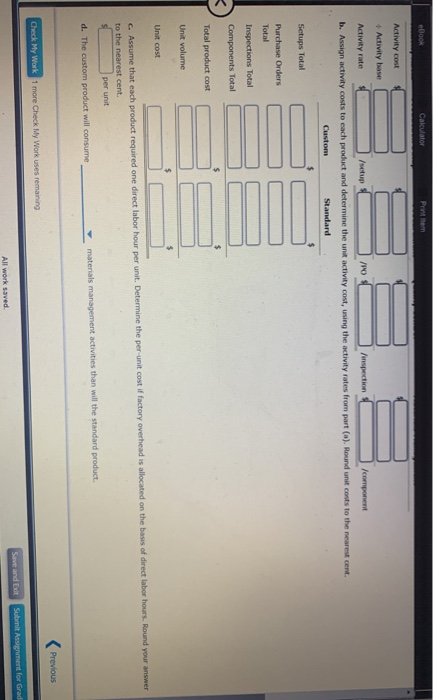
eBook Calculator Printem The Theater Arts Guild of Dallas (TAG-D) employs live people in its cation Department. These people layout pages for parphlets, brochures, magazines, and other publications for the TAG- productions. The pages we delivered to an outside company for printing. The company is considering an outside publication service for the layout work. The outside service is quoting a price of $12 per layout page. The budget for the Publication Department for the current year is as follows: $190,100 Benefits 43,200 Supplies 23,000 Office expenses 28,800 Office depreciation 25,800 Computer depreciation 17,300 Total $328,300 The department expects to lay out 24,000 pages for the current year. The Publication Department office space and equipment would be used for future administrative needs, if the department's function were purchased from the outside a. Prepare a differential analysis dated February 22 to determine whether TAG D should layout pages internally (Alternative 1) or purchase layout services from the outside (Alternative 2). If an amount is zero, enter "o". For those boxes in which you must enter subtracted or negative numbers use a minus sign. Differential Analysis Lay out Pages Internally (Alt. 1) or Purchase Layout Services (Alt. 2) February 22 Lay out Purchase Differential Pages Lay out Effect Internally Services on Income (Alternative 1) (Alternative 2) (Alternative 2) Sales price Costs: Purchase price of lay out works Previous Nex Check My Work 1 more Check My Work uses remaining Save and Edt Submit Assignment for All work saved eBOOK Car (Alternative 2). If an amount is zero, enter "0". For those boxes in which you must enter subtracted or negative numbers use a minus sign. Differential Analysis Lay out Pages Internally (Alt. 1) or Purchase Layout Services (Alt. 2) February 22 Lay out Purchase Differential Pages Lay out Effect Internally Services on Income (Alternative 1) (Alternative 2) (Alternative 2) Sales price Costs: Purchase price of lay out work Salaries Benefits Supplies Office expenses Office depreciation Computer depreciation Income (loss) b. The benefit from using an outside service is shown to be to the decision. Thus, the work should than performing the layout work internally. The fixed costs (depreciation expenses) purchased from the outside on a strictly financial basis. of the decision c. Before electing to the five employees, the Guild should consider the Prey Check My Work 1 more Check My Work uses remaining Subm eBook Calculator Print Item Differential Analysis for Machine Replacement Kim Kwon Digital Components Company assembles circuit boards by using a manually operated machine to insert electronic components. The original cost of the machine is $61,200, the accumulated depreciation is $25,700, its remaining useful life is five years, and its residual value is negligible. On May 4 of the current year, a proposal was made to replace the present manufacturing procedure with a fully automatic machine that has a purchase price of $133,500. The automatic machine has an estimated useful le of five years and no significant residual value. For use in evaluating the proposal, the accountant accumulated the following annual data on present and proposed operations: Present Proposed Operations Operations Sales $203,500 $203,500 Direct materials $69,300 $69,300 Direct labor 48,200 Power and maintenance 4,500 23,800 Taxes, insurance, etc. 1,600 5,300 Selling and administrative expenses 48,200 48,200 Total expenses $171,800 $146,600 a. Prepare a differential analysis dated May 4 to determine whether to continue with the old machine (Alternative 1) or replace the old machine (Alternative 2). Prepare the analysis over the useful life of the new machine. If an amount is zero, enter"0". For those boxes in which you must enter subtracted or negative numbers use a minus sign. Differential Analysis Continue with Old Machine (Alt. 1) or Replace Old Machine (Alt. 2) May 4 Continue Replace Differential with Old Old Effect Machine Machine on Income (Alternative 1) (Alternative 2) (Alternative 2) Revenues: Previous Next Check My Work 1 more Check My Work uses remaining Save and Exit Submit Assignment for All work saved ** 1:14 79 a Oo O II E eBook Calculator Print item a. Prepare a differential analysis dated May 4 to determine whether to continue with the old machine (Alternative 1) or replace the old machine (Alternative 2). Prepare the analysis over the useful life of the new machine. If an amount is zero, enter 'o'. For those boxes in which you must enter subtracted or negative numbers use a minus sgn. Differential Analysis Continue with Old Machine (Alt. 1) or Replace Old Machine (Alt. 2) May 4 Continue Replace Differential with Old Old Effect Machine Machine on Income (Alternative 1) (Alternative 2) (Alternative 2) Revenues: Sales (5 years) Costs: Purchase price Direct materials (5 years) Direct labor (5 years) Power and maintenance (5 years) Taxes, insurance, etc. (5 years) Selling and admin. expenses (5 years) buii 0 b 0 I W1100 Income (Loss) b. Based only on the data presented, should the proposal be accepted? to consider before a final decision is made. c. Differences in capacity between the two alternatives is Previous Ne Check My Work 1 more Check My Work uses remaining Save and Edt Submit Assignment for All work saved a > O BI eBook Calculator Accepting Business at a Special Price Power Serve Company expects to operate at 85% of productive capacity during July. The total manufacturing cents for buy for the production of 38,250 batteries are bundprted as follow Direct materials $291,300 Direct labor 107,100 Variable factory overhead 30,000 Fixed factory overhead 60,000 Total manufacturing costs $488,400 The company has an opportunity to submit a bid for 3,000 batteries to be delivered by July 31 to a government agency. If the contract is obtained, it is anticipated that the additional activity will not interfere with normal production during July or increase the selling or administrative expenses. What is the unit cost below which Power Serve Company should not go in bidding on the government contract? Round your answer to two decimal places. per unit Previous Next Check My Work 1 more Check My Work uses remaining Save and all Submit Assignment for All work saved Zeus Industries manufactures two types of electrical power units, custom and standard, which involve four factory overhead activities production setup, procurement, quality control, and materials management. An activity analysis of the overhead revealed the following estimated activity costs and activity bases for these activities: Activity Activity Cost Activity Base Production setup $ 87,750 Number of setups Procurement 121,000 Number of purchase orders (PO) Quality control 165,000 Number of inspections Materials management 76,000 Number of components Total $449,750 The activity-base usage quantities for each product are as follows: Setups Purchase Orders Inspections Components Unit Volume Custom 350 850 1,700 250 2,000 2,000 Standard 300 250 500 150 Total 650 1,100 2,200 400 4,000 a. Determine an activity rate for each activity, Activity Rates Production Setup Procurement Quality Control Materials Management Activity cost + Activity base Activity rate /setup /PO Jinspection /component b. Assign activity costs to each product and determine the unit activity cost, using the activity rates from part (a). Round unit costs to the nearest cent. Custom Standard Previous Check My Work 1 more Check My Work uses remaining All work saved Save and Submit Assignment for eBook Calculator Priem Activity cost Activity base Activity rate /setup /PO inspection /component b. Assign activity costs to each product and determine the unit activity cost, using the activity rates from part (a). Round unit costs to the nearest cent. Custom Standard Setups Total Purchase Orders Total Inspections Total Components Total Total product cost Unit volume $ $ Unit cost C. Assume that each product required one direct labor hour per unit. Determine the per-unit cost if factory overhead is allocated on the basis of direct labor hours. Round your answer to the nearest cent. per unit d. The custom product will consume materials management activities than will the standard product.