Question: Please help me understand the following problems. DETAILS PREVIOUS ANSWERS MY NOTES ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER on a completely random and design, aight asparimental
Please help me understand the following problems.
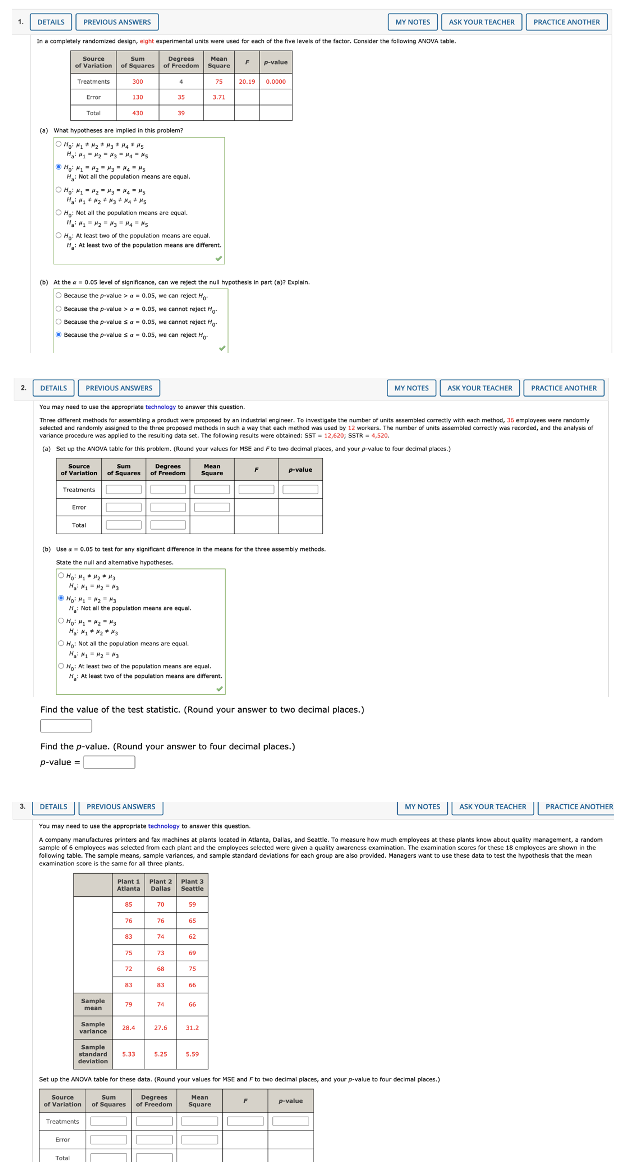
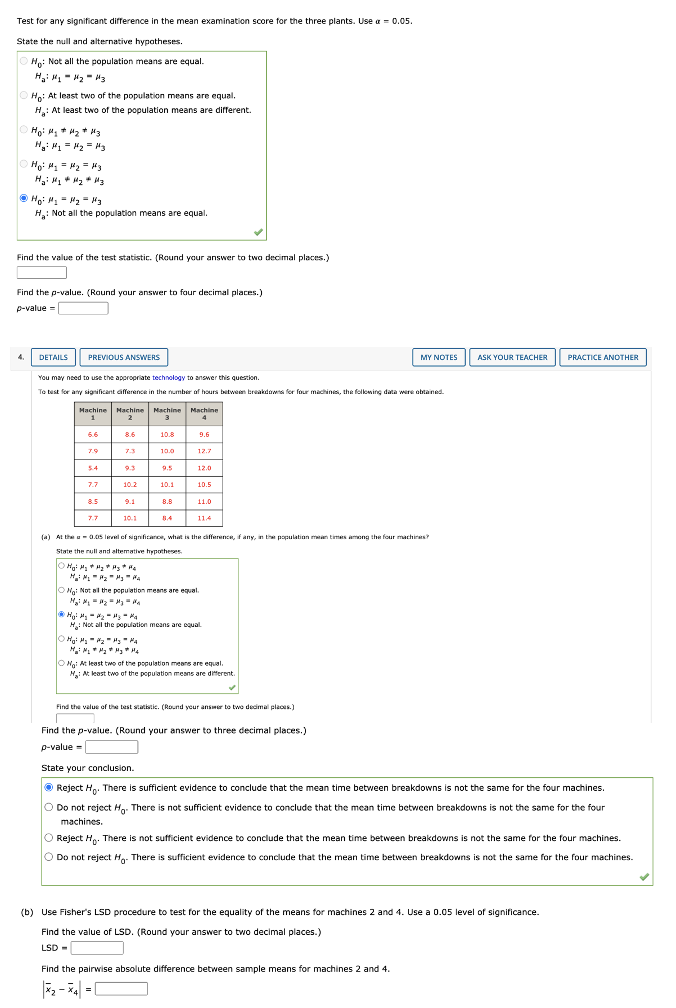
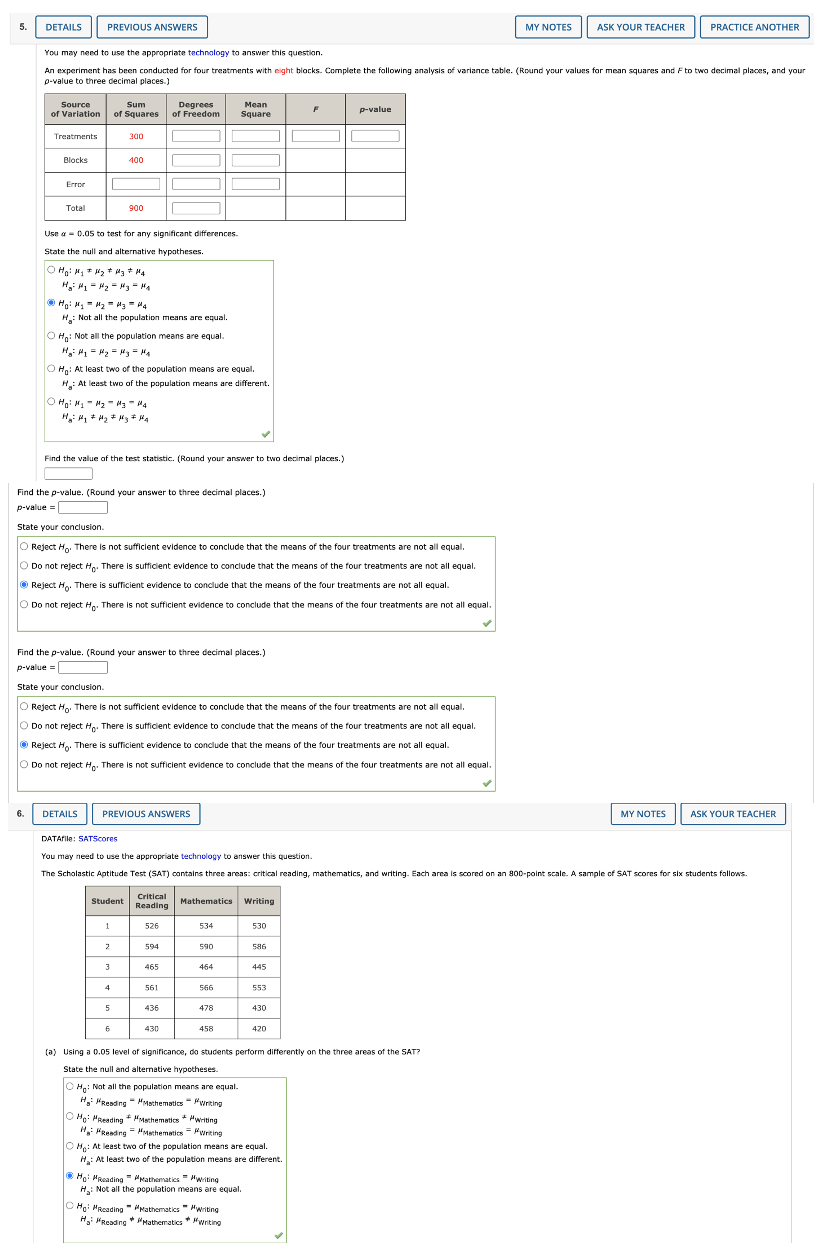
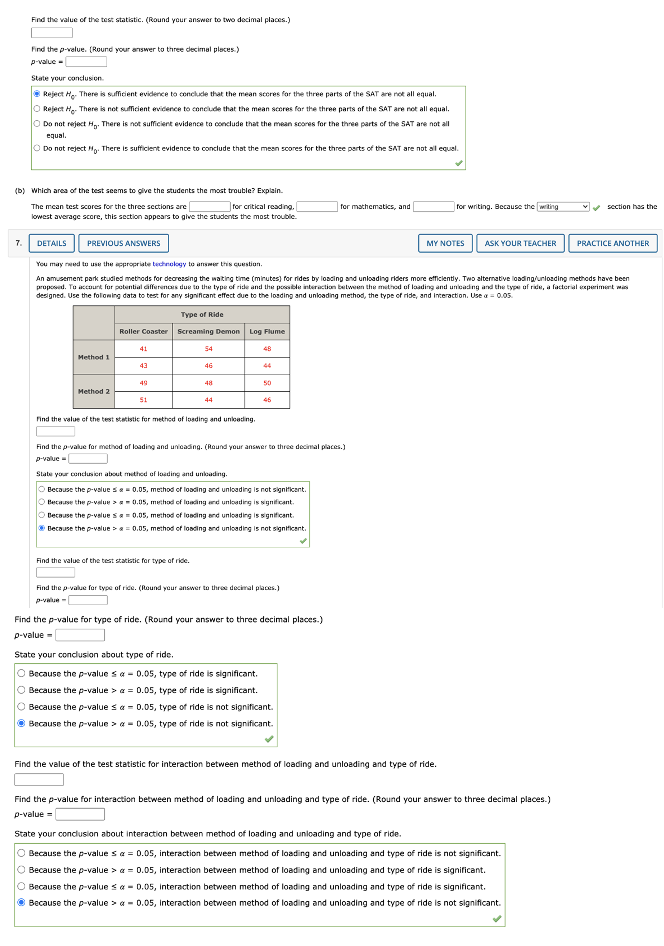
DETAILS PREVIOUS ANSWERS MY NOTES ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER on a completely random and design, aight asparimental units were wand for each of the five levels of the factor. Consider the following ANOVA table. Source Sum Degrees Mean of Variation of Squares of Freedom Square p-value Treatments 300 20.19 0.0300 130 3.71 Tatal 430 (#) What hypotheses are Implies in this problem? Hi Not all the population means are equal. OH,: Net all the population means are equal. OH,: At least two of the population means are equal. " : At least two of the population mears are diferent. (5) At the a = 0.05 keel of significance, can we reject the null hypothesis In part (a]7 Explain. Because the p-value > a = 0.05, me can reject Ho Because the p-value > a = 0.05, we cannot reject My. [ Because the prvalue s a = 0.05, we cannot reject My- " Because the prvalue s a = 0.05, me can reject My 2. DETAILS PREVIOUS ANSWERS MY NOTES ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER You may need to use the appropriate technology to answer this question. Three different methods for assembling a product we're proposed by an Industrial enpineer. To Investigate the number of units assembled correctly with each method, 15 employees were randomly selected and randomly assigned to the three proposed methods in such a way that each method was used by 12 workers. The number of units assembled correctly with recorded, and the analyst ul varlance procedure was applied to the resulting data set. The following results were obtained: SST = 12420, SSTR = 4.520. [o) Set up the ANOVA table for this problem. Dioand your values for HSE and Foo twee decimal places, and your p value to four decimal places.} Source Sum Degrees Mean of Variation of Squares of Foundem -value Treatments Emer Tota [b) Use w = 0.05 to test for any significant difference in the mears for the three assembly methods State the null and abemotive hypotheses. /1 : Not all the population ments are equal. O He: Not all the population moans are equal O Wo: At least toe of the population means are equal. /f : At least two of the population means are different. Find the value of the test statistic. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) Find the p-value. (Round your answer to four decimal places.) p-value = J. DETAILS PREVIOUS ANSWERS MY NOTES ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER You may need to use the appropriate technology to answer this question A company manufactures printers and fax machines at plans located in Atlanta, Dallas, and Seattle. To measure how much employees at these plants knew about quality management, a random sample of & employees was selected from each plant and the employees selected were given a quality awareness examination. The examination scores for these 18 employees are shown in the allowing table. The sample means, sample variances, and sample standard deviations for each group are also provided. Managers want to use these data to test the hypothesis that the mean examination score is the same for all three plants. Plant 1 Plant 2 Plaint 3 Atlanta | Dallas Seattle 85 70 59 26 76 65 83 74 62 25 73 72 68 25 83 Sample mean Sample 28.4 27.6 variance 31.2 Sample standard 5.13 5.35 5.59 deviation Set up the ANDVA table for these data, (Round your values for MSE and F to two decimal places, and your p-value to four decimal places.) Source Sum Degree Hean of Variation of Squares of Freedom Square p-value Treatments Error TomTest for any significant difference in the mean examination score for the three plants. Use a = 0.05. State the null and alternative hypotheses O N: Not all the population means are equal. O Ho: At least two of the population means are equal. H: At least two of the population means are different. He : Not all the population means are equal. Find the value of the test statistic. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) Find the p-value. (Round your answer to four decimal places.) p-value = DETAILS PREVIOUS ANSWERS MY NOTES ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER You may need to use the appropriate technology to answer this question. To best for any significant cifference in the number of hours between breakdowns for four machines, the following data were abrained Machine Machine Machine Machine 1 5.6 10.8 9.6 79 10.0 12.7 5 4 12.0 7.7 10.2 10.1 10.5 85 9.1 B.5 11.0 10- 1 114 11,4 (a) At the a = 0.05 level of significance, what is the difference, if any, in the population mann times among the four machicast State the rull and alternative hypotheses O Wai Not all the population means are equal. He: Not all the population means are equal My huy # H4 O Wai At least two of the population means are equal H, : At least two of the population means are different. Find the value of the best scacback. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) Find the p-value. (Round your answer to three decimal places.) p-value = State your conclusion. Reject H. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the mean time between breakdowns is not the same for the four machines O Do not reject Ho. There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the mean time between breakdowns is not the same for the four machines. O Reject Ho. There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the mean time between breakdowns is not the same for the four machines. O Do not reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the mean time between breakdowns is not the same for the four machines. (b) Use Fisher's LSD procedure to test for the equality of the means for machines 2 and 4. Use a 0.05 level of significance. Find the value of LSD. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) LSD - Find the pairwise absolute difference between sample means for machines 2 and 4. * 2 - X4 = [DETAILS PREVIOUS ANSWERS MY NOTES ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER You may need to use the appropriate technology to answer this question. An experiment has been conducted for four treatments with eight blocks. Complete the following analysis of variance table. (Round your values for mean squares and F to two decimal places, and your "-value to three decimal places.) Source Sum Degrees Mean of Variation of Squares of Freedom Square p-value Treatments 300 Blocks 100 Error Total 900 Use = = 0.05, method of loading and unloading is significant. Because the p-value s a = 0.05, method of loading and unloading is significant. " Because the p-value > a = 0.05, method of loading and unloading Is not significant Find the value of the beast statistic for type of ride. Find the p value for type of rice. (Round your answer to three decimal places.) p-value = Find the p-value for type of ride. (Round your answer to three decimal places.) p-value = state your condusion about type of ride. O Because the p-value s a = 0.05, type of ride is significant. Q Because the p-value > a = 0.05, type of ride is not significant. Find the value of the test statistic for interaction between method of loading and unloading and type of ride. Find the p-value for interaction between method of loading and unloading and type of ride. (Round your answer to three decimal places.) p-value = State your conclusion about interaction between method of loading and unloading and type of ride. Because the p-value s a = 0.05, interaction between method of loading and unloading and type of ride is not significant. " Because the p-value > & = 0.05, interaction between method of loading and unloading and type of ride is significant. Because the p-value s a = 0.05, interaction between method of loading and unloading and type of ride is significant. "Because the p-value >
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


