Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
PLEASE HELP! really need some help going through these problems since she doesnt give us the ansers for these practice assignments With $33billion in cash
PLEASE HELP! 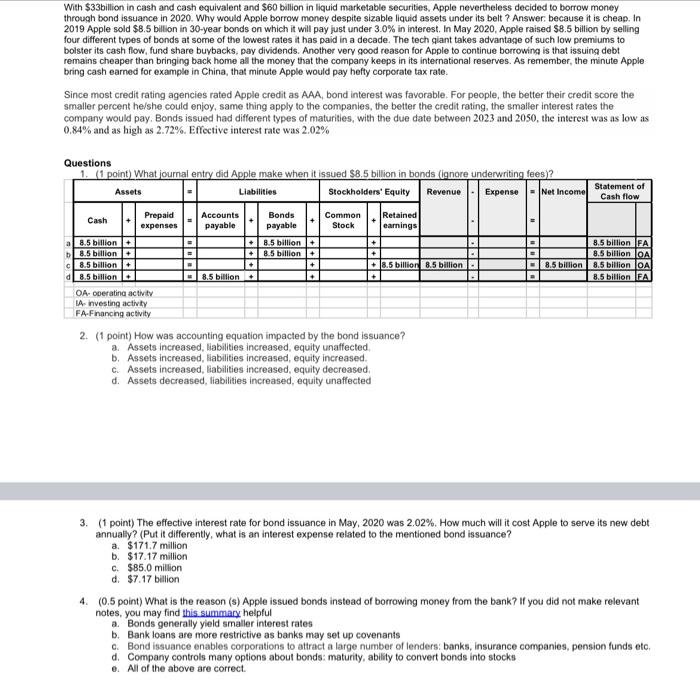
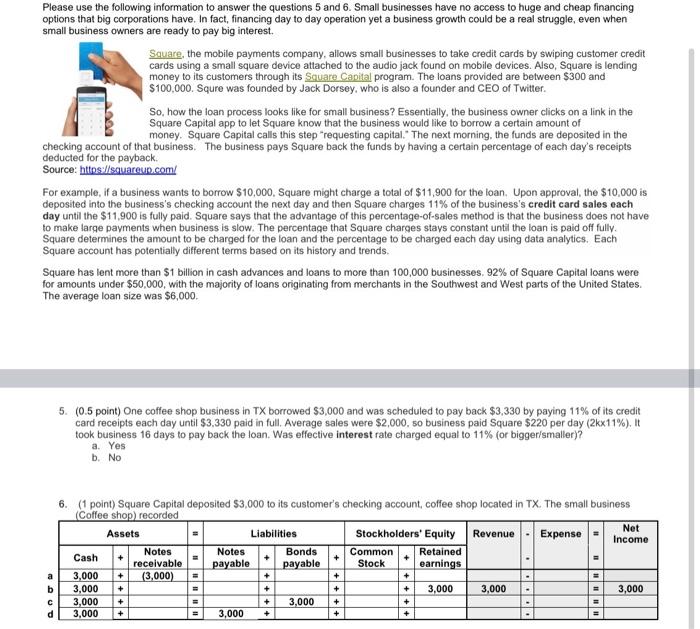
With $33billion in cash and cash equivalent and $60 billion in liquid marketable securities, Apple nevertheless decided to borrow money through bond issuance in 2020. Why would Apple borrow money despite sizable liquid assets under its belt? Answer: because it is cheap. In 2019 Apple sold $8.5 billion in 30-year bonds on which it will pay just under 3.0% in interest. In May 2020, Apple raised $8.5 billion by selling four different types of bonds at some of the lowest rates it has paid in a decade. The tech giant takes advantage of such low premiums to bolster its cash flow, fund share buybacks, pay dividends. Another very good reason for Apple to continue borrowing is that issuing debt remains cheaper than bringing back home all the money that the company keeps in its international reserves. As remember, the minute Apple bring cash earned for example in China, that minute Apple would pay hefty corporate tax rate. Since most credit rating agencies rated Apple credit as AAA, bond interest was favorable. For people, the better their credit score the smaller percent he/she could enjoy, same thing apply to the companies, the better the credit rating, the smaller interest rates the company would pay, Bonds issued had different types of maturities, with the due date between 2023 and 2050, the interest was as low as 0.84% and as high as 2.72%. Effective interest rate was 2.02% + + Questions 1. (1 point) What journal entry did Apple make when it issued $8.5 billion in bonds (ignore underwriting fees)? Statement of Assets Liabilities Stockholders' Equity Revenue Expense - Net Income Cash flow Prepaid Accounts Bonds Cash Common Retained expenses payable payable Stock earnings a8.5 billion 8.5 billion 8.5 billion FA 8.5 billion 8.5 billion 8.5 billion OA C8.5 billion 18.5 billion 8.5 billion 8.5 billion 8.5 billion OA al 8.5 billion 8.5 billion + 8.5 billion EA OA operating activity 1A-nvesting activity FA Financing activity 2. (1 point) How was accounting equation impacted by the bond issuance? a. Assets increased, liabilities increased, equity unaffected b. Assets increased, liabilities increased, equity increased C. Assets increased, liabilities increased, equity decreased d. Assets decreased, liabilities increased, equity unaffected . + + 3. (1 point) The effective interest rate for bond issuance in May, 2020 was 2.02%. How much will it cost Apple to serve its new debt annually? (Put it differently, what is an interest expense related to the mentioned bond issuance? a. $171.7 million b. $17.17 million C. $85.0 million d. $7.17 billion 4. (0.5 point) What is the reason (s) Apple issued bonds instead of borrowing money from the bank? If you did not make relevant notes, you may find this summary helpful a. Bonds generally yield smaller interest rates b. Bank loans are more restrictive as banks may set up covenants c. Bond issuance enables corporations to attract a large number of lenders, banks, insurance companies, pension funds etc, d. Company controls many options about bonds: maturity, ability to convert bonds into stocks e. All of the above are correct Please use the following information to answer the questions 5 and 6. Small businesses have no access to huge and cheap financing options that big corporations have. In fact, financing day to day operation yet a business growth could be a real struggle, even when small business owners are ready to pay big interest. Square, the mobile payments company, allows small businesses to take credit cards by swiping customer credit cards using a small square device attached to the audio jack found on mobile devices. Also, Square is lending money to its customers through its Square Capital program. The loans provided are between $300 and $100,000. Squre was founded by Jack Dorsey, who is also a founder and CEO of Twitter So, how the loan process looks like for small business? Essentially, the business owner clicks on a link in the Square Capital app to let Square know that the business would like to borrow a certain amount of money. Square Capital calls this step "requesting capital. The next morning, the funds are deposited in the checking account of that business. The business pays Square back the funds by having a certain percentage of each day's receipts deducted for the payback Source: https://squareup.com/ For example, if a business wants to borrow $10,000. Square might charge a total of $11,900 for the loan. Upon approval, the $10,000 is deposited into the business's checking account the next day and then Square charges 11% of the business's credit card sales each day until the $11.900 is fully paid. Square says that the advantage of this percentage-of-sales method is that the business does not have to make large payments when business is slow. The percentage that Square charges stays constant until the loan is paid off fully Square determines the amount to be charged for the loan and the percentage to be charged each day using data analytics. Each Square account has potentially different terms based on its history and trends Square has lent more than $1 billion in cash advances and loans to more than 100,000 businesses. 92% of Square Capital loans were for amounts under $50,000, with the majority of loans originating from merchants in the Southwest and West parts of the United States. The average loan size was $6,000. 5. (0.5 point) One coffee shop business in TX borrowed $3,000 and was scheduled to pay back $3,330 by paying 11% of its credit card receipts each day until $3,330 paid in full. Average sales were $2,000, 50 business paid Square $220 per day (2kx11%). It took business 16 days to pay back the loan. Was effective interest rate charged equal to 11% (or bigger/smaller)? b. No a. Yes 11 6. (point) Square Capital deposited $3,000 to its customer's checking account, coffee shop located in TX. The small business (Coffee shop) recorded Assets Liabilities Net Expense Stockholders' Equity Revenue Income Notes Notes Bonds Cash Retained Common receivable payable payable Stock earnings 3,000 (3,000) + 3,000 3,000 3,000 3,000 3,000 3,000 3,000 3,000 + + + = + + + = + a b d + + " = + + + + + + + really need some help going through these problems since she doesnt give us the ansers for these practice assignments


Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


