

Please help me write conclusion using the following data/screenshots
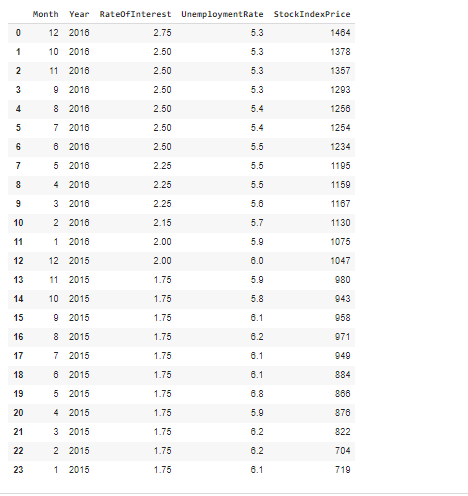
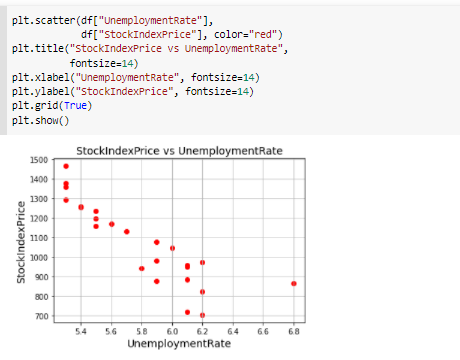
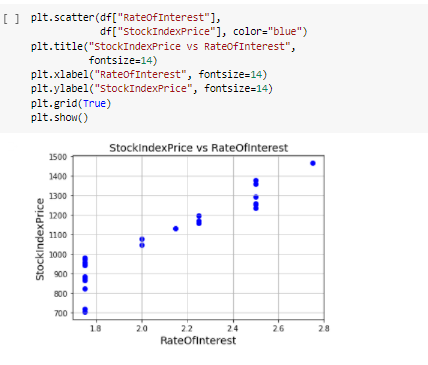
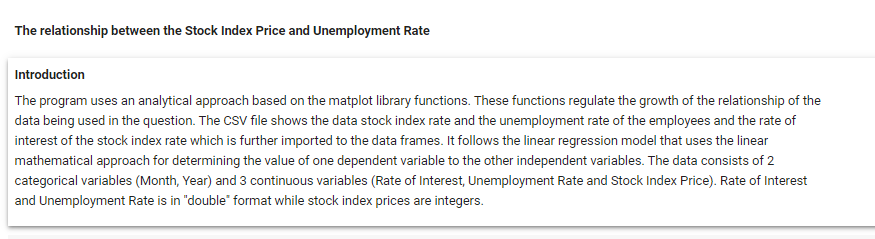
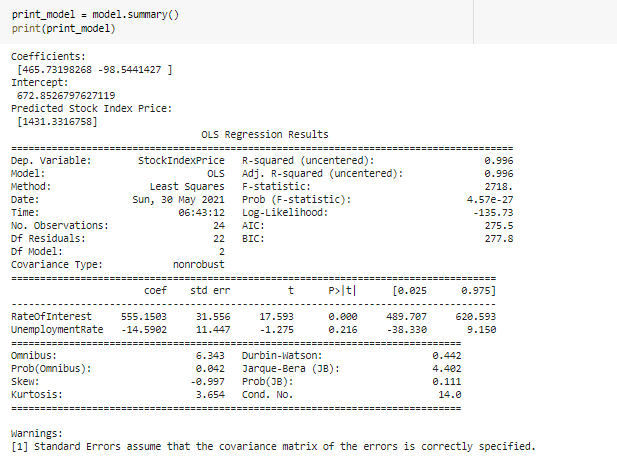
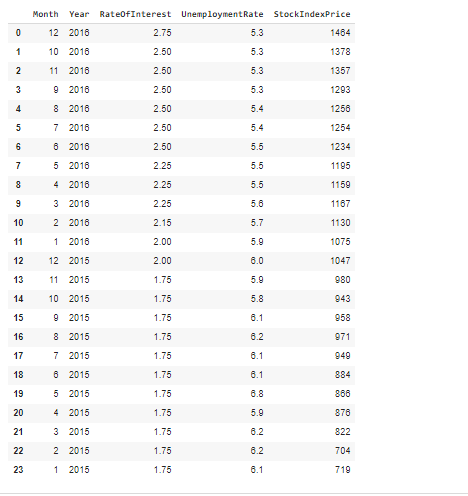
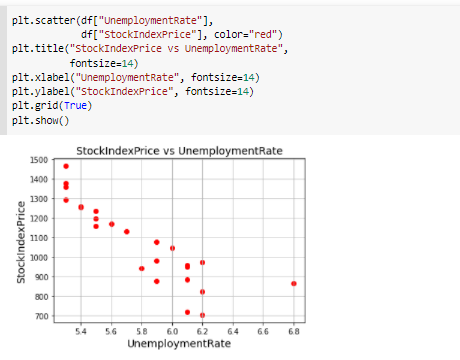
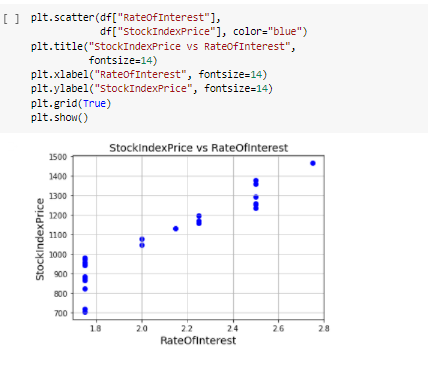
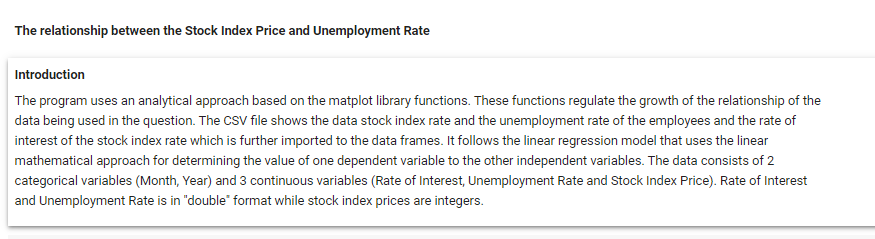
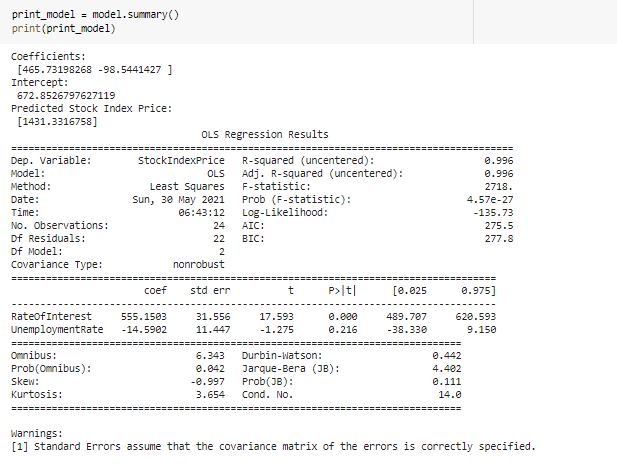
\fMonth Year RateOfInterest UnemploymentRate StockIndexPrice 12 2016 2.75 5.3 1464 10 2016 2.50 5.3 1378 11 2016 2.50 5.3 1357 3 9 2016 2 50 1293 4 8 2016 2.50 5.4 1256 en 7 2016 2.50 54 1254 2016 2.50 5.5 1234 5 2016 2.25 5.5 1195 8 4 2016 2 25 5.5 1159 3 2016 2.25 5.6 1167 10 2 2016 2.15 5.7 1130 11 2016 2.00 5.0 1075 12 12 2015 2.00 8.0 1047 13 11 2015 1.75 5.9 080 14 10 2015 1.75 5.8 043 15 9 2015 1.75 8.1 958 16 8 2015 1.75 6.2 971 17 2015 1.75 8.1 049 18 2015 1.75 8.1 884 19 5 2015 1.75 168 20 4 2015 1.75 5.9 276 21 3 2015 1.75 8.2 822 22 2 2015 1.75 6.2 704 23 2015 1.75 8.1 719\f[ ] pit. scatter (of["RateOfInterest"], df["stockIndexPrice"], color="blue") pit. title("StockIndexPrice vs RateOfInterest", fontsize=14) plt. xlabel("RateOfInterest", fontsize=14) plt. ylabel("StockIndexPrice", fontsize=14) plt. grid(True) plt. show() StockIndexPrice vs RateOfinterest 1500 1400 1300 1200 1100 StockIndexPrice 1000 900 700 20 24 26 RateOfinterestThe relationship between the Stool: Index Price and Unemployment Rate Introduction The program uses an analytical approach based on the matplot library functions. 'lhese functions regulate the growt of the relationship of the data being used in the question. The CSV le shows the data stock index rate and the unemployment rate ofthe employees and the rate of interest ofthe stock index rate which is further imported to the data frames. It follows the linear regression model that uses the linear mathematical approach for determining the value of one dependent variable to the other independent van'a bles. The data consists of 2 categorical variables (Month, Year] and 3 continuous variables [Rate of Interestr Unemployment Rate and Stock Index Price). Rate of Interest and Unemployment Rate is in "double' format while stock index prices are integers. print_model = model. summary ( ) print (print_model) Coefficients: [465. 73198268 -98.5441427 ] Intercept: 672. 8526797627119 Predicted Stock Index Price: [1431.3316758] OLS Regression Results Dep. Variable: StockIndexPrice R-squared (uncentered) : 0.996 Model : OLS Adj. R-squared (uncentered) : 0.996 Method : Least squares F-statistic: 2718. Date: sun, 30 May 2021 Prob (F-statistic): 4.57e-27 Time: 06:43:12 Log-Likelihood: -135.73 No. Observations: 24 AIC: 275.5 Of Residuals: 2.2 BIC: 277.8 Of Model: 2 Covariance Type: nonrobust coef std err t P>It| [@. 025 0.975] RateOf Interest 555. 1503 31.556 17.593 0.080 489.707 620.593 UnemploymentRate -14.5902 11. 447 -1. 275 0. 216 -38.330 9.150 Omnibus : 6.343 Durbin-Watson: 0.442 Prob (Omnibus ) : 0. 042 Jarque-Bera (JB) : 4.482 Skew: -0.997 Prob(JB) : 0. 111 Kurtosis: 3.654 Cond. No. 14.0 warnings: [1] Standard Errors assume that the covariance matrix of the errors is correctly specified.What is the relationship between Stock Index Price and Rate 0! Interest inelud'ng its impact? The relationship between the Stock Index Price and the Rate of Interest as shown in the data has a direcy proportional eect. This means as the Stock Index Price increases the Rate of Interest also increases. As shown in the data, 1.3 Rate of Interest yields TDD Stock Index Price. The data also shows that as the Stock Index Price decreases the Flate of Interest also decreases. As shown nearly 2.8 Rate of Interest gives 145D Stock Index Price. The overall impact of Rate of Interest shows the status of the economic growth. As the Rate of Interest increases, the economic growth decreases. As the Rate of Interest decreases a boost in economic growth is experienced. As shown in the data, the higher the Stool-r Index Price is, the higher the Rate of Interest becomes. The impact is explained by Laura Wagg as she states, 'Hig her interest rates may slow economic growth.' She explained that borrowing becomes more expensive and there is more incentive to save money, so people may be encouraged to spend less. Because of the high interest rates, people are discouraged to borrow and spend. As shown in the data, the lower the Stock Index Price is, the lower Rate of Interest is yielded. The impact to the economy is explained by Laura Wagg as, 'Lower interest rates may boost economic growth." According to her borrowing becomes cheaper and there is less incentive to save money. As a result, people may be encouraged to spend or invest. Because of lower interest rates, consumers will be more likely to spend. What is the relationship between the Stock Index Price and Unemployment Rate? As shown in the scatter diagram, when the Unemployment rate is low, the Stock Index Price is high. In the diagram, 5.4 unemployment rate gives 1250 Stock Index Price. The scatter diagram shows that a low unemployment rate results to a high stock index price. (in the other hand, when the Stock Index Price is low, the Unemployment Rate is high. In the diagram, TDD Stock Index Price was produced by 6.2 Unemployment rate.The scatter diagram shows a tendency for the Stock Index Price to decrease as the unemployment rate increases. This may have caused from the reduction of the supply due to the lessening of the demand. The consumers may demand lesser because they have lesser resources because of being jobless. The Law of Supply and Dem and also applies in this case. We can see in this diagram that the prices are high when the unemployment rate is low. This is mainly because the sup ply and demand are also high. According to Corporatenanceinstitutecom, the Law of Supply and Demand states, ' if a company produces a good that not many others produce or a good that is highly desired or necessary, the price of its stock will climb because the demand is high. When the supply of the good balances out with the demand, stock pn'ces will tend to plateau. If the supply is greater than the demand, the company's share price will likely drop.' {Kiril}. In addition, we can infer the inversely proportional relationship between the Stock Index Pn'ce and the Unemployment rate. As the StocI-c Index Price increases the Unemployment Rate decreases. As the Stock Index Price decreases the Unemployment Rate increases. We can conclude that the relationships shown in the data are related to the principle of supply and demand