Please help me fill in the blanks, many thanks.

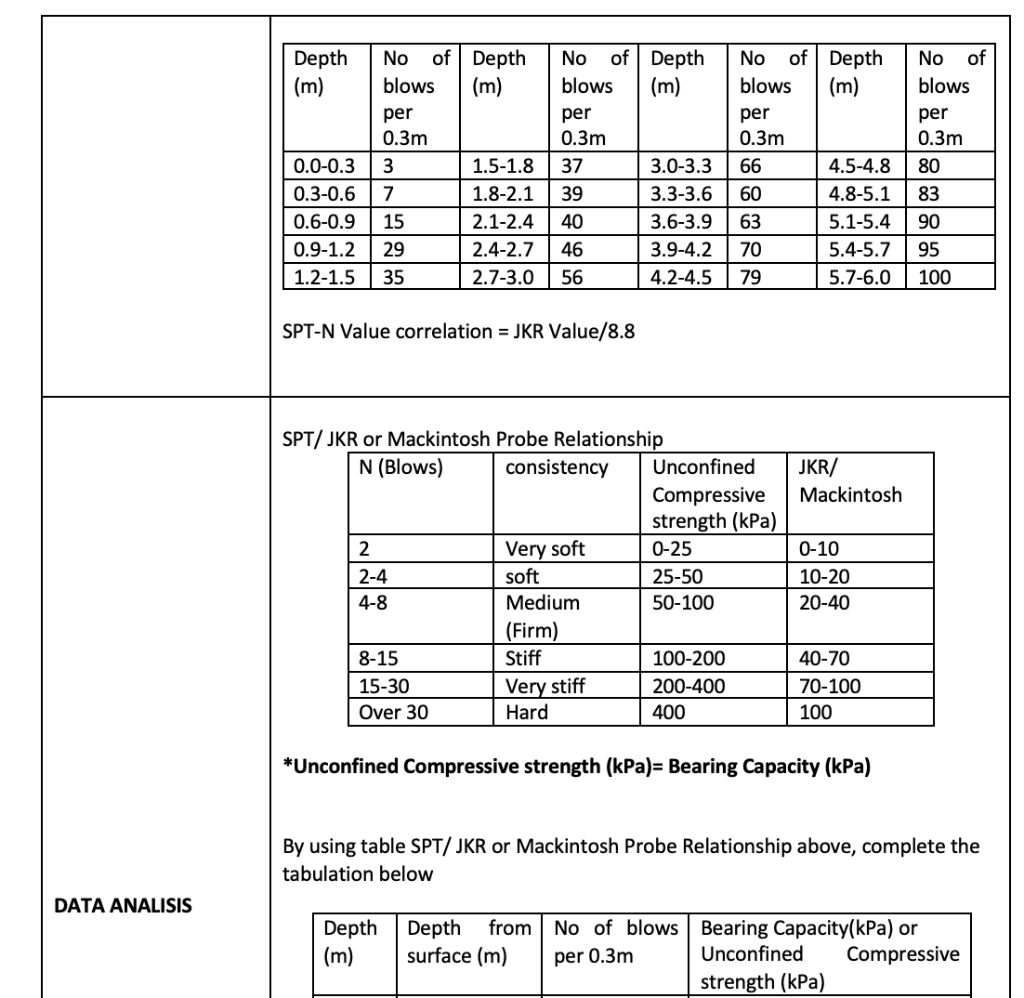
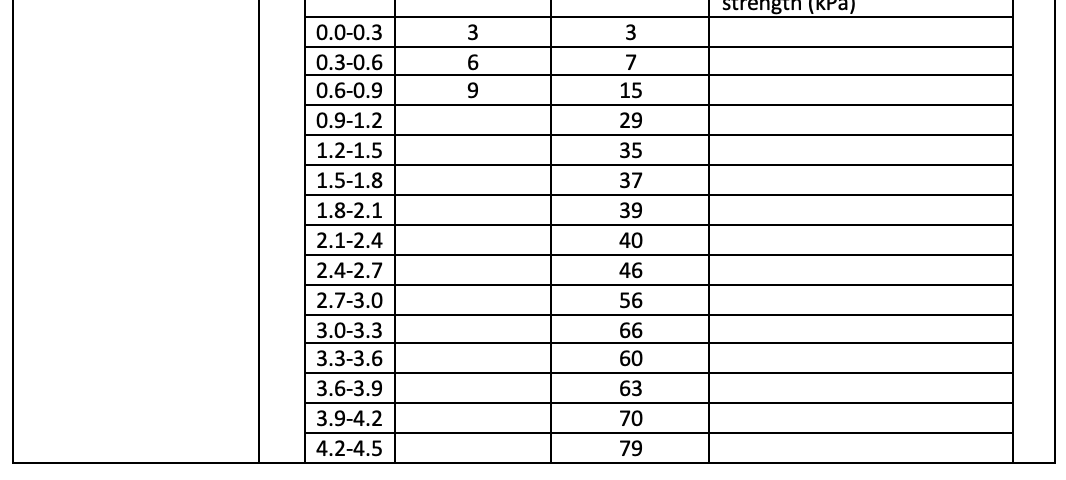
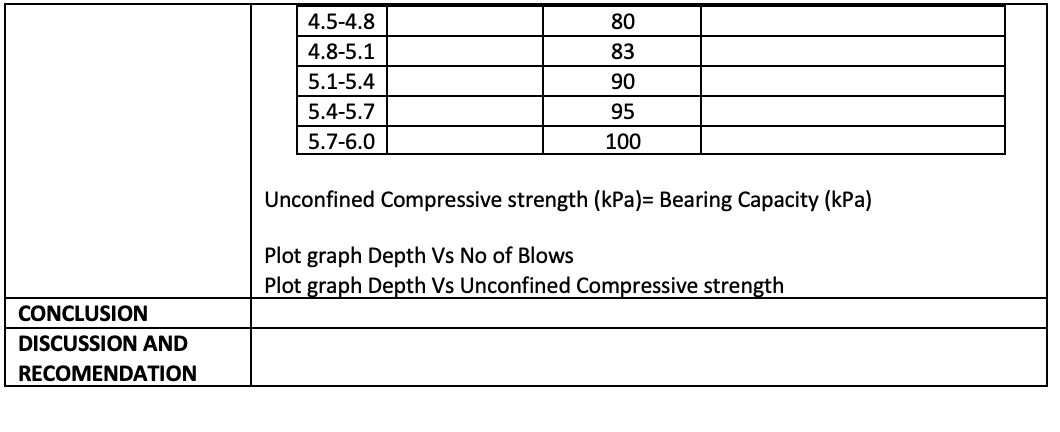
DETERMINATION OF SOIL CONSISTANCY (With referenced to clause 7 of BS1377: Part 7: 1990) + Introduction JKR Probe Test is a dynamic penetrometer test used to check the consistency of the subsoil. Mackintosh Probe which is has 30 cone penetrometer while JKR probe has 60 cone penetrometer. This is a light dynamic test, and the cone is driven directly into the soil by driving a hammer 5kg. Weight dropping through a free height of 280mm. The probe is unable to penetrate medium strength soil and gravelly ground. Mackintosh/JKR probe is used to determine thickness of unsuitable material to be removed, the underlying area and the preliminary design of embankments. The maximum depth tested is down to 12 m or at a maximum of 400 blows/300 mm. The shear strength parameters can be determined indirectly from the Tables provided by Bowles (1993). Objectives PREAMBLE To determine the coefficient of permeability of soil. To determine the sub-surface stratigraphy and identify materials present. To estimate geotechnical parameters. To determine soil classification. To determine allowable bearing capacity of the ground using JKR dynamic cone penetrometer. Learning Outcomes At the end of the laboratory activities, students would be able to: 1. acquire the understanding of engineering properties of soils in determination of the bearing capacity of the ground 2. acquire the necessary skill to prepare sample and conduct force measuring device. 3. calculate and analyze data to report and present result in a proper engineering format. PROBLEM STATEMENT WAYS & MEANS RESULTS Depth No of (m) No of Depth blows (m) No of Depth blows (m) No of Depth blows (m) blows per 0.3m per 0.3m per 0.3m per 0.3m 0.0-0.3 3 1.5-1.8 37 3.0-3.3 66 80 4.5-4.8 4.8-5.1 0.3-0.6 7 1.8-2.1 39 3.3-3.6 60 83 0.6-0.9 15 2.1-2.4 40 3.6-3.9 63 5.1-5.4 90 0.9-1.2 29 46 3.9-4.2 70 5.4-5.7 95 2.4-2.7 2.7-3.0 1.2-1.5 35 56 4.2-4.5 79 5.7-6.0 100 SPT-N Value correlation = JKR Value/8.8 JKR/ Mackintosh 0-10 SPT/ JKR or Mackintosh Probe Relationship N (Blows) consistency Unconfined Compressive strength (kPa) 2 Very soft 0-25 2-4 soft 25-50 4-8 Medium 50-100 (Firm) 8-15 Stiff 100-200 15-30 Very stiff 200-400 Over 30 Hard 400 10-20 20-40 40-70 70-100 100 *Unconfined Compressive strength (kPa)= Bearing Capacity (kPa) By using table SPT/JKR or Mackintosh Probe Relationship above, complete the tabulation below DATA ANALISIS Depth (m) Depth from No of blows Bearing Capacity(kPa) or surface (m) per 0.3m Unconfined Compressive strength (kPa) Strength (Kra) 0.0-0.3 3 3 0.3-0.6 6 7 0.6-0.9 9 15 0.9-1.2 29 1.2-1.5 35 1.5-1.8 37 1.8-2.1 39 2.1-2.4 40 2.4-2.7 46 2.7-3.0 56 3.0-3.3 66 3.3-3.6 60 3.6-3.9 63 3.9-4.2 70 4.2-4.5 79 4.5-4.8 80 83 4.8-5.1 5.1-5.4 90 5.4-5.7 95 5.7-6.0 100 Unconfined Compressive strength (kPa)= Bearing Capacity (kPa) Plot graph Depth Vs No of Blows Plot graph Depth Vs Unconfined Compressive strength CONCLUSION DISCUSSION AND RECOMENDATION DETERMINATION OF SOIL CONSISTANCY (With referenced to clause 7 of BS1377: Part 7: 1990) + Introduction JKR Probe Test is a dynamic penetrometer test used to check the consistency of the subsoil. Mackintosh Probe which is has 30 cone penetrometer while JKR probe has 60 cone penetrometer. This is a light dynamic test, and the cone is driven directly into the soil by driving a hammer 5kg. Weight dropping through a free height of 280mm. The probe is unable to penetrate medium strength soil and gravelly ground. Mackintosh/JKR probe is used to determine thickness of unsuitable material to be removed, the underlying area and the preliminary design of embankments. The maximum depth tested is down to 12 m or at a maximum of 400 blows/300 mm. The shear strength parameters can be determined indirectly from the Tables provided by Bowles (1993). Objectives PREAMBLE To determine the coefficient of permeability of soil. To determine the sub-surface stratigraphy and identify materials present. To estimate geotechnical parameters. To determine soil classification. To determine allowable bearing capacity of the ground using JKR dynamic cone penetrometer. Learning Outcomes At the end of the laboratory activities, students would be able to: 1. acquire the understanding of engineering properties of soils in determination of the bearing capacity of the ground 2. acquire the necessary skill to prepare sample and conduct force measuring device. 3. calculate and analyze data to report and present result in a proper engineering format. PROBLEM STATEMENT WAYS & MEANS RESULTS Depth No of (m) No of Depth blows (m) No of Depth blows (m) No of Depth blows (m) blows per 0.3m per 0.3m per 0.3m per 0.3m 0.0-0.3 3 1.5-1.8 37 3.0-3.3 66 80 4.5-4.8 4.8-5.1 0.3-0.6 7 1.8-2.1 39 3.3-3.6 60 83 0.6-0.9 15 2.1-2.4 40 3.6-3.9 63 5.1-5.4 90 0.9-1.2 29 46 3.9-4.2 70 5.4-5.7 95 2.4-2.7 2.7-3.0 1.2-1.5 35 56 4.2-4.5 79 5.7-6.0 100 SPT-N Value correlation = JKR Value/8.8 JKR/ Mackintosh 0-10 SPT/ JKR or Mackintosh Probe Relationship N (Blows) consistency Unconfined Compressive strength (kPa) 2 Very soft 0-25 2-4 soft 25-50 4-8 Medium 50-100 (Firm) 8-15 Stiff 100-200 15-30 Very stiff 200-400 Over 30 Hard 400 10-20 20-40 40-70 70-100 100 *Unconfined Compressive strength (kPa)= Bearing Capacity (kPa) By using table SPT/JKR or Mackintosh Probe Relationship above, complete the tabulation below DATA ANALISIS Depth (m) Depth from No of blows Bearing Capacity(kPa) or surface (m) per 0.3m Unconfined Compressive strength (kPa) Strength (Kra) 0.0-0.3 3 3 0.3-0.6 6 7 0.6-0.9 9 15 0.9-1.2 29 1.2-1.5 35 1.5-1.8 37 1.8-2.1 39 2.1-2.4 40 2.4-2.7 46 2.7-3.0 56 3.0-3.3 66 3.3-3.6 60 3.6-3.9 63 3.9-4.2 70 4.2-4.5 79 4.5-4.8 80 83 4.8-5.1 5.1-5.4 90 5.4-5.7 95 5.7-6.0 100 Unconfined Compressive strength (kPa)= Bearing Capacity (kPa) Plot graph Depth Vs No of Blows Plot graph Depth Vs Unconfined Compressive strength CONCLUSION DISCUSSION AND RECOMENDATION










