Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Please help me answer the conceptual framework for financial reporting consisting of true or false and multiple choice questions. Topics are presentation of financial statements,
Please help me answer the conceptual framework for financial reporting consisting of true or false and multiple choice questions. Topics are presentation of financial statements, inventory, statement of cash flows, accounting policies, changes in accounting estimates and errors, events after the reporting period, income taxes, and property, plant and equipment.







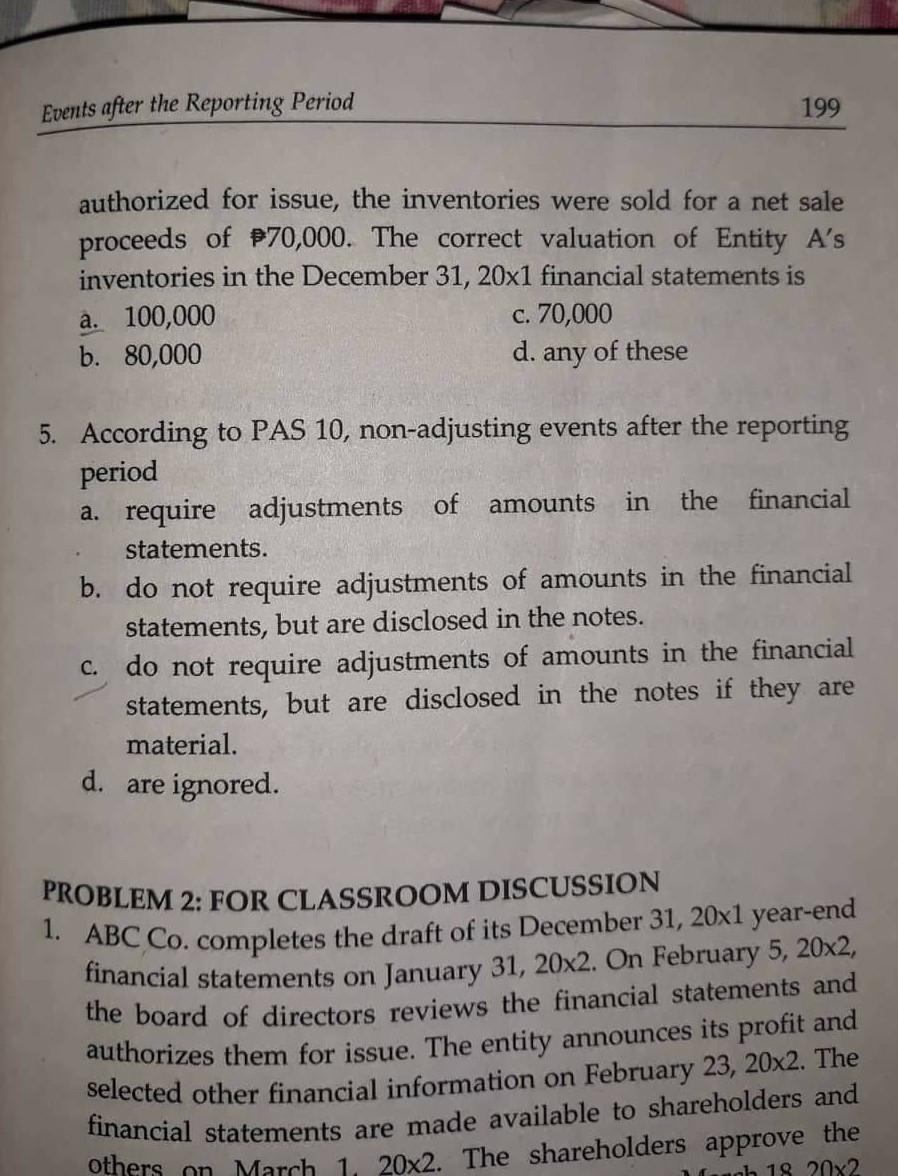





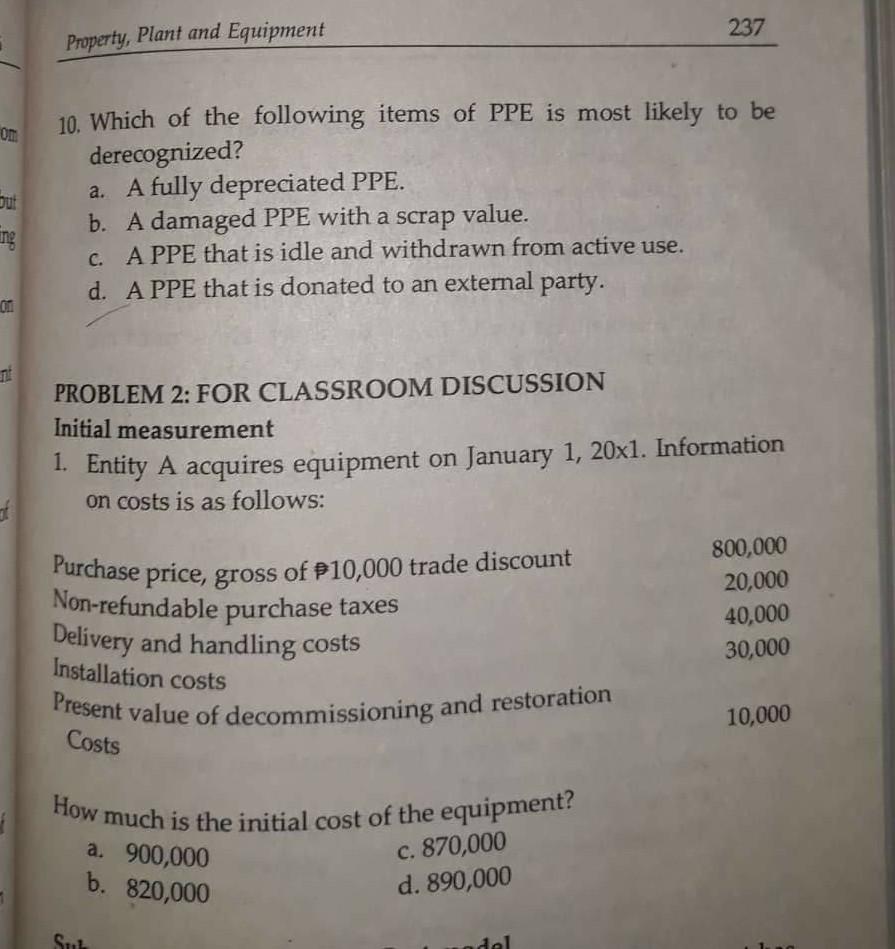
PROBLEMS PROBLEM 1: TRUE OR FALSE 1. All events and transactions of an entity are recognized the books of accounts. 2. The accounting process of assigning numbers, commonly in monetary terms, to the economic transactions and events is referred to as classifying. 3. The basic purpose of accounting is to provide information about economic activities intended to be useful in making economic decisions. 4. Financial accounting is the branch of accounting that focuses on general purpose reports of financial position and operating results known as the financial statements. 5. General purpose financial statements are those statements that cater to the common and specific needs of a wide range of external users. 6. The financial statements are the only source of information when making economic decisions. 7. All information presented in the financial statements are sourced from the accounting records of the entity. 8. Entity A's accounting period starts on July 1 and ends on June 30 of the following year. Entity A uses a fiscal year period. 9. Once promulgated, accounting standards are never changed. 10. The entity's management is responsible for the selection of appropriate accounting policies, not the accountant. Conceptual Framework 93 PROBLEMS a PROBLEM 1: TRUE OR FALSE 1. All changes in an entity's economic resources and claims to those resources result from the entity's financial performance. 2. The qualitative characteristics of useful information apply only to the financial information provided in the financial statements. 3. According to IFRS Practice Statement 2 Making Materiality Judgments, cost is an important consideration when making materiality judgments. 4. When making materiality judgments, quantitative assessment alone is not always sufficient to conclude that an item of information is not material. 5. Materiality judgments apply only to items that are recognized but not to those that are unrecognized. 6. The more significant the qualitative factors are, the lower the quantitative thresholds will be. Thus, an item with a zero amount can be material in light of qualitative thresholds. 7. When making materiality judgments, an entity should judge an item's materiality only on its own and not in combination with other information in the complete set of financial statements. 8. The Conceptual Framework and the Standards specify a uniform quantitative threshold for materiality. 9. To meet the objectives of general purpose financial reporting, a Standard sometimes contains requirements that depart from the Conceptual Framework. 10. The Conceptual Framework is concerned with the provision of financial information to both external users and internal users. PROBLEM 2: TRUE OR FALSE 1. The Conceptual Framework may be revised from time to time. Revisions in the Conceptual Framework automatically result to changes in the Standards. PROBLEMS PROBLEM 1: TRUE OR FALSE 1. The application of PFRSs, with additional disclosure when necessary, is presumed to result in financial statements that achieve a fair presentation. 2. According to PAS 1, an entity shall make an explicit and unreserved statement of compliance with the PFRSs in the notes only if the entity complies with all the requirements of PFRSs. 3. PAS 1 encourages, but does not require, the presentation of the preceding year's financial statements as comparative information to the current year's financial statements. 4. According to PAS 1, assets and liabilities or income and expenses are offset, unless separate presentation is required or permitted by a PFRS. 5. According to PAS 1, PFRSs apply to financial statements as well as to other information presented in an annual report, a regulatory filing, or another document. 6. According to PAS 1, the line item "Cash and cash equivalents" should always be presented first in the statement of financial position. 7. PAS 1 prescribes an order or format of presenting items in the financial statements. 8. An entity may omit the notes when presenting general purpose financial statements. 9. If profit or loss is $100 while other comprehensive income is P20, total comprehensive income must be p130. 10. PAS 1 encourages, but does not require, the disclosure of an entity's domicile and legal form, its country of incorporation and the address of its registered office and a description of the nature of its operations and its principal activities. 165 Inventories PROBLEMS PROBLEM 1: TRUE OR FALSE 1. According to PAS 2, inventories are measured at net realizable value. 2. According to PAS 2, net realizable value and fair value less costs to sell are the same. 3. Storage costs of part-finished goods may be included in the cost of inventory, but not storage costs of finished goods. 4. Trade discounts are added to the cost of inventories. 5. Import duties, freight-in and non-refundable purchase taxes form part of the cost of inventories. 6. Raw materials inventory is not written down below cost if the finished goods to which they will be incorporated are expected to be sold at or above cost. 7. Reversals of inventory write-downs may exceed the amount of the original write-down previously recognized. 8. The cost of factory management is included in the cost of inventory 9. The maintenance costs of a machine used in the manufacturing process are not included in the cost of inventories. 10. If the cost of an inventory is $8 while its net realizable value is 6, the amount of write-down is 2. PROBLEM 2: MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following is not included as part of the cost of an inventory? a. Purchase cost, net of trade discount b Direct labor cost 180 PAS 7 PROBLEMS PROBLEM 1: TRUE OR FALSE 1. Cash flows are presented in the statement of cash flows into four activities. 2. Non-financial institutions have the option of classifying interest income received as either investing activities or operating activities. 3. Cash flows relating to income and expenses are normally classified as investing activities in the statement of cash flows. 4. Only transactions that have affected cash and cash equivalents are included in the statement of cash flows. Non-cash transactions are excluded and disclosed only. 5. According to PAS 7, the indirect method of presenting cash flows relating to operating activities shows each major class of gross cash receipts and gross cash payments. PROBLEM 2: MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Entity A had the following balances at December 31, 20x1: Cash in bank 35,000 Cash in 90-day money market account 75,000 Treasury bill, purchased 11/1/x1, maturing 1/31/x2 350,000 Treasury bill, purchased 12/1/X1,maturing 3/31/x2 400,000 How much is the cash and cash equivalents to be PAS8 192 PROBLEMS P 1. PROBLEM 1: MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. change in measurement basis is most likely a a. change in accounting policy. c. error. b. change in accounting estimate. d. any of these 2. A correction of prior period error is accounted for by a. retrospective application. c. prospective application. b. retrospective restatement. d. impracticable application. 3. Which of the following is a change in accounting estimate? a. Change from the cost model to the fair value model of measuring investment property. b. Change in business model for classifying financial assets resulting to the reclassification of a financial asset from being measured at amortized cost to fair value. c. Change in the method of recognizing revenue from long- term construction contracts. d. Change in the depreciation method, useful life or residual value of an item of property, plant and equipment. 4. These result from new information or new developments. a. Changes in accounting estimates b. Changes in accounting policies Correction of errors d. All of these C. 5. The effect of which of the following is presented in profit or loss in the current period (or current and future periods, both are affected) rather than as an adjustment to the opening balance of retained earnings. a. Correction of a prior period error. b. Change in accounting policy. C. Change in accounting estimate. d. All of these. PAS 10 198 PROBLEMS PROBLEM 1: MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. ABC Co. completes the draft of its December 31, 20x1 year-end financial statements on January 31, 20x2. On March 1, 20x2, the management of ABC Co. authorizes the financial statements for issue to its supervisory board. The supervisory board is made up solely of non-executives and includes representatives of employees and other outside interests. The supervisory board approves the financial statements on March 10, 20x2. The financial statements are made available to shareholders and others on March 14, 20x2. The shareholders approve the financial statements at their annual meeting on March 23, 20x2 and the financial statements are then filed with a regulatory body on April 1, 20x2. For purposes of PAS 10, what is the date of authorization of the financial statements? a. March 1, 20x2 c. March 14, 20x2 b. March 10, 20x2 d. March 23, 20x2 2. According to PAS 10, these are events that provide evidence of conditions that existed at the end of the reporting period. a. Events after the reporting period c. Adjusting events b. Non-adjusting events d. all of these 3. Which of the following events after the reporting period are treated as adjusting events? a. A significant decline in the fair value of investments in stocks. b. A litigation arising from an accident that occurred after the reporting period. Declaration of dividends after the reporting period. d. Discovery of prior-period fraud or errors. 4. Entity A's inventories on December 31, 20x1 have a cost of P100,000 and a net realizable value of P80,000. Shortly after December 31, 20x1, but before the financial statements were Events after the Reporting Period 199 authorized for issue, the inventories were sold for a net sale proceeds of $70,000. The correct valuation of Entity A's inventories in the December 31, 20x1 financial statements is a. 100,000 c. 70,000 b. 80,000 d. any of these 5. According to PAS 10, non-adjusting events after the reporting period a. require adjustments of amounts in the financial statements. b. do not require adjustments of amounts in the financial statements, but are disclosed in the notes. c. do not require adjustments of amounts in the financial statements, but are disclosed in the notes if they are material. d. are ignored. PROBLEM 2: FOR CLASSROOM DISCUSSION 1. ABC Co. completes the draft of its December 31, 20x1 year-end financial statements on January 31, 20x2. On February 5, 20x2, the board of directors reviews the financial statements and authorizes them for issue. The entity announces its profit and selected other financial information on February 23, 20x2. The financial statements are made available to shareholders and others on March 1, 20x2. The shareholders approve the h 18 20x2 PAS 12 a. C. Recognizing deferred tax assets and liabilities results to 214 PROBLEMS PROBLEM 1: MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. In layman's terms, to "defer" means to postpone. Thus, a deferred tax liability a. increases the tax payment in the current period. b. increases the tax payment in a future period. c. decreases the tax payment in the current period. d. decreases the tax payment in a future period. 2. If the change in deferred tax asset exceeds the change in deferred tax liability during the period, the net change is referred to as deferred tax expense. C. current tax benefit. b. deferred tax income. d. deferred tax asset. 3. Entity A reports an income tax expense of 1,000 and a current tax expense of P800 during the period. The difference between these amounts is best described as a. deferred tax expense. c. deferred tax liability. b. deferred tax income. d. deferred tax asset. 4. Entity A computes a current tax expense of $700 using relevant tax laws. If the change in deferred tax assets exceeds the change in deferred tax liabilities during the period by P100, Entity A's income tax expense is P800. c. 700. b. P600 d. none of these 5. Which of the following is not correct regarding the recognition of a deferred tax asset or a deferred tax liability? a. A deferred tax liability will ultimately result to a tax payment in a future period. b. A deferred tax asset is expected to cause a reduction in the tax payment in a future period. a. higher proper matching of items in the financial statements. Income Taxes 215 d. Recognizing a deferred tax asset reduces the tax payment in the current period, below the amount that would have to be paid if only the tax laws are used to compute for the bone. The tax due. Od. hod. 6. If the economic benefits from an asset will not be taxable when they are recovered, the tax base of the asset is equal to a. its carrying amount. c. a or b b. zero. d. neither a nor b Che chane net chats 7. PAS 12 requires the use of this method in accounting for deferred taxes. a. Asset-liability method c. Straight-line method b. Income statement method d. Discounted method benefit X asset. and a cu rence bet 8. Deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities do not alter the tax to be paid in the current period. However, they cause tax payments to either increase or decrease when they reverse in a future period. The reversal of which of the following will cause a decrease in tax payment? Deferred tax liability c. Deferred tax expense b. Deferred tax asset d. Deferred tax benefit liability a. X asset of P70 assets en the perio 9. Which of the following is correct regarding the presentation of deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities in the statement of financial position? a. Deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities are presented as either current or noncurrent items depending on their expected reversal dates. b. Deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities are generally offset unless they qualify for separate presentation Deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities are generally presented separately unless they qualify for offsetting the rezug C. ult to all eduction 216 PAS 12 d. Deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities are off- balance sheet items, meaning they are not recognized but disclosed only in the notes. 10. According to PAS 12, the tax effects of transactions or other events are recognized in a. profit or loss. c. directly in equity. b. other comprehensive income. d. a, borc PROBLEM 2: FOR CLASSROOM DISCUSSION 1. If it is probable that recovery or settlement of a carrying amount of an asset or liability will make future tax payments larger than they would be if such recovery or settlement were to have no tax consequences, an entity shall recognize a deferred tax asset. c. a orb b. deferred tax liability, d. neither a norb a. are differences that do not have future tax 2. These consequences. a. Permanent differences b. Temporary differences c. Taxable differences d. Deductible differences 3. This type of difference will give rise to defom Property, Plant and Equipment 235 omprises the as trade anda tial estimate PROBLEMS rial substance PROBLEM 1: MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following is not classified as property, plant and equipment? Land held for future plant site b. Building used in business c. Equipment held for environmental and safety reasons d. Minor spare parts and short-lived stand-by equipment I up, (b) fair he asset Groen PPE acquire a. en up f an item op and contes in the man 2. Which of the following does not form part of the initial cost of an item of PPE? a. Purchase price, net of trade discounts and rebates b. Freight costs Installation and testing costs d. Advertising and promotional costs c. all choose eit s its account: class of PPE the depreci te. or residuals 3. Depreciation does not cease in which of the following instances? a. The item of PPE is classified as held for sale or included in a disposal group in accordance with PFRS 5. b. The item of PPE is derecognized through disposal. c. The item of PPE is fully depreciated. d. The item of PPE becomes idle or is retired from active use. Cable for ed as held fors amount is. ecomes ide 4. In which of the following cases is an asset not considered to be fully depreciated? a, When the asset's carrying amount is zero b. When the asset's carrying amount is equal to its residual value. c. When the sum of the asset's accumulated depreciation, accumulated impairment losses and residual value is equal to its cost. d. When the asset's cost is equal to its carrying amount. -Residual I life mount eeds - Cam 9. According to PAS 16, an entire class of PPE is subsequently PAS 16 5. Which of the following instances precludes an recognizing depreciation? carrying amount model. c. PRE parts. Ini 1. a. the fair value of the asset exceeds its carrying amount bul b. the asset is subsequently measured under the revaluation the asset comprises several significant and insignificant a composite method that is applied to a group of items of d. a retirement method that recognizes depreciation when a 236 entity the asset's residual value does not exceed its d. the asset is classified as held for sale under PFRS 5. 6. Which of the following does not affect the determination of depreciation charges on an item of PPE? a. Useful life c. Residual value b. Cost d. Repairs and maintenance 7. The depreciation method prescribed by PAS 16 is a. straight-line. c. units of production b. diminishing balance. d. none 8. Which of the following is not an acceptable choice of depreciation method under PAS 16? a. a method that results to the same amount of depreciation charge from period to period b. a method that is based on the levels of revenue earned PPE PE N D P small item of PPE is retired measured under the a. cost model b. revaluation model. c. fair value model. d. a or b How much is the initial cost of the equipment? om BP Purchase price, gross of P10,000 trade discount Present value of decommissioning and restoration Property, Plant and Equipment 237 10. Which of the following items of PPE is most likely to be derecognized? a. A fully depreciated PPE. b. A damaged PPE with a scrap value. C. A PPE that is idle and withdrawn from active use. d. A PPE that is donated to an external party. on PROBLEM 2: FOR CLASSROOM DISCUSSION Initial measurement 1. Entity A acquires equipment on January 1, 20x1. Information on costs is as follows: 800,000 Non-refundable purchase taxes 20,000 Delivery and handling costs 40,000 30,000 Installation costs 10,000 Costs a. 900,000 b. 820,000 c. 870,000 d. 890,000 Sul del
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


