Please help me find the solution to these problems. No explantion is requires as long as the answers are correct.
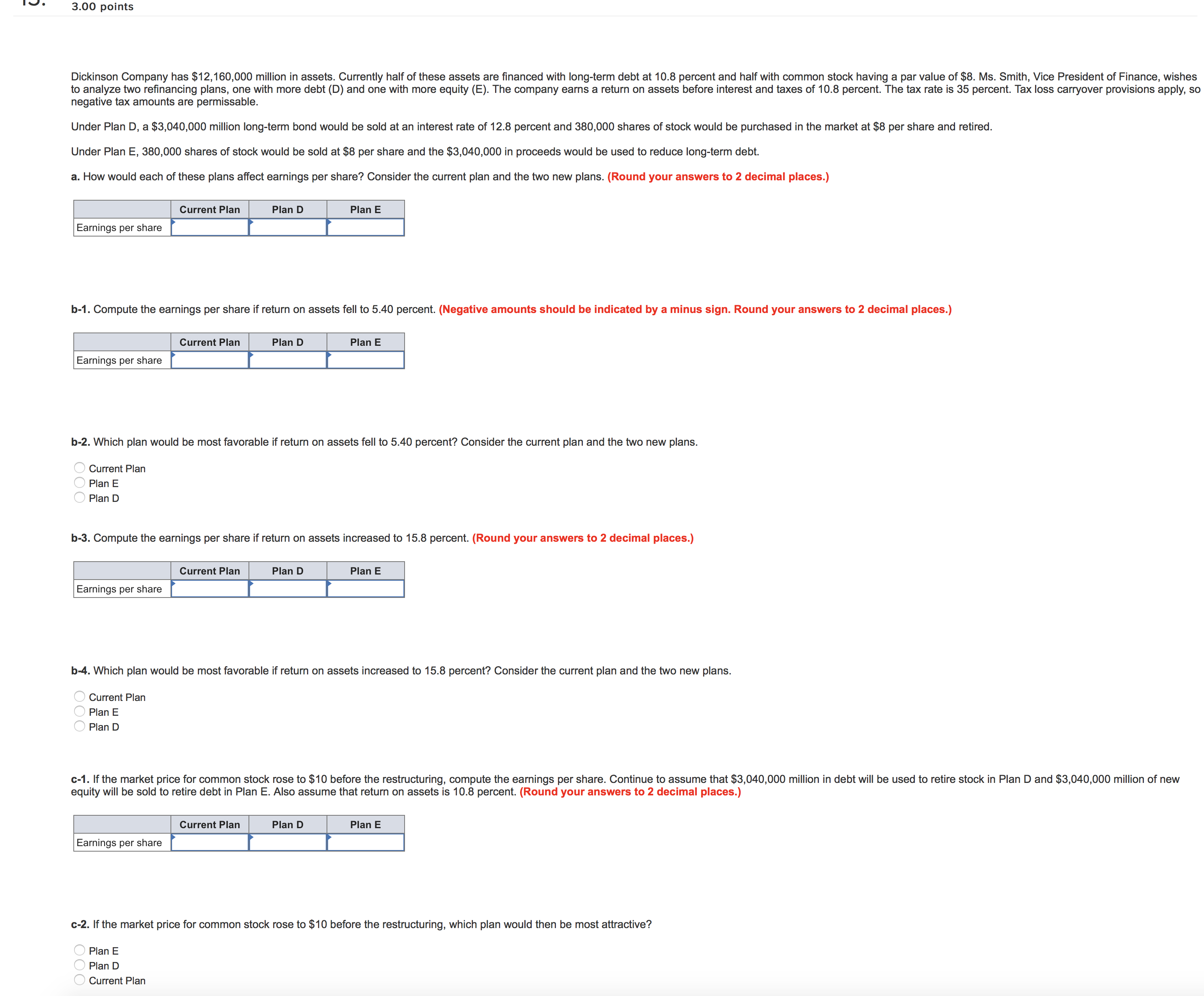
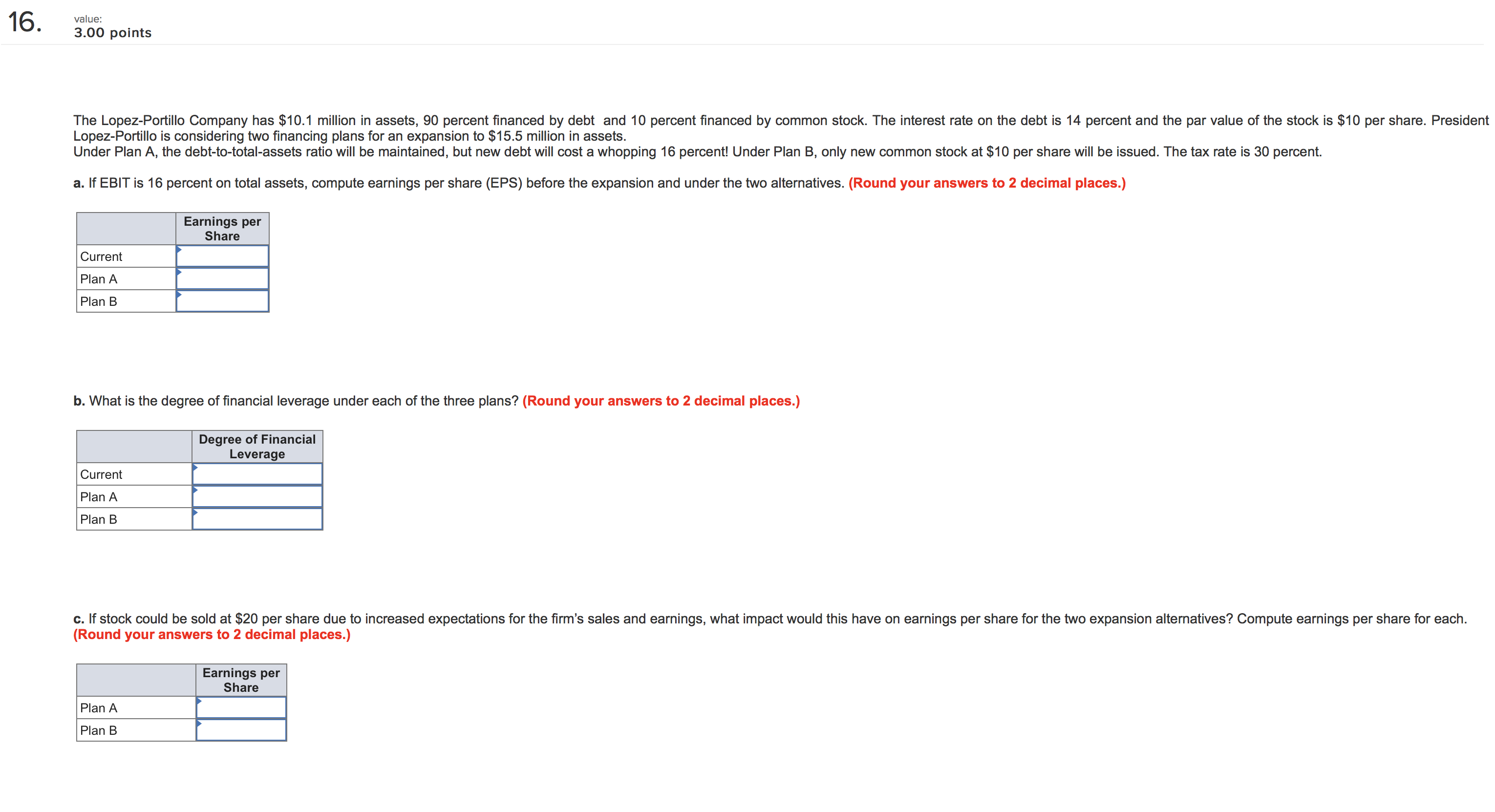
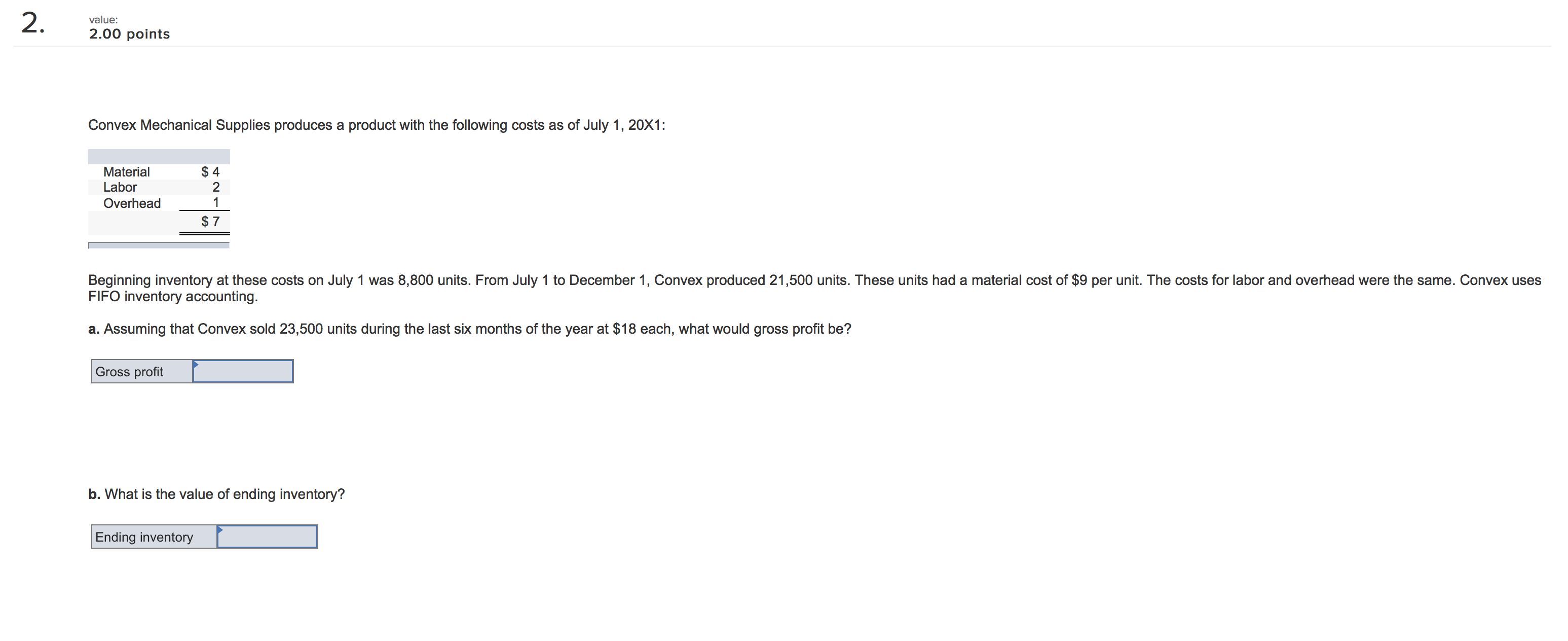
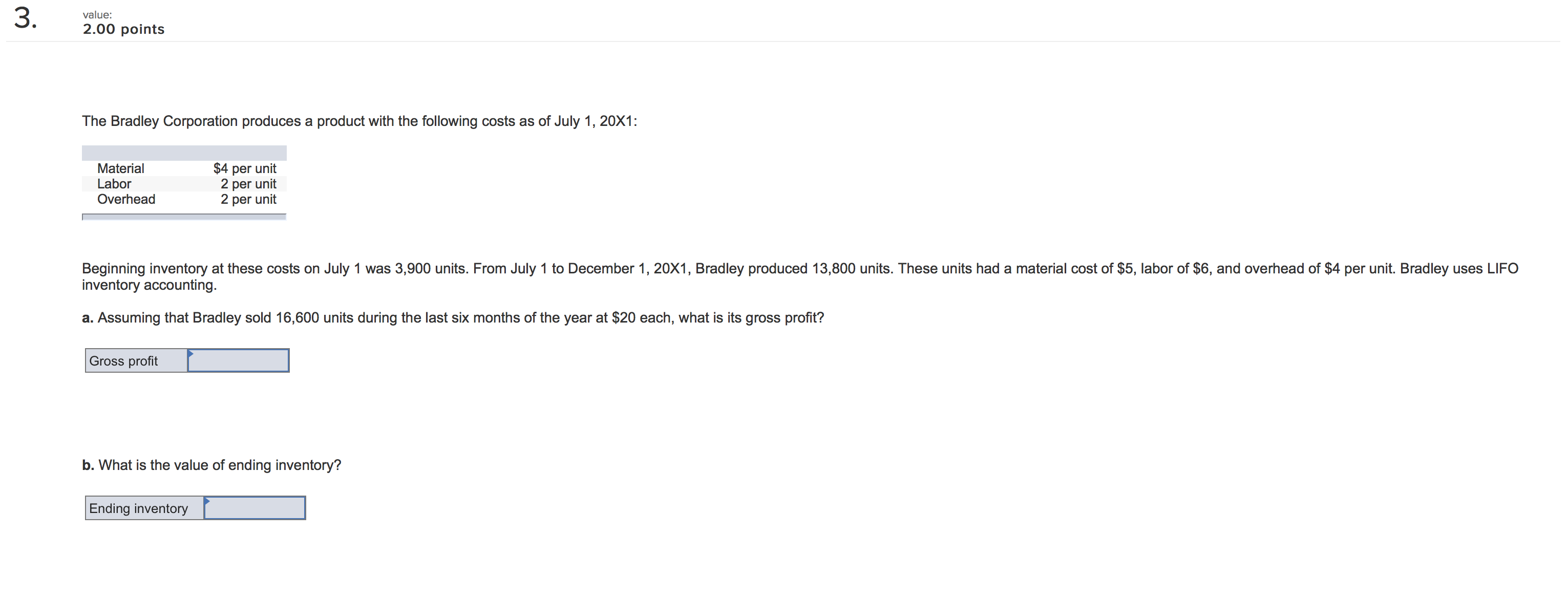
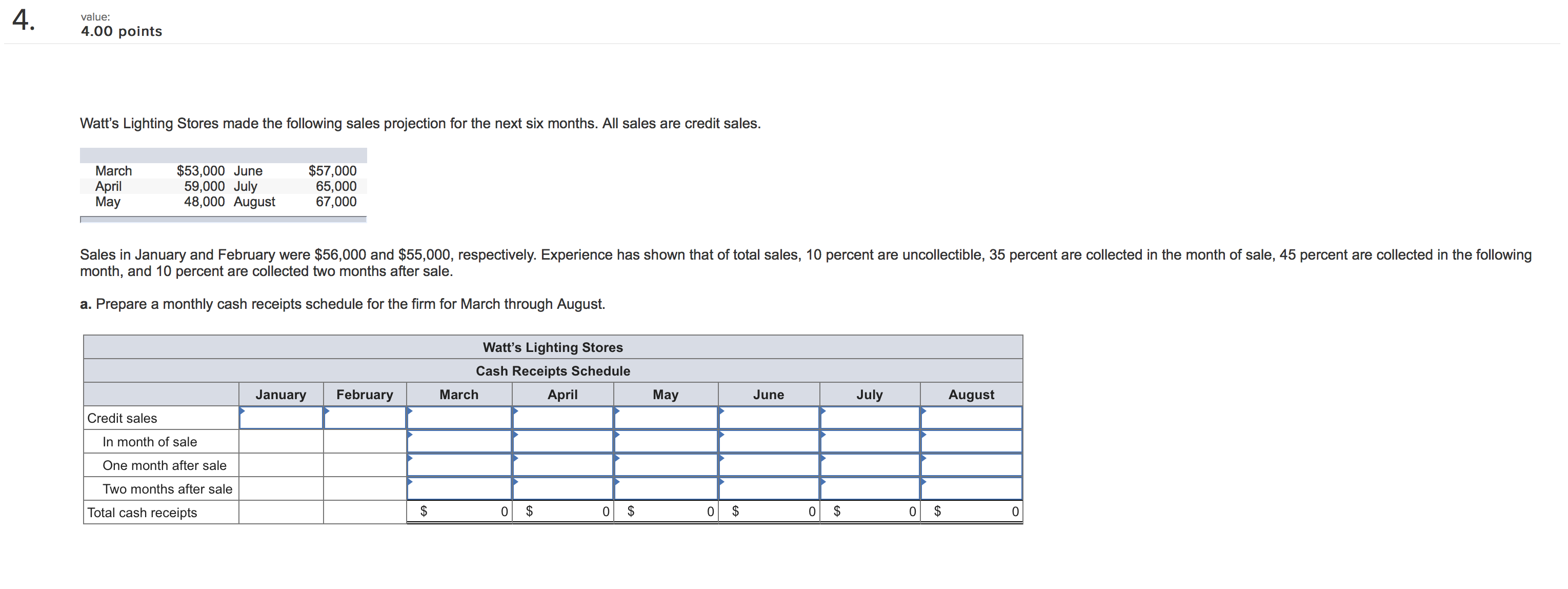
IU- 3.00 points Dickinson Company has $12,160,000 million in assets. Currently half of these assets are nanced with long-term debt at 10.8 percent and half with common stock having a par value of $8. Ms. Smith, Vice President of Finance, wishes to analyze two renancing plans, one with more debt (D) and one with more equity (E). The company earns a return on assets before interest and taxes of 10.8 percent. The tax rate is 35 percent. Tax loss carryover provisions apply, so negative tax amounts are permissable. Under Plan D, a $3,040,000 million long-term bond would be sold at an interest rate of 12.8 percent and 380,000 shares of stock would be purchased in the market at $8 per share and retired. Under Plan E, 380,000 shares of stock would be sold at $8 per share and the $3,040,000 in proceeds would be used to reduce long-term debt. a. How would each of these plans aect earnings per share? Consider the current plan and the two new plans. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) Current Plan Plan D Plan E Earnings per share b-1. Compute the earnings per share if return on assets fell to 5.40 percent. (Negative amounts should be indicated by a minus sign. Round your answers Ito 2 decimal places.) Current Plan Plan D Plan E Earnings per share b-Z. Which plan would be most favorable if return on assets fell to 5.40 percent? Consider the current plan and the two new plans. 5 Current Plan " Plan E A Plan D b-3. Compute the earnings per share if return on assets increased to 15.8 percent. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) Current Plan Plan D Plan E Earnings per share b4. Which plan would be most favorable if return on assets increased to 15.8 percent? Consider the current plan and the two new plans. 7,\" Current Plan A, Plan E " Plan D c-1. if the market price for common stock rose to $10 before the restructuring, compute the earnings per share. Continue to assume that $3,040,000 million in debt will be used to retire stock in Plan D and $3,040,000 million of new equity will be sold to retire debt in Plan E. Also assume that return on assets is 10.8 percent. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) Currant Plan Plan D Plan E Earnings per share c-Z. If the market price for common stock rose to $10 before the restructuring, which plan would then be most attractive? " Plan E " Plan D '7 Current Plan 16' :3?) points The Lopez-Portillo Company has $10.1 million in assets, 90 percent nanced by debt and 10 percent nanced by common stock. The interest rate on the debt is 14 percent and the par value of the stock is $10 per share. President Lopez-Pcrlillo is considering two nancing plans for an expansion to $15.5 million in assets. Under Plan A, the debt-to-tolal-assets ratio will be maintained, but new debt will cost a whopping 16 percent! Under Plan B, only new common stock at $10 per share will be issued. The tax rate is 30 percent. a. If EBIT is 16 percent on total assets, compute earnings per share (EPS) before the expansion and under the two alternatives. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) Eamlngs per share Current Plan A Plan B b. What is the degree of nancial leverage under each of the three plans? (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) Degree of Financial Leverage Plan B c. If stock could be sold at $20 per share due to increased expectations for the n'n's sales and earnings, what impact would this have on earnings per share for the two expansion alternatives? Compute earnings per share for each. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) Eamlngs per Share Plan A Plan B 2 wlue: 2.00 points Convex Mechanical Supplies produces a product with the following costs as of July 1, 20x1: Material 5 4 Labor 2 Overhead 1 Beginning inventory at these costs on July 1 was 8,500 units. From July 1 to December 1, Convex produced 21,500 units. These units had a material cost of $9 per unit. The costs for labor and overhead were the same. Convex uses FIFO inventory accounting. 9. Assuming that Convex sold 23,500 units during the last six months of the year at $18 each, what would gross prot be? b. What is the value of ending inventory? Ending inventory I value: 2.00 points The Bradley Corporation produces a product with the following costs as of July 1, 20x1: Material $4 per unit Labor 2 per unit Overhead 2 per unit ' Beginning inventory at these costs on July 1 was 3,900 units' From July 1 to December 1, 20x1, Bradley produced 13,800 units. These units had a material cost of $5, labor of $6, and overhead of $4 per unit. Bradley uses LIFO inventory accounting. 3. Assuming that Bradley sold 16,600 units during the last six months at the year at $20 each, what is its gross prot? b. What is the value of ending inventory? Ending inventory I 4 value: 4.00 points Watt's Lighting Stores made the following sales projection for the next six months. All sales are credit sales. March $53,000 June $57,000 April 59,000 July 65,000 May 45,000 August 67,000 , Sales in January and February were $56,000 and $55,000, respectively. Experience has shown that of total sales, 10 percent are uncollectible, 35 percent are collected in the month of sale, 45 percent are collected in the following month, and 10 percent are collected two months after sale. a. Prepare a monthly cash receipts schedule for the rm for March through August, Watt's Lighting Stores cash Reoelpts Schedule February Credit sales In month of sale One month after sale Two months after sale Totalcashreceipts $ 0 $ 0 $ 0 $ 0 $ 0 S 0