Question
Please help me out with this question, I absolutely give the thumbs up to anyone can do it as the question requires. Thank you. General
Please help me out with this question, I absolutely give the thumbs up to anyone can do it as the question requires. Thank you.
General Overview: In this assignment, your task is to implement the encoding and decoding algorithms for Huffman coding. Huffman coding will be discussed in class and therefore we will not spend much time talking about how the algorithms work.
There are three major steps to the solution that needs to be dealt with:
1. Using these frequencies, build an Huffman encoding tree and encode the data file using it. 2. Using the encoding of the data file and the Huffman tree, decode to obtain original data file.
Symbols and their frequencies k:1 T:1 .:2
n:2 i:1 f:1 m:1 I:1:3 ?:1 u:2
y:2 a:3 w:1 ,:1 r:2 t:1:8 o:4
l:2
e:5
h:4
1- Building the Huffman encoding tree
In this step, you are to build a Huffman encoding tree, which is a binary tree (but not a BST) which will encode each of the characters in your input as a sequence of zeros and ones. Initially create a Huffman tree for each data item in your linked list . To build the Huffman encoding tree, you successive remove the two items (trees) in your heap, combine them and then insert the resulting tree into the heap. The data that you need to store for this new node is the concatenation of the symbols of the two joined nodes and the sum of the frequencies of the two joined nodes. Remember that the frequency of a node is used as the priority in the heap. Repeat this process until there is one tree left in the heap. This algorithm is also stated on slide 15 of the lecture notes.
The sole tree in the heap is the Huffman encoding tree you want. This tree is used to encode the input file. The encoding for a character is obtained by traversing the tree from the root to a leaf, where traversing a left child means encoding contains a 0 and traversing a right child means encoding a 1.
Using the Huffman encoding tree, output the encoding of each distinct character that is encoded by the Huffman tree. This can be done by traversing the tree and printing the encoding for a character when you encounter a leaf node. For example: An output will look something like: Huffman Encoding
n:000
s:001
:01
t:10
e:11
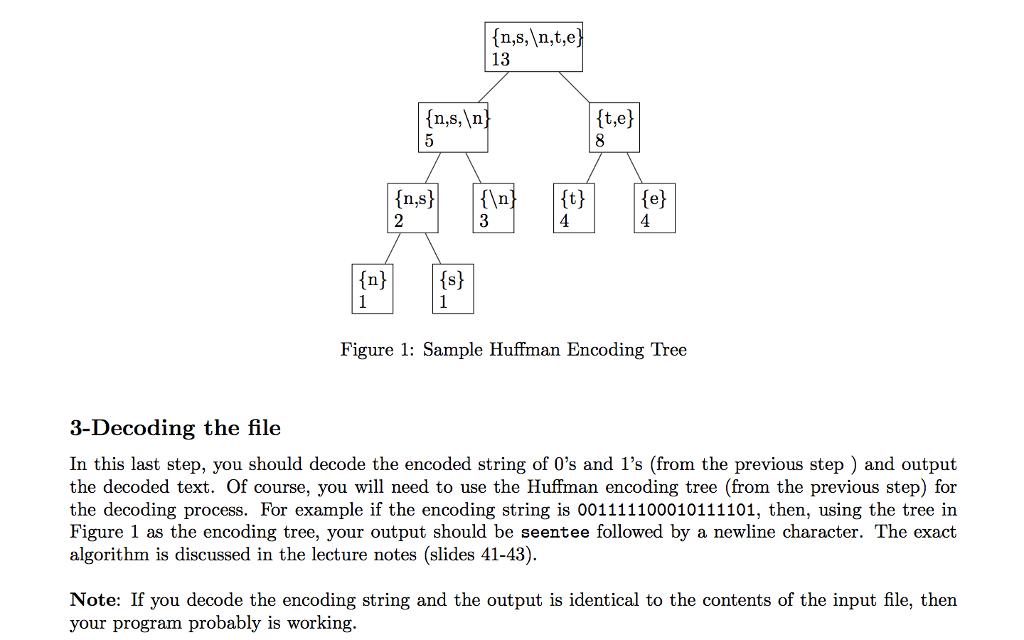
Then, encode the entire input file and output the encoding. This will be a sequence of 0s and 1s. For each line of the input text, you should print the encoding on a separate line. For example, if the input file contains the line seentee , you should output 001111100010111101 when encoding using the tree given by Figure 1. In addition you should store the entire encoding of the input file in a string variable.
At a minimum, you should create Java classes to represent a heap, and a Huffman tree.
FREQUENCYLIST.JAVA
//The linked list of nodes containing frequency data
class FrequencyList {
Node head;
int count;
FrequencyList() {
head = null;
count = 0;
}
//search for node in linked list that contains key. Returns a reference to node if found, else returns null.
public Node search(String key) {
Node curr=head;
while (curr != null) {
if (key.compareTo(curr.data.symbol) == 0) {
break;
}
curr = curr.next;
}
return curr;
}
//print contents of linked list.
public void printList() {
Node curr;
curr = head;
while (curr != null) { //print each node
curr.print();
curr = curr.next;
}
}
//insert a new node if key is not in the linked list. Otherwise increment frequency by 1.
public void insert(String key) {
Node curr;
curr = search(key);
if (curr == null) { //key not in list, add it to front.
curr = new Node(key); //insert new node at front of list
curr.next = head;
head = curr;
count = count + 1;
}
else { //already in list. Increment the frequency by 1.
curr.data.frequency = curr.data.frequency + 1; //increment frequency of symbol
}
}
}
//A node of the Linked List class FrequencyList.
class Node {
FrequencyData data;
Node next;
Node(String key) {
data = new FrequencyData(key,1);
}
void print() {
data.print();
}
}
//This class contains a symbol and its frequency
class FrequencyData {
String symbol; //using a string type will become handy when build the Huffman encoding tree.
int frequency;
FrequencyData (FrequencyData data) {
symbol = data.symbol;
frequency = data.frequency;
}
FrequencyData(String s, int freq) {
symbol = s;
frequency = freq;
}
//print content of symbol (which may contain more than one character
//for debugging purposes only.
void printSymbol() {
int i;
int a;
String s="";
for (i = 0; i
a = (int) symbol.charAt(i);
if (a==10)
s = s+"
else if (a == 32)
s =s+"
else if (a == 9)
s =s+"
else
s = s+ symbol.charAt(i);
}
System.out.print(s);
}
/*used to print symbol(s) and frequency*/
/*used for debugging*/
void print() {
printSymbol();
System.out.println(":"+frequency);
}
}
FREQUENCYTESTER.JAVA
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
//This class shows how to use compute the frequencies of the symbols in a file.
public class FrequencyTester {
FrequencyList fList;
public FrequencyTester() {
fList = null;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
String fileName;
Scanner file;
String s;
String inputLine;
int i;
FrequencyList fList;
FrequencyTester ft = new FrequencyTester();
ft.fList = new FrequencyList();
fList = ft.fList;
fileName = JOptionPane.showInputDialog("Enter filename.");
System.out.println("Input File:"+fileName);
System.out.println("**********Content of Input File**************");
try {
file = new Scanner( new File( fileName ) );
while (file.hasNextLine()) { //read in line
inputLine = file.nextLine();
System.out.println(inputLine);
for ( i = 0;i
s = ""+inputLine.charAt(i);
fList.insert(s); //insert symbol into linked list (increment count by 1 if already in list)
}
s = " "; //each line ends with a newline character (which is not captured in inputLine)
fList.insert(s); //add it manually
}
System.out.println("**********End of Input File*************");
System.out.println("Symbols and their frequencies");
fList.printList(); //print the contents of the linked list of symbols and their frequencies.
file.close();
}catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("IO Error: " + e.getMessage());
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Error: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
SMALLTEST.TXT
hello there, how are you? I am fine. Thank you.13 In.s,In t,e) 2 Figure 1: Sample Huffman Encoding Tree 3-Decoding the file In this last step, you should decode the encoded string of 0's and 1's (from the previous step) and output the decoded text. Of course, you will need to use the Huffman encoding tree (from the previous step) for the decoding process. For example if the encoding string is 001111100010111101, then, using the tree in Figure 1 as the encoding tree, your output should be seentee followed by a newline character. The exact algorithm is discussed in the lecture notes (slides 41-43) Note: If you decode the encoding string and the output is identical to the contents of the input file, then your program probably is working 13 In.s,In t,e) 2 Figure 1: Sample Huffman Encoding Tree 3-Decoding the file In this last step, you should decode the encoded string of 0's and 1's (from the previous step) and output the decoded text. Of course, you will need to use the Huffman encoding tree (from the previous step) for the decoding process. For example if the encoding string is 001111100010111101, then, using the tree in Figure 1 as the encoding tree, your output should be seentee followed by a newline character. The exact algorithm is discussed in the lecture notes (slides 41-43) Note: If you decode the encoding string and the output is identical to the contents of the input file, then your program probably is working
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


