Question
Please help me with this! I'm so confused about how to prepare the trial balance before adjustment . Here is all the information: The 2019
Please help me with this! I'm so confused about how to prepare the trial balance before adjustment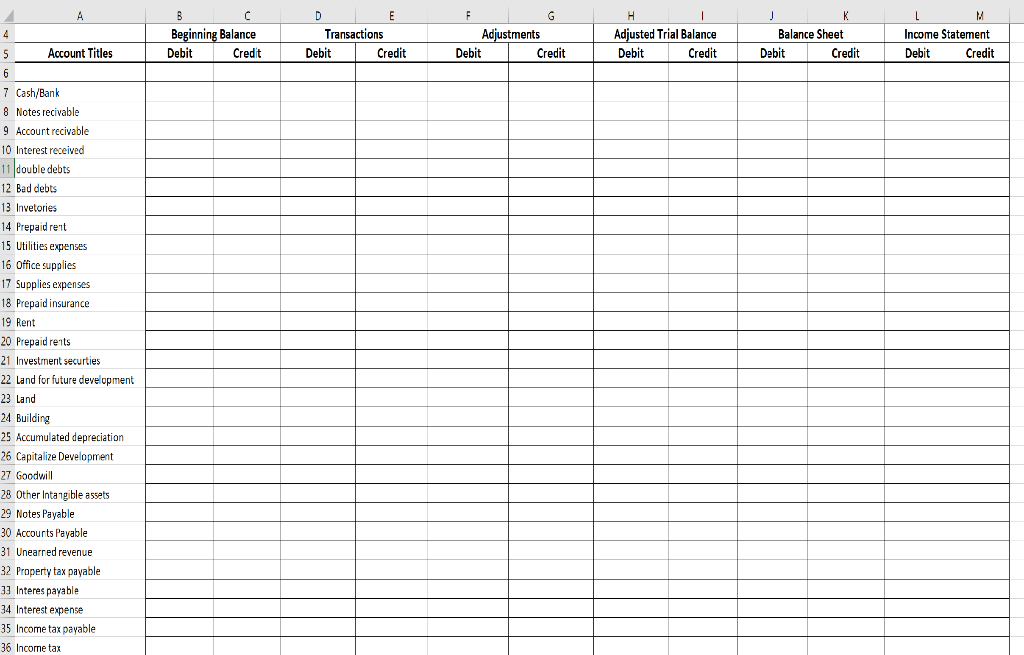 . Here is all the information:
. Here is all the information:
The 2019 Balance Sheet of the Victoria Co. is as follows:
| Victoria Co. Balance Sheet As of December 31, 2019
|
| Cash | 85,000 | Notes Payable | 150,000 |
| Notes Receivable | 34,590 | Accounts Payable | 125,000 |
| Accounts Receivable | 35,000 | Unearned Revenue | 1,000 |
| Less: Allowance for Doubtful A/Cs | (2,930) | Property Tax Payable | 0 |
| Inventories | 65,000 | Interest Payable | 3,500 |
| Office Supplies | 0 | Income Tax Payable | 13,000 |
| Prepaid Insurance | 540 | Salary and Wages Payable | 6,500 |
| Prepaid Rent | 4,800 | Utilities Payable | 12,000 |
| Total Current Assets | 222,000 | Total Current Liabilities | 311,000 |
| Long-term Investments | Provisions Related to Pensions | 93,100 | |
| Investments in securities | 180,000 | Bonds Payable | 300,000 |
| Land for future development | 60,000 | Total Non-Current Liab. | 393,100 |
| Property, Plant, and Equipment | Total Liabilities | 704,100 | |
| Land | 145,000 | Common Stock | 240,000 |
| Buildings | 800,000 | Paid-in-capital - Common Stock | 96,000 |
| Less: Accu. Depreciation | (240,000) | Preferred Stock | 97,000 |
| Intangible Assets | Paid-in-capital - Preferred Stock | 7,400 | |
| Capitalized Development Costs | 15,000 | Retained Earnings | 210,500 |
| Goodwill | 120,000 | Accu. Other Comp. Income | 5,000 |
| Other Intangible Assets | 48,000 | Less: Treasury Stock | (10,000) |
| Total Non-Current Assets | 1,128,000 | Total Shareholders Equity | 645,900 |
| Total Assets | 1,350,000 | Total Liab. and Total Equity | 1,350,000 |
During 2020, the following events occurred in the company. Additional information available at the end of 2020 is as follows:
- On January 8, received checks, $20,000 from Kent and $15,000 from Montana, for sales on account made in December 2019 after discount period has lapsed.
- On January 15, paid cash $125,000 to Hermann for merchandise purchased last year after discount period has lapsed.
- On January 18, received checks, $34,590 for outstanding note receivable and associated interest of $410.
- On January 25, paid off the utilities bill of $12,000 and income tax of 13,000, and wages payable of 6,500.
- On January 26, purchased merchandise on account from Charles $90,000 and Georgia 120,000. Terms 3/10, n/30, F.O.B. destination.
- On February 4, send checks to Charles for 90,000 less 2% cash discount, and to Georgia for $120,000 less 3% cash discount.
- On February 13, sold merchandise on account to Franklin $110,000 and Thompson $150,000. Terms 2/10, n/30, F.O.B. shipping point.
- On February 15, issued credit of $6,000 to Franklin for the merchandise returned.
- On February 20, received payment in full from Franklin and Thompson before discount period has lapsed.
- On February 28, the prepaid rent balance was expired.
- On March 1, paid off notes payable $150,000 (issued in 2019) and associated interest of $7,500 (including $3,500 interest payable on the balance sheet).
- On March 1, paid rent of $30,000 for one-year term starting from March 1, 2020.
- On April 15, paid $8,000 cash for office supplies. The company expenses all of the supplies purchased during the year.
- On June 5, declared cash dividends totaling $30,000.
- On June 30, paid cash dividends totaling $30,000 to stockholders.
- On July 1, issued a note of $250,000 to bank (one year, annual interest rate 5%) for cash.
- On July 15, the company CEO paid $80,000 from her savings bank account to purchase a car for personal use.
- On August 1, issued common stock 3,000 shares, $10 par, in exchange of a land with a fair market value of $80,000.
- On September 8, paid utilities expense, $12,000.
- On October 7, sold merchandise to Utah on account $220,000, term 1/10, n/30, FOB shipping point.
- On October 16, Utah paid off its balance.
- On November 9, purchased merchandise from Pensacola $60,000, terms 3/10, n/30.
- On November 12, returned $3,000 of merchandise to Pensacola and received credit.
- On November 18, paid off the balance to Pensacola.
- On December 27, 2020, the company paid the 2020 federal income tax of $12,500 and 2020 property tax of $6,600.
- On December 28, sold merchandise to Kent on account $90,000, term 1/10, n/30, FOB shipping point.
- On December 29, purchased merchandise from Hermann $160,000, terms 3/10, n/30.
- Over the year, daily cash sales were $1,000 on average per day.
- Over the year, sales and office employees earned $120,000 in salaries and wages, of which $15,000 remained as payable at the end of year.
- Depreciation expense for the year was $80,000.
- The utilities bill of $18,000 as of December 31, 2020 is due in January 2021.
- The balance of unearned revenues was increased by $12,000 during 2020.
- Based on its historical data, the bad debts are about 2% of net credit sales (credit sales minus sales discounts and sales returns in the year of 2020).
Additional information available at the end of 2020 is as follows:
- No insurance policy was effective during the year.
- After physical counting, the company decided that the ending inventory was $60,000.
- Charles, Georgia, Pensacola, Franklin, Thompson, and Utah had zero balance on account as of Jan 1, 2020.
- The company uses the gross method to record its purchases and sales on credit.
- The company adopts the periodic inventory system. In order to report the purchase activities the firm used the purchases, purchases discounts, and purchase returns & allowances accounts.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


