Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Please help me with number 4. I attached my lab results which are highlighted as well. Will give feedback :) 1) Part 1: In the
Please help me with number 4. I attached my lab results which are highlighted as well. Will give feedback :) 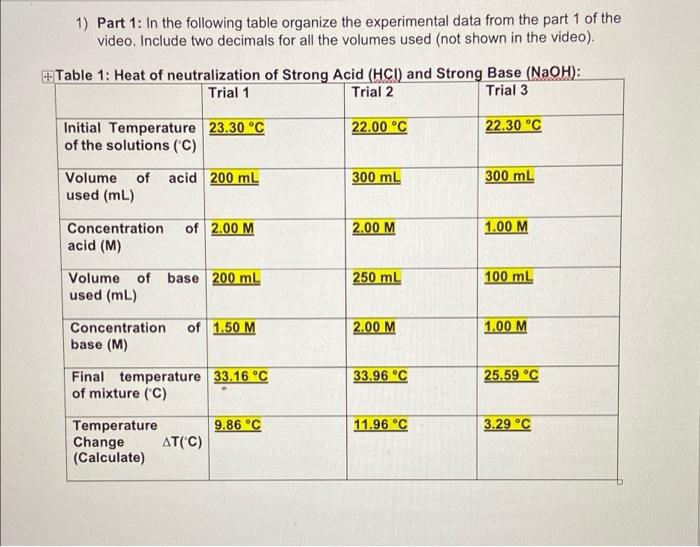
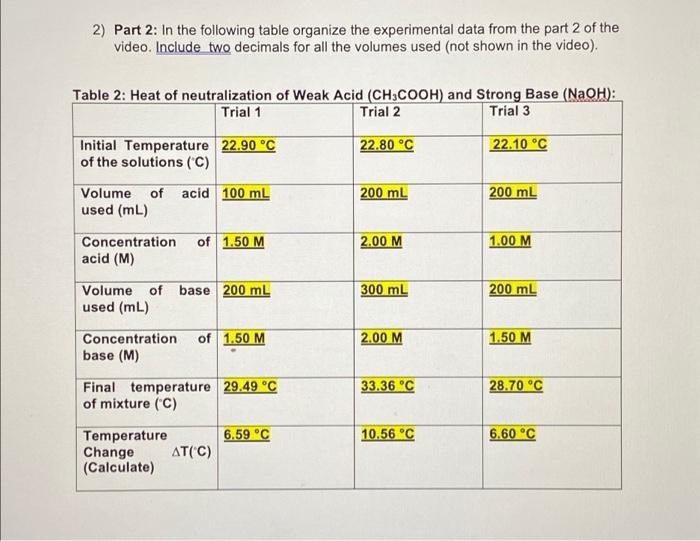
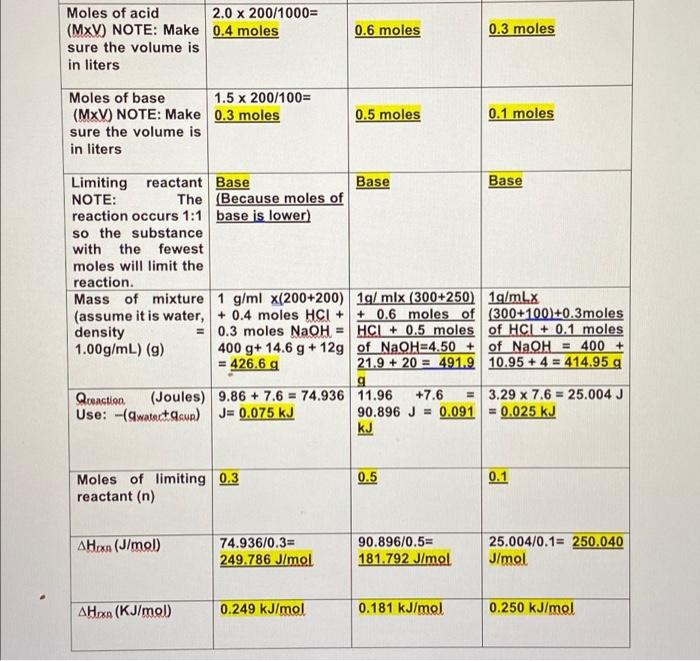
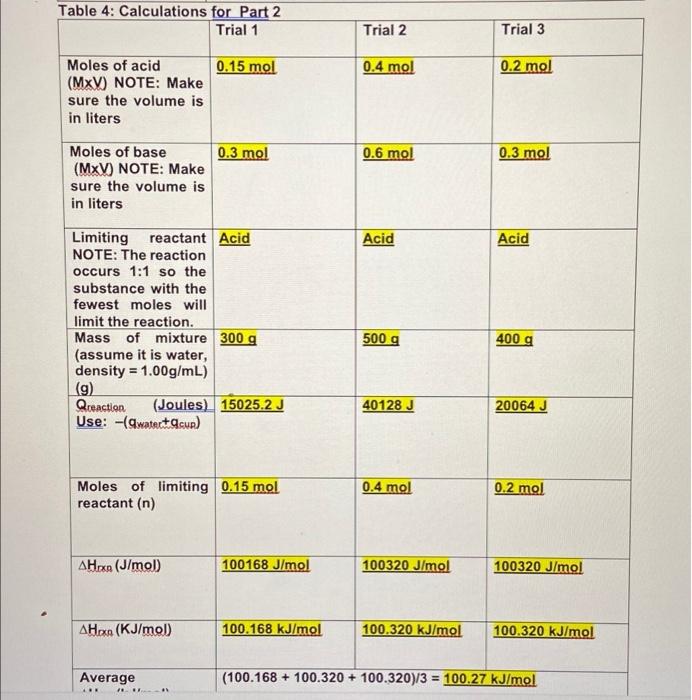
 1) Part 1: In the following table organize the experimental data from the part 1 of the video. Include two decimals for all the volumes used (not shown in the video) + Table 1: Heat of neutralization of Strong Acid (HCI) and Strong Base (NaOH): Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 22.00 C 22.30 C Initial Temperature 23.30 C of the solutions (C) acid 200 mL 300 mL 300 mL Volume of used (mL) Concentration acid (M) of 2.00 M 2.00 M 1.00 M Volume of base 200 ml used (mL) 250 ml 100 ml of 1.50 M 2.00 M 1.00 M Concentration base (M) 33.96 C 25.59 C Final temperature 33.16 C of mixture (C) 9.86 C 11.96 C 3.29 C Temperature Change AT("C) (Calculate) 2) Part 2: In the following table organize the experimental data from the part 2 of the video. Include two decimals for all the volumes used (not shown in the video) Table 2: Heat of neutralization of Weak Acid (CH3COOH) and Strong Base (NaOH): Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 22.80 C 22.10 C Initial Temperature 22.90 C of the solutions (C) Volume of acid 100 mL used (mL) 200 ml 200 ml of 1.50 M 2.00 M Concentration acid (M) 1.00 M Volume of base 200 mL used (mL) 300 ml 200 mL of 1.50 M Concentration base (M) 2.00 M 1.50 M 33.36 C 28.70 C Final temperature 29.49 C of mixture (C) 6.59 C 10.56 C 6.60C Temperature Change AT(C) (Calculate) Moles of acid 2.0 x 200/1000= (MxV) NOTE: Make 0.4 moles sure the volume is in liters 0.6 moles 0.3 moles 0.5 moles 0.1 moles Moles of base 1.5 x 200/100= (MxV) NOTE: Make 0.3 moles sure the volume is in liters Limiting reactant Base Base Base NOTE: The (Because moles of reaction occurs 1:1 base is lower) so the substance with the fewest moles will limit the reaction. Mass of mixture 1 g/ml x(200+200) 1g/ mix (300+250) 1g/ml.x (assume it is water, + 0.4 moles HCI + + 0.6 moles of (300+100)+0.3moles density = 0.3 moles NaOH = HCL + 0.5 moles of HCL + 0.1 moles 1.00g/mL) (9) 400 g+ 14.6 g + 12g of NaOH=4.50 + of NaOH = 400 + = 426.6 g 21.9 + 20 = 491.9 10.95 + 4 = 414.95 g g Qceaction (Joules) 9.86 + 7.6 = 74.936 11.96 +7.6 = 3.29 x 7.6 = 25.004 J Use: -(watertasun) J= 0.075 kJ 90.896 J = 0.091 = 0.025 kJ kJ = 0.5 0.1 Moles of limiting 0.3 reactant (n) A Hoxe (J/mol) 74.936/0.3= 249.786 J/mol 90.896/0.5= 181.792 J/mol 25.004/0.1= 250.040 J/mol AHO (KJ/mol 0.249 kJ/mol 0.181 kJ/mol 0.250 kJ/mol Table 4: Calculations for Part 2 Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 0.15 mol 0.4 mol 0.2 mol Moles of acid (MxV) NOTE: Make sure the volume is in liters 0.3 mol 0.6 mol 0.3 mol Moles of base (MxV) NOTE: Make sure the volume is in liters Acid Acid Limiting reactant Acid NOTE: The reaction occurs 1:1 so the substance with the fewest moles will limit the reaction. Mass of mixture 300 g (assume it is water, density = 1.00g/mL) (9) Qreaction (Joules) 15025.2 J Use: -(watectacun) 500 g 400 g 40128 J 20064 J 0.4 mol Moles of limiting 0.15 mol reactant (n) 0.2 mol A Hoxn (J/mol 100168 J/mol 100320 J/mol 100320 J/mol AHO (KJ/mol 100.168 kJ/mol 100.320 kJ/mol 100.320 kJ/mol Average . (100.168 + 100.320 + 100.320)/3 = 100.27 kJ/mol 4.Theoretical values for the enthalpy of neutralization for the reactions you observed in this lab can be found in the link below. Look at the values given and briefly discuss how do you compare these values with your results. 1) Part 1: In the following table organize the experimental data from the part 1 of the video. Include two decimals for all the volumes used (not shown in the video) + Table 1: Heat of neutralization of Strong Acid (HCI) and Strong Base (NaOH): Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 22.00 C 22.30 C Initial Temperature 23.30 C of the solutions (C) acid 200 mL 300 mL 300 mL Volume of used (mL) Concentration acid (M) of 2.00 M 2.00 M 1.00 M Volume of base 200 ml used (mL) 250 ml 100 ml of 1.50 M 2.00 M 1.00 M Concentration base (M) 33.96 C 25.59 C Final temperature 33.16 C of mixture (C) 9.86 C 11.96 C 3.29 C Temperature Change AT("C) (Calculate) 2) Part 2: In the following table organize the experimental data from the part 2 of the video. Include two decimals for all the volumes used (not shown in the video) Table 2: Heat of neutralization of Weak Acid (CH3COOH) and Strong Base (NaOH): Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 22.80 C 22.10 C Initial Temperature 22.90 C of the solutions (C) Volume of acid 100 mL used (mL) 200 ml 200 ml of 1.50 M 2.00 M Concentration acid (M) 1.00 M Volume of base 200 mL used (mL) 300 ml 200 mL of 1.50 M Concentration base (M) 2.00 M 1.50 M 33.36 C 28.70 C Final temperature 29.49 C of mixture (C) 6.59 C 10.56 C 6.60C Temperature Change AT(C) (Calculate) Moles of acid 2.0 x 200/1000= (MxV) NOTE: Make 0.4 moles sure the volume is in liters 0.6 moles 0.3 moles 0.5 moles 0.1 moles Moles of base 1.5 x 200/100= (MxV) NOTE: Make 0.3 moles sure the volume is in liters Limiting reactant Base Base Base NOTE: The (Because moles of reaction occurs 1:1 base is lower) so the substance with the fewest moles will limit the reaction. Mass of mixture 1 g/ml x(200+200) 1g/ mix (300+250) 1g/ml.x (assume it is water, + 0.4 moles HCI + + 0.6 moles of (300+100)+0.3moles density = 0.3 moles NaOH = HCL + 0.5 moles of HCL + 0.1 moles 1.00g/mL) (9) 400 g+ 14.6 g + 12g of NaOH=4.50 + of NaOH = 400 + = 426.6 g 21.9 + 20 = 491.9 10.95 + 4 = 414.95 g g Qceaction (Joules) 9.86 + 7.6 = 74.936 11.96 +7.6 = 3.29 x 7.6 = 25.004 J Use: -(watertasun) J= 0.075 kJ 90.896 J = 0.091 = 0.025 kJ kJ = 0.5 0.1 Moles of limiting 0.3 reactant (n) A Hoxe (J/mol) 74.936/0.3= 249.786 J/mol 90.896/0.5= 181.792 J/mol 25.004/0.1= 250.040 J/mol AHO (KJ/mol 0.249 kJ/mol 0.181 kJ/mol 0.250 kJ/mol Table 4: Calculations for Part 2 Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 0.15 mol 0.4 mol 0.2 mol Moles of acid (MxV) NOTE: Make sure the volume is in liters 0.3 mol 0.6 mol 0.3 mol Moles of base (MxV) NOTE: Make sure the volume is in liters Acid Acid Limiting reactant Acid NOTE: The reaction occurs 1:1 so the substance with the fewest moles will limit the reaction. Mass of mixture 300 g (assume it is water, density = 1.00g/mL) (9) Qreaction (Joules) 15025.2 J Use: -(watectacun) 500 g 400 g 40128 J 20064 J 0.4 mol Moles of limiting 0.15 mol reactant (n) 0.2 mol A Hoxn (J/mol 100168 J/mol 100320 J/mol 100320 J/mol AHO (KJ/mol 100.168 kJ/mol 100.320 kJ/mol 100.320 kJ/mol Average . (100.168 + 100.320 + 100.320)/3 = 100.27 kJ/mol 4.Theoretical values for the enthalpy of neutralization for the reactions you observed in this lab can be found in the link below. Look at the values given and briefly discuss how do you compare these values with your results
1) Part 1: In the following table organize the experimental data from the part 1 of the video. Include two decimals for all the volumes used (not shown in the video) + Table 1: Heat of neutralization of Strong Acid (HCI) and Strong Base (NaOH): Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 22.00 C 22.30 C Initial Temperature 23.30 C of the solutions (C) acid 200 mL 300 mL 300 mL Volume of used (mL) Concentration acid (M) of 2.00 M 2.00 M 1.00 M Volume of base 200 ml used (mL) 250 ml 100 ml of 1.50 M 2.00 M 1.00 M Concentration base (M) 33.96 C 25.59 C Final temperature 33.16 C of mixture (C) 9.86 C 11.96 C 3.29 C Temperature Change AT("C) (Calculate) 2) Part 2: In the following table organize the experimental data from the part 2 of the video. Include two decimals for all the volumes used (not shown in the video) Table 2: Heat of neutralization of Weak Acid (CH3COOH) and Strong Base (NaOH): Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 22.80 C 22.10 C Initial Temperature 22.90 C of the solutions (C) Volume of acid 100 mL used (mL) 200 ml 200 ml of 1.50 M 2.00 M Concentration acid (M) 1.00 M Volume of base 200 mL used (mL) 300 ml 200 mL of 1.50 M Concentration base (M) 2.00 M 1.50 M 33.36 C 28.70 C Final temperature 29.49 C of mixture (C) 6.59 C 10.56 C 6.60C Temperature Change AT(C) (Calculate) Moles of acid 2.0 x 200/1000= (MxV) NOTE: Make 0.4 moles sure the volume is in liters 0.6 moles 0.3 moles 0.5 moles 0.1 moles Moles of base 1.5 x 200/100= (MxV) NOTE: Make 0.3 moles sure the volume is in liters Limiting reactant Base Base Base NOTE: The (Because moles of reaction occurs 1:1 base is lower) so the substance with the fewest moles will limit the reaction. Mass of mixture 1 g/ml x(200+200) 1g/ mix (300+250) 1g/ml.x (assume it is water, + 0.4 moles HCI + + 0.6 moles of (300+100)+0.3moles density = 0.3 moles NaOH = HCL + 0.5 moles of HCL + 0.1 moles 1.00g/mL) (9) 400 g+ 14.6 g + 12g of NaOH=4.50 + of NaOH = 400 + = 426.6 g 21.9 + 20 = 491.9 10.95 + 4 = 414.95 g g Qceaction (Joules) 9.86 + 7.6 = 74.936 11.96 +7.6 = 3.29 x 7.6 = 25.004 J Use: -(watertasun) J= 0.075 kJ 90.896 J = 0.091 = 0.025 kJ kJ = 0.5 0.1 Moles of limiting 0.3 reactant (n) A Hoxe (J/mol) 74.936/0.3= 249.786 J/mol 90.896/0.5= 181.792 J/mol 25.004/0.1= 250.040 J/mol AHO (KJ/mol 0.249 kJ/mol 0.181 kJ/mol 0.250 kJ/mol Table 4: Calculations for Part 2 Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 0.15 mol 0.4 mol 0.2 mol Moles of acid (MxV) NOTE: Make sure the volume is in liters 0.3 mol 0.6 mol 0.3 mol Moles of base (MxV) NOTE: Make sure the volume is in liters Acid Acid Limiting reactant Acid NOTE: The reaction occurs 1:1 so the substance with the fewest moles will limit the reaction. Mass of mixture 300 g (assume it is water, density = 1.00g/mL) (9) Qreaction (Joules) 15025.2 J Use: -(watectacun) 500 g 400 g 40128 J 20064 J 0.4 mol Moles of limiting 0.15 mol reactant (n) 0.2 mol A Hoxn (J/mol 100168 J/mol 100320 J/mol 100320 J/mol AHO (KJ/mol 100.168 kJ/mol 100.320 kJ/mol 100.320 kJ/mol Average . (100.168 + 100.320 + 100.320)/3 = 100.27 kJ/mol 4.Theoretical values for the enthalpy of neutralization for the reactions you observed in this lab can be found in the link below. Look at the values given and briefly discuss how do you compare these values with your results. 1) Part 1: In the following table organize the experimental data from the part 1 of the video. Include two decimals for all the volumes used (not shown in the video) + Table 1: Heat of neutralization of Strong Acid (HCI) and Strong Base (NaOH): Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 22.00 C 22.30 C Initial Temperature 23.30 C of the solutions (C) acid 200 mL 300 mL 300 mL Volume of used (mL) Concentration acid (M) of 2.00 M 2.00 M 1.00 M Volume of base 200 ml used (mL) 250 ml 100 ml of 1.50 M 2.00 M 1.00 M Concentration base (M) 33.96 C 25.59 C Final temperature 33.16 C of mixture (C) 9.86 C 11.96 C 3.29 C Temperature Change AT("C) (Calculate) 2) Part 2: In the following table organize the experimental data from the part 2 of the video. Include two decimals for all the volumes used (not shown in the video) Table 2: Heat of neutralization of Weak Acid (CH3COOH) and Strong Base (NaOH): Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 22.80 C 22.10 C Initial Temperature 22.90 C of the solutions (C) Volume of acid 100 mL used (mL) 200 ml 200 ml of 1.50 M 2.00 M Concentration acid (M) 1.00 M Volume of base 200 mL used (mL) 300 ml 200 mL of 1.50 M Concentration base (M) 2.00 M 1.50 M 33.36 C 28.70 C Final temperature 29.49 C of mixture (C) 6.59 C 10.56 C 6.60C Temperature Change AT(C) (Calculate) Moles of acid 2.0 x 200/1000= (MxV) NOTE: Make 0.4 moles sure the volume is in liters 0.6 moles 0.3 moles 0.5 moles 0.1 moles Moles of base 1.5 x 200/100= (MxV) NOTE: Make 0.3 moles sure the volume is in liters Limiting reactant Base Base Base NOTE: The (Because moles of reaction occurs 1:1 base is lower) so the substance with the fewest moles will limit the reaction. Mass of mixture 1 g/ml x(200+200) 1g/ mix (300+250) 1g/ml.x (assume it is water, + 0.4 moles HCI + + 0.6 moles of (300+100)+0.3moles density = 0.3 moles NaOH = HCL + 0.5 moles of HCL + 0.1 moles 1.00g/mL) (9) 400 g+ 14.6 g + 12g of NaOH=4.50 + of NaOH = 400 + = 426.6 g 21.9 + 20 = 491.9 10.95 + 4 = 414.95 g g Qceaction (Joules) 9.86 + 7.6 = 74.936 11.96 +7.6 = 3.29 x 7.6 = 25.004 J Use: -(watertasun) J= 0.075 kJ 90.896 J = 0.091 = 0.025 kJ kJ = 0.5 0.1 Moles of limiting 0.3 reactant (n) A Hoxe (J/mol) 74.936/0.3= 249.786 J/mol 90.896/0.5= 181.792 J/mol 25.004/0.1= 250.040 J/mol AHO (KJ/mol 0.249 kJ/mol 0.181 kJ/mol 0.250 kJ/mol Table 4: Calculations for Part 2 Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 0.15 mol 0.4 mol 0.2 mol Moles of acid (MxV) NOTE: Make sure the volume is in liters 0.3 mol 0.6 mol 0.3 mol Moles of base (MxV) NOTE: Make sure the volume is in liters Acid Acid Limiting reactant Acid NOTE: The reaction occurs 1:1 so the substance with the fewest moles will limit the reaction. Mass of mixture 300 g (assume it is water, density = 1.00g/mL) (9) Qreaction (Joules) 15025.2 J Use: -(watectacun) 500 g 400 g 40128 J 20064 J 0.4 mol Moles of limiting 0.15 mol reactant (n) 0.2 mol A Hoxn (J/mol 100168 J/mol 100320 J/mol 100320 J/mol AHO (KJ/mol 100.168 kJ/mol 100.320 kJ/mol 100.320 kJ/mol Average . (100.168 + 100.320 + 100.320)/3 = 100.27 kJ/mol 4.Theoretical values for the enthalpy of neutralization for the reactions you observed in this lab can be found in the link below. Look at the values given and briefly discuss how do you compare these values with your results





Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


