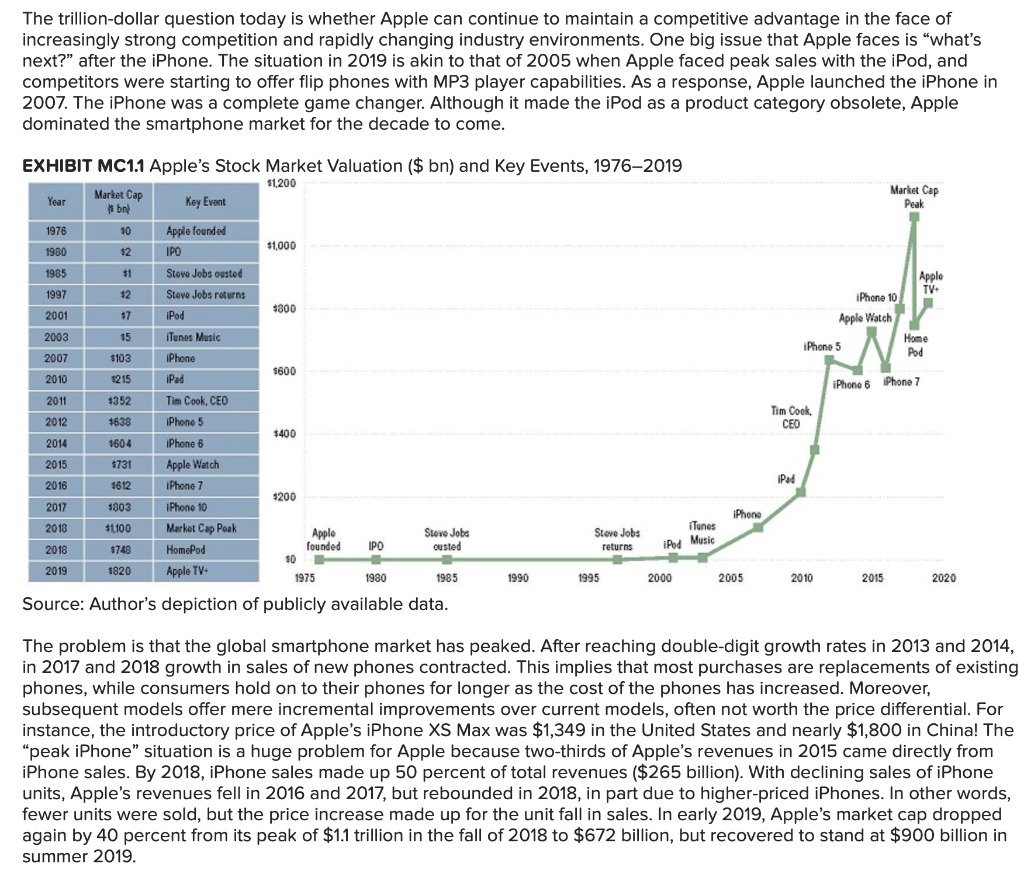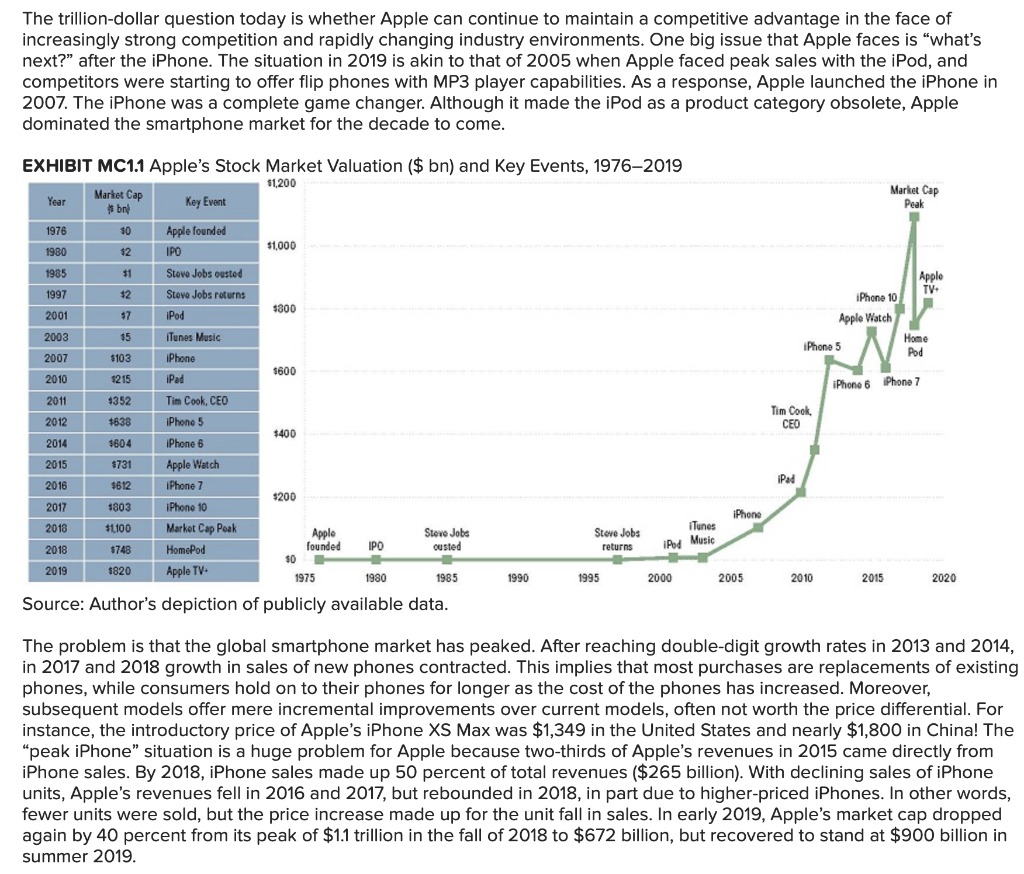

Please help me answer the following questions correctly.
Company assembles bicycles and sells them at $3,500 each. Company's costs are as follows:
Direct materials $ 1,100 per unit
Direct labor 300 per unit
Variable MOH 120 per unit
Variable selling 200 per unit
Fixed MOH $ 300,000 total
Fixed period costs $ 200,680 total
CALCULATE the number of bicycles that the company must sell to earn $400,000 operating income.
Number of bicycles.
45. Assume the yield curve is flat at 4%. There are a 3-year zero coupon bond and a 3-year coupon bond that pays a 5% coupon annually. (a) What are the YTMs of these two bonds? (b) Suppose the yield curve does not change in the future. You invest $100 in each of the two bonds. You re-invest all coupons in zero coupon bonds that mature in year 3. How much would you have at the end of year 3? 46. The attached chart shows the fixed obligations of the Edison Mills pension plan, which is also managed by the Renssalear Advisors. Year Benefits ($MM) 2000 $10.60 2001 $11.24 2002 $11.91 2003 $12.62 Total $46.37 Using an assumed interest rate of 6%, the present value of this stream of fixed cash outflows is $40 million. You are given $40 million to invest in U.S. Treasury bonds for the pension plan. Your boss insists that you only invest in 1 year and 10 year STRIPS. Your task is to minimize the exposure of the Edison Mills pension fund to unexpected changes in the level of interest rates. Your performance will be evaluated after one year. Answer the following questions. Use the backs of this page and the next page if needed to complete your answer. Fall 2008 Page 21 of 66 (a) What is duration of your obligation? (b) Describe - step by step - how you would choose and manage the portfolio of 1-year and 10-year STRIPS to minimize the exposure to interest rate risk. 47. Bond underwriting. Bond underwriters agree to purchase a corporate client's new bonds at a specific price. usually near 100% of face value, and then attempt to resell the bonds to the public. The act of reselling takes some time. Underwriting fees increase with the maturity of the bonds. Provide an explanation for this pattern of fees. 48. You have just been given the following bond portfolio: Bond Maturity (yrs) Coupon rate (%) Holdings ($ million) 7.00 10 7.25 20 10 7.50 20 20 8.00 10 Coupons are paid semi-annually. The current yield curve is flat at 6%. (a) What is duration for each of the bonds in your portfolio? (b) What is the duration of your total portfolio? (c) What is the percentage change in the value of your portfolio if the yield moves up by 20 basis points? 19. A U.S. Treasury bond makes semi-annual payments of $300 for 10 years. (The investor receives 20 $300 payments at 6-month intervals.) At the end of 10 years, the bonds principal amount of $10,000 is paid to the investor. (a) What is the present value of the bond if the annual interest rate is 5%? (b) Suppose the bond is observed trading at $11,240. What discount rate are investors using to value the bonds cash flows? (This discount rate is called the bonds "yield to maturity.")1. Minicase 1Apple: What's Next? Apple: What's Next? This activity is important because, as a manager, you should be able to understand and enable innovation and its impact on the product life cycle. In order to do this, you will need to identify the stages of your product's life cycle and choose appropriate innovation [and other) strategies. The goal of this exercise is to demonstrate your understanding of innovation and the product life cycle by identifying how elements of Apple's product strategies relate to each of these concepts. Read the case beiow and answer the questions that follow. Apple is the rst company whose stock market valuation crossed the $1 trillion threshold (in 2018}. Some 20 years earlier, however, Apple would likely have gone bankrupt if archrival Microsoft (which enjoyed a valuation of $615 billion in December 1999}1 had not invested $150 million in Apple. Under investigation by the Department of Justice at the time for alleged abuse of monopoly power, Microsoft was eager to not have another competitor go out of business. The Apple Ecosystem Apple achieved its success over two decades by implementing a potent competitive strategy. That strategy. conceptualized by cofounder Steve Jobs, combined innovation in products, services, and business models. In 1997, Apple was near bankruptcy. But in 2001, its revitalization took off with the introduction of the iPod, a portable digital music player; this was the same year Apple opened its first retail stores {see Exhibit MC1J}. Today. Apple's stores earn some of the highest sales per square foot of any retail outlets. including Tiffany 8. Co., a luxuryjeweler. and LVMH. a purveyor of fine handbags and other highend goods. In 2003. Apple soared even higher when It launched its digitai store iTunes. And it didn't stop there. In 2007. the California tech company revolutionized the smartphone market with the introduction of the iPhone. Just three years later, Apple re created the tablet segment by introducing the iPad. For each of its iPod, iPhone, and iPad lines of businesses. Apple followed up with incremental product innovations that extended each product category. In 2017. Apple launched the 10th anniversary edition ofthe iPhone 10 and in 2018 it introduced the iPhone X5 Max. Giobally. Apple has also sold more than 1 billion iPhones. (The classic iPod was discontinued in 2014; the intent was always that the iPhone would subsume the MP3 capability. In 2019. Apple phased out iTunes and replaced it with three apps: Apple Music, Podcasts. and Apple TV.) Also. in 2019. Apple introduced the iPhone 11 and Apple TV+. its new streaming service. By combining tremendous brainpower, intellectual property. and iconic brand value, Apple has enjoyed dramatic increases in revenues. profits. and stock market valuation. By 2019. it was one of the most profitable companies ever. with $225 billion in cash holdings alone. A Good Strategy Why was Apple so successful? Why did Apple's competitors, such as Sony, Dell, HewlettPackard {HP}, Nokia, and BlackBerry. struggle or go out of business? The shon answer is: Apple had a better strategy. But this raises the question: What is a good strategy? A good strategy is more than a mere goal or a company slogan. A good strategy denes the competitive challenges facing an organization through a critical and honest assessment of the status quo. A good strategy also provides an overarching approach (policy) on how to deal with the competitive challenges identied. Last, a good strategy requires effective implementation through a coherent set of actions. A good strategy, therefore, consists of three elements:2 {1} A diagnosis of the competitive challenge. {2) A guiding policy to address the competitive challenge. {3) A set of coherent actions to implement the rm's guiding policy. THE COMPETITIVE CHALLENGE. First, consider the diagnosis of the competitive challenge. Above, we briefly traced Apple's renewal from the year 2001, when it hit upon the product and business-model innovations of the iPodiiTunes combination. Before that, Apple was merely a niche player in the desktop-computing industry and struggling financially. Steve Jobs turned the sinking company around by focusing on only two computer models (one laptop and one desktop) in each of two market segments [the professional market and the consumer market) as opposed to dozens of non- differentiated products within each segment. This streamlining of its product lineup enhanced Apple's strategic focus. Even so, the ouook for Apple was grim. Jobs believed that Apple, with less than 5 percent market share, could not win in the personal computer industry where desktops and laptops had become commoditized gray boxes. In that world, Microsoft, Intel. and Dell were the star performers. Jobs knew that he needed to create the "next big thing.\"3 A GUIDING POLICY. Second, Apple shifted its competitive focus away from personal computers to mobile devices. In doing so. Apple disrupted several industries through its product and business-model innovations. Combining hardware {i.e., the lF'od} with a complementary service product 0.9., the iTunes Store) enabled Apple to devise a new business model. Users could download individual songs legally (at 99 cents} rather than buying an entire CD or downloading the songs illegally using Napster and other file-sharing services. The availability of the iTunes Store drove sales ofiPods. Along with rising sales for the new iPod and iTunes products, demand rose for iMacs. The new products helped disrupt the existing personal computer market because people wanted to manage their music and photos on a computer that worked seamlessly with their mobile device. Apple then leveraged the success ofthe iPodeTunes business-model innovation, following up with product-category-defining innovations when launching the iPhone [in 2007] and the iPad (in 2010). COHERENT ACTIONS. Third, Apple implemented its guiding policy with a set of coherent actions. Apple's coherent actions took a two-pronged approach: It drastically streamlined its product lineup through a simple rule\"we will make only one laptop and one desktop model for each of the two markets we serve, professional and consumer.\"4 It also disrupted the industry status quo through a potent combination of product and business-model innovations. executed at planned intervals. These actions allowed Apple to create a string of temporary competitive advantages [see Exhibit MC1.1}. Taken together, this enabled Apple to sustain its superior performance for over a decade. Peak iPhone: What's Next? Past performance, however, is no guarantee of future performance. Although Microsoft struggled to keep up with Apple, by spring 2019 it surpassed Apple to become the world's most valuable company once again with its renewed focus on cloud and mobile computing. In the same fashion, Amazon has also surpassed Apple in stock market valuation, while Alpha bet is closing in. At the same time, Apple continues to face stiff competition from such non-U5. rivals as Samsu ng {a South Korean rm} and Huawei. Xiaomi, and Oppo {all Chinese rms]. The trillion-dollar question today is whether Apple can continue to maintain a competitive advantage in the face of increasingly strong competition and rapidly changing industry environments. One big issue that Apple faces is "what's next?" after the iPhone. The situation in 2019 is akin to that of 2005 when Apple faced peak sales with the iPod, and competitors were starting to offer flip phones with MP3 player capabilities. As a response, Apple launched the iPhone in 2007. The iphone was a complete game changer. Although it made the ipod as a product category obsolete, Apple dominated the smartphone market for the decade to come. EXHIBIT MC1.1 Apple's Stock Market Valuation ($ bn) and Key Events, 1976-2019 $1,200 Market Cap Market Cap Peak Year Key Event 1976 Apple founded 1980 IPO $1,000 1985 #1 Stove Jobs ousted Apple TV+ Phone 10 1997 $2 Stove Jobs roturns $800 2001 iPod Apple Watch Home 2003 iTunes Music iPhone 5 Pod 2007 $103 iPhone $600 2010 $215 iPad iPhone 6 iphone 7 2011 $352 Tim Cook, CEO Tim Cook, 2012 $638 iPhone 5 CED $400 2014 $604 iPhone 6 2015 $731 Apple Watch iPad 2016 1612 IPhone 7 $200 2017 $803 iPhone 10 iPhone ITunes 2018 $1.10 Market Cap Peak Apple Steve Jobs Steve Jobs PO returns Pod Music 2018 $748 HomePod founded ousted 2019 1820 Apple TV+ 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 2020 Source: Author's depiction of publicly available data. The problem is that the global smartphone market has peaked. After reaching double-digit growth rates in 2013 and 2014, in 2017 and 2018 growth in sales of new phones contracted. This implies that most purchases are replacements of existing phones, while consumers hold on to their phones for longer as the cost of the phones has increased. Moreover, subsequent models offer mere incremental improvements over current models, often not worth the price differential. For instance, the introductory price of Apple's iPhone XS Max was $1,349 in the United States and nearly $1,800 in China! The "peak iPhone" situation is a huge problem for Apple because two-thirds of Apple's revenues in 2015 came directly from iPhone sales. By 2018, iphone sales made up 50 percent of total revenues ($265 billion). With declining sales of iPhone units, Apple's revenues fell in 2016 and 2017, but rebounded in 2018, in part due to higher-priced iPhones. In other words, fewer units were sold, but the price increase made up for the unit fall in sales. In early 2019, Apple's market cap dropped again by 40 percent from its peak of $1.1 trillion in the fall of 2018 to $672 billion, but recovered to stand at $900 billion in summer 2019.In recent years, sales in China made up 20 percent of Apple's revenues. However, Apple's popularity in China is declining rapidly in the face of local competition and trade tensions. The Chinese smartphone makers Huawei, Xiaomi, and Oppo offer phones of similar capabilities and user-friendliness for one-half the price or less. Moreover, given the trade tensions between the United States and China, Apple can expect more headwinds in China. For example, a consumer boycott could be instigated, or a stiff tax could be levied on Apple products by the Chinese authorities. In 2019, Huawei was facing several U.S. charges, among them misleading the U.S. government about its business dealings with Iran (while it was under U.S. economic sanctions) and allegations of bank fraud and technology theft (Huawei has denied both claims). Will Apple introduce another game changer like the iPhone? In 2015, it introduced the Apple Watch, the first new product category launched since the iPad in 2010. Despite the unfulfilled potential of AirPower, which would have disrupted the charging industry and redefined the way consumers charge their Apple products, the Apple Watch is gaining more traction and has become the most popular smartwatch. In mobile payment systems (Apple Pay launched in 2014), music streaming (Apple Music launched in 2015), smart speaker systems (Apple's HomePod launched in 2018), and streaming services (Apple TV+ launched in 2019), Apple was a late mover. Going forward, Apple CEO Tim Cook has explained that Apple will focus on services to make up for losses resulting from declining iPhone sales. In 2019, Apple had more than 1 billion users in its ecosystem, which comprises mobile devices (iPhone, iPad, iMac, or Apple Watch) combined with services such as iTunes, iCloud, and ApplePay. The Apple ecosystem is centered around its proprietary iOS operating system, which anchors a family of Apple products with its accompanying, co-dependent services. This allows the firm to benefit from customer lock-in and network effects. In other words, if a user is embedded in the Apple ecosystem, that makes it much harder for that user to switch to a mobile phone that relies on Google's Android operating system. Endnotes 1. Inflation adjusted, Microsoft's 1999 stock market valuation of $615 billion is about $940 billion in today's dollars. 2. This discussion is based on Rumelt, R. (2011), Good Strategy, Bad Strategy (New York: Crown Business). 3. Rumelt, R. (2011), Good Strategy, Bad Strategy (New York: Crown Business). 4. Ibid. Sources: Apple Inc. annual reports (various years); Sull, D., and K.E. Eisenhardt (2015), Simple Rules: How to Thrive in a Complex World (New York: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt); Sull, D., and K.E. Eisenhardt (2012, September), "Simple rules for a complex world," Harvard Business Review, Isaacson, W. (2011), Steve Jobs (New York: Simon & Schuster); and Rumelt, R. (2011), Good Strategy, Bad Strategy (New York: Crown Business).1a. Apple developed iTunes as a complement to drive ... Apple developed iTunes as a complement to drive iPod sales. Which aspect of differentiation strategy does this move represent? Multiple Choice O cost parity O competitive advantage O value driver O economic value O economies of scope1c. Every September, Apple releases new versions... Every September, Apple releases new versions of its iPhone, boasting improved functions-for example, wireless charging, Which type of innovation does this action reflect? Multiple Choice O radical O architectural O incremental O radical and disruptive O disruptive