Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Please help me identify my mistake, and it would be great if I could see your calculations! Chapter 4 - Master it! Financial planning can
Please help me identify my mistake, and it would be great if I could see your calculations!
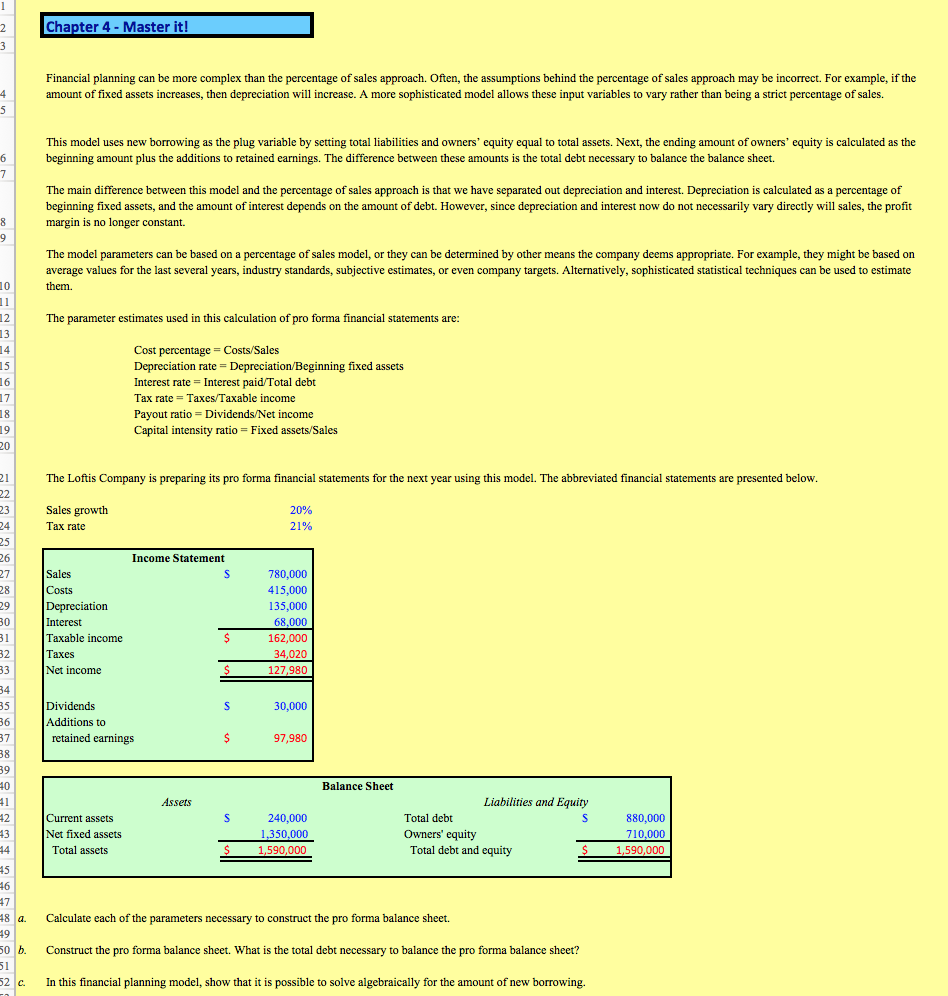
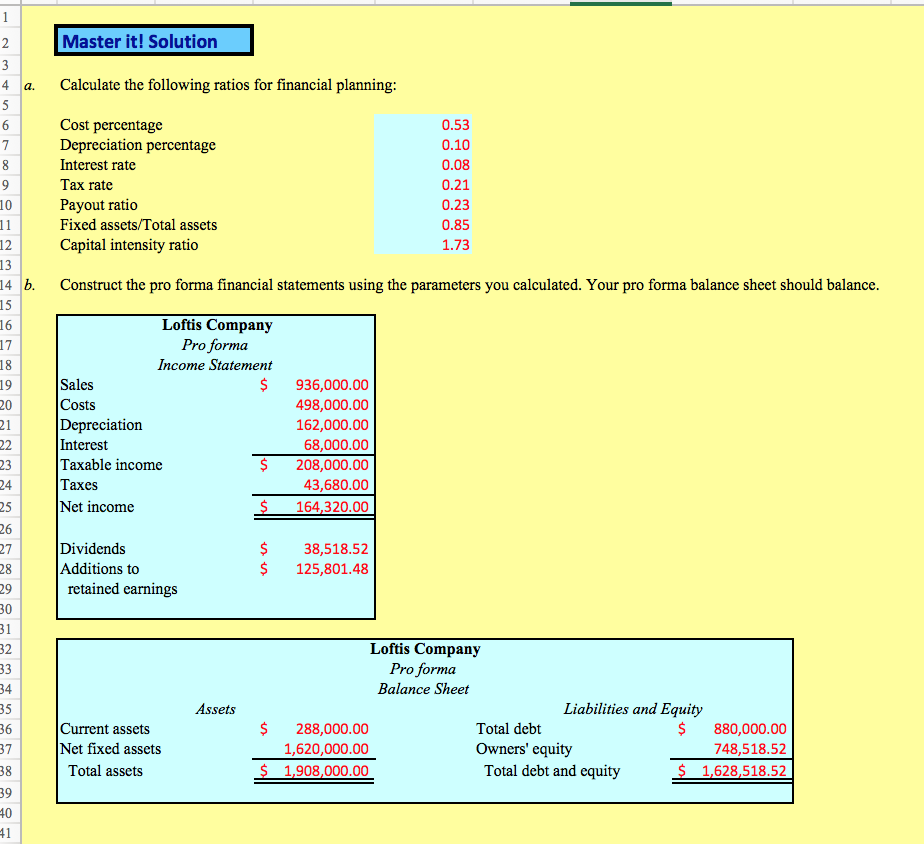
Chapter 4 - Master it! Financial planning can be more complex than the percentage of sales approach. Often, the assumptions behind the percentage of sales approach may be incorrect. For example, if the amount of fixed assets increases, then depreciation will increase. A more sophisticated model allows these input variables to vary rather than being a strict percentage of sales. This model uses new borrowing as the plug variable by setting total liabilities and owners' equity equal to total assets. Next, the ending amount of owners' equity is calculated as the beginning amount plus the additions to retained earnings. The difference between these amounts is the total debt necessary to balance the balance sheet. The main difference between this model and the percentage of sales approach is that we have separated out depreciation and interest. Depreciation is calculated as a percentage of beginning fixed assets, and the amount of interest depends on the amount of debt. However, since depreciation and interest now do not necessarily vary directly will sales, the profit margin is no longer constant. The model parameters can be based on a percentage of sales model, or they can be determined by other means the company deems appropriate. For example, they might be based on average values for the last several years, industry standards, subjective estimates, or even company targets. Alternatively, sophisticated statistical techniques can be used to estimate The parameter estimates used in this calculation of pro forma financial statements are: Depreciation rate Depreciation/Beginning fixed assets Interest rate- Interest Tax rate = Taxes/Taxable income Payout ratio Dividends/Net income Capital intensity ratio Fixed assets/Sales 16 paid Total debt The Loftis Company is preparing its pro forma financial statements for the next year using this model. The abbreviated financial statements are presented below 23 Sales growth 20% 21% Tax rate 25 Income Statement 780,000 415,000 135,000 68,000 162,000 34,020 127,980 Depreciation Taxable income Taxes Net income Dividends Additions to 30,000 retained earnings 97,980 40 Balance Sheet Assets Liabilities and Equity Current assets Net fixed assets Total assets 240,000 1,350,000 ,590,000 Total debt Owners' equity 880,000 710,000 ,590,000 Total debt and equity 48 a. Calculate each of the parameters necessary to construct the pro forma balance sheet. 50 b. Construct the pro forma balance sheet. What is the total debt necessary to balance the pro forma balance sheet? 52 c. In this financial planning model, show that it is possible to solve algebraically for the amount of new borrowingStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


