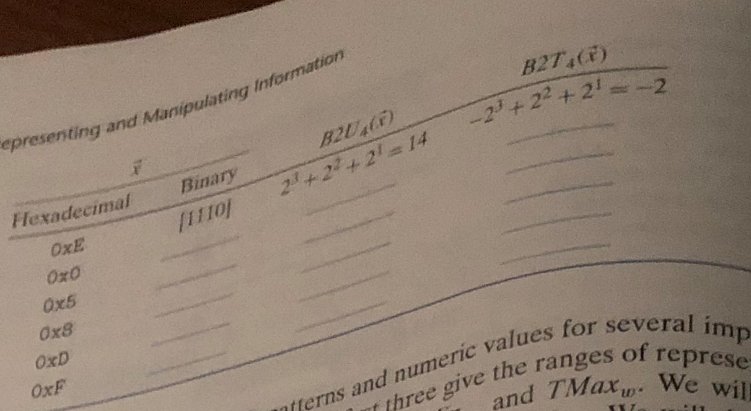Please help me solve these Computer System problem 2.17. Please show work so that I may follow and understand.


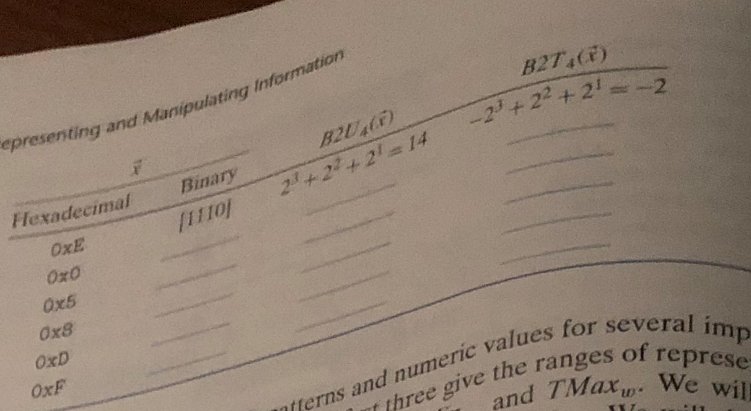
Figure 2.12 Unsigned number Section 22 Integes Representations 63 When bit in the binary 127 contributes to the 255 32.767 65,535 32,767 65.535 2.147-483 647 4.294,967.295 2.147.483,647 4.294.967,295 78910 11 12 13 14 16 16 01011 [10111 ans igsed char PRINCIPLE: Definition of unsigned encoding iat -2,1474R long 2.147,483.65 unsigned long 372.036.854,775,807 44.073,709-551.615 751464073.709 551.615 uint32 t Guaranteed ranges for C integral data types. The C data oypes huve at least these ranges of values standards require In this equation, the notation means that the left-hand side is defined to be equal to the right-hand side. The function B2Uw maps strings of zeros and ones of length w to nonnegative integers. As examples, Figure 2.12 shows the mapping given by B2U, from bit vectors to integers for the following cases: ulot64, t Figure 2.11 We also see that data type B2U4(10011) = 0-23 +0.22 +0.21 + 1.2 0+0+0+1-1 B2U4([O101) 0.23 + 1 .22 +0.21 +1-2 -0+4+0+1 5 B2U4(1011)1-23+0-22 +1-21+1.28+0+2+111 B2U4([1111) -1.23 + 1.22 +1.21 +1 .20 = 8+4+2+1-15 rive numbebugh this is mostly a throwbasi with 4-byte numbers and it typically is for 32-bit programs The fixedsmente types guarantee har the ranges of values will e exactly those given by thez da numhers of Figure 29, including the asymmetry berwcen negative ai symmetric could be implemented with 2-byte nunm to the days of 16-bit machines We also see that size long can be range of positive and negative numbers We also positi (2.2) 222 Unsigned Encodings et us consider an integer data type of w bits We write a bit vector In the figure, we represent each bit position i by a rightward-pointing blue bar of length 2'. The numeric value associated with a bit vector then equals the sum of the lengths of the bars for which the corresponding bit values are1 as either i, to ol to denote the individual bit Let us consider the range of values that can be represented using w bits. The least value is given by bit vector [00.0] having integer value 0, and the greatest value is given by bit vector [11-.-1] having integer value UMa, 2 2 1. Using the 4-bit case as an example, we have UMax-B2U41111 24-1s 15. Thus, the function B2U, can be defined as a mapping B2U w: (01)" ctoeiuber writen in binary notation, we obtain the of i. In this encoding, each bit ay has value 0 or 1, with the , denote the entire vector, or as I, latter case indicating that value 2 should be included as part of the numeriae We can express this interpretation as a function B2U, (for "binary to unsigned The unsigned binary representation has the important property that every number between 0 and 2 1 has a unique encoding as a u-bit value. For example, length w