Question
Please help me answer the following questions , thanks.,,, Consider the two-period endowment economy with N consumers, and a government. Assume that the current and

Please help me answer the following questions , thanks.,,,
Consider the two-period endowment economy with N consumers, and a government. Assume that the current and future consumption are perfect compliments. at is the preferences of each consumer are represented by the following Leontief utility function: U (c, c0 ) = min {ac, c0 } , where a > 0.
As Williamson (2014) puts it, perfect complementarity is an extreme case of a desire for consumption smoothing, in that the consumer never wants to deviate from having current and future consumption in fixed proportions. Suppose the current and future government expenditures are given exogenously by G and G0 , and current and future endowments of the consumers are given by y1, y2, . . . , yN and y 0 1 , y0 2 , . . . , y0 N .
(a) Define a competitive equilibrium of this economy in which the government levies the same lump-sum tax of t and t' on all the consumers in the current and future periods, respectively, and issues B units of bonds in the current period.
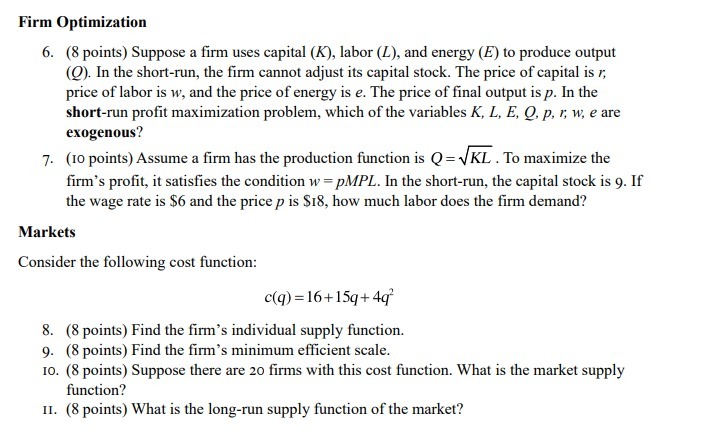
(b) Derive consumer's present value budget constraint, and write down the consumer's problem analytically, subject to the lifetime budget constraint.
(c) Given t, t 0 , yi , y 0 i , and the real interest rate r, solve for the current and future consumption of the consumer i. (d) Find the aggregate private savings, Sp , in the economy, and use it to and the equilibrium interest rate in terms of the exogenous variables.
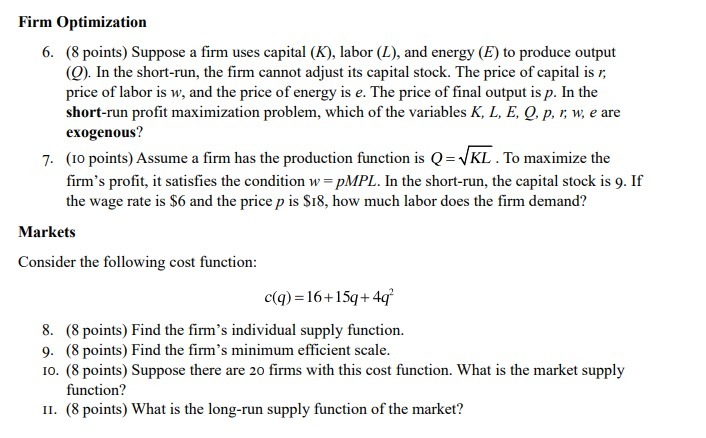

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


