Question
Please help me thouroughly answer this question. Please include calculations and how you got to the answer. I have provided templates for the answers, where
Please help me thouroughly answer this question. Please include calculations and how you got to the answer. I have provided templates for the answers, where the highlighted yellow is the answer box. Thank you!
Case 7-65. Cost-Volume-Profit with Multiple Products, Sales Mix Changes, Changes in Fixed and Variable Costs Objective 1, 4
Artistic Woodcrafting Inc. began several years ago as a one-person, cabinet-making operation. Employees were added as the business expanded. Last year, sales volume totaled $850,000. Volume for the first five months of the current year totaled $600,000, and sales were expected to be $1.6 million for the entire year. Unfortunately, the cabinet business in the region where Artistic is located is highly competitive. More than 200 cabinet shops are all competing for the same business.
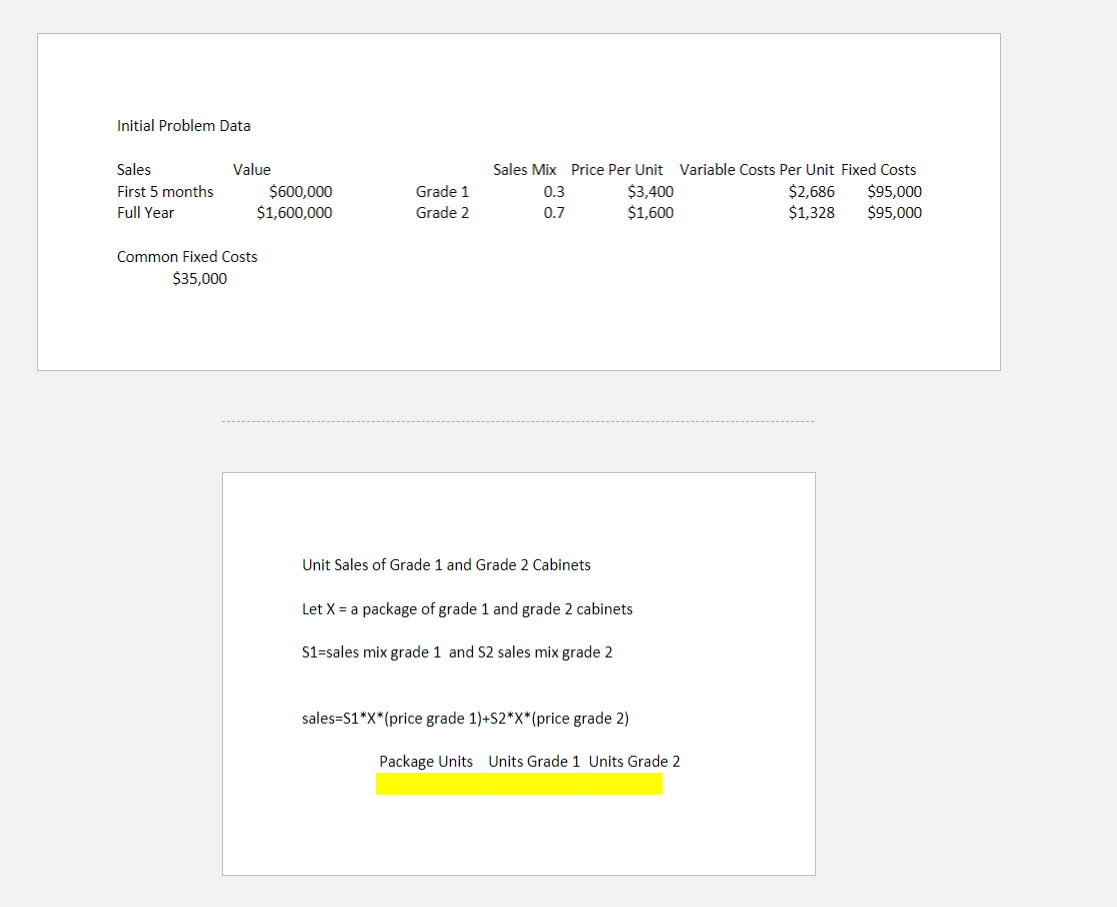
Artistic currently offers two different quality grades of cabinets: Grade I and Grade II, with Grade I being the higher quality. The average unit selling prices, unit variable costs, and direct fixed costs are as follows:
Unit Price Unit Variable Cost Direct Fixed Cost Grade I $3,400 $2,686 $95,000 Grade II 1,600 1,328 95,000 Common fixed costs (fixed costs not traceable to either cabinet) are $35,000. Currently, for every three Grade I cabinets sold, seven Grade II cabinets are sold.
Required:
Calculate the number of Grade I and Grade II cabinets that are expected to be sold during the current year.
Calculate the number of Grade I and Grade II cabinets that must be sold for Artistic to break even.
Artistic can buy computer-controlled machines that will make doors, drawers, and frames. If the machines are purchased, the variable costs for each type of cabinet will decrease by 9%, but common fixed cost will increase by $44,000. Compute the effect on operating income, and also calculate the new break-even point. Assume the machines are purchased at the beginning of the sixth month. Fixed costs for the company are incurred uniformly throughout the year.
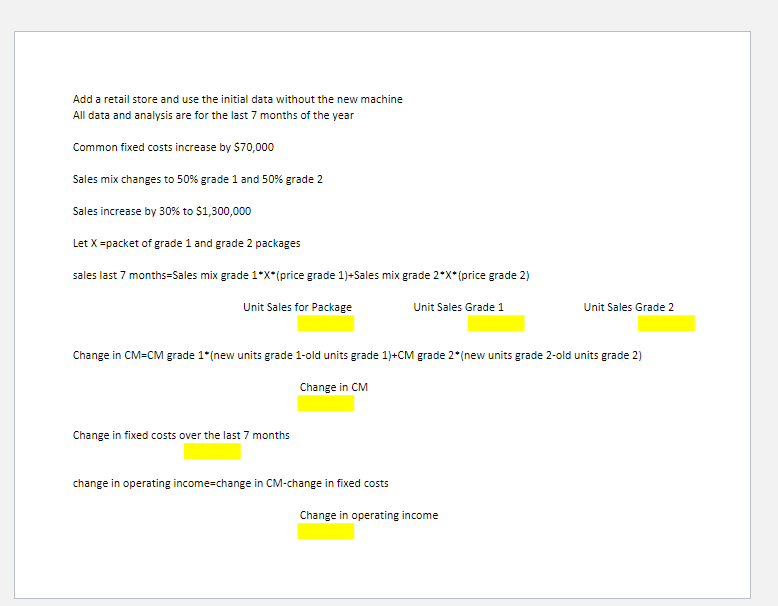
Refer to the original data. Artistic is considering adding a retail outlet. This will increase common fixed cost by $70,000 per year. As a result of adding the retail outlet, the additional publicity and emphasis on quality will allow the firm to change the sales mix to 1:1. The retail outlet is also expected to increase sales by 30%. Assume that the outlet is opened at the beginning of the sixth month. Calculate the effect on the company's expected profits for the current year, and calculate the new break-even point. Assume that fixed costs are incurred uniformly throughout the year.

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


