Please help solve these Excel problems!!!!


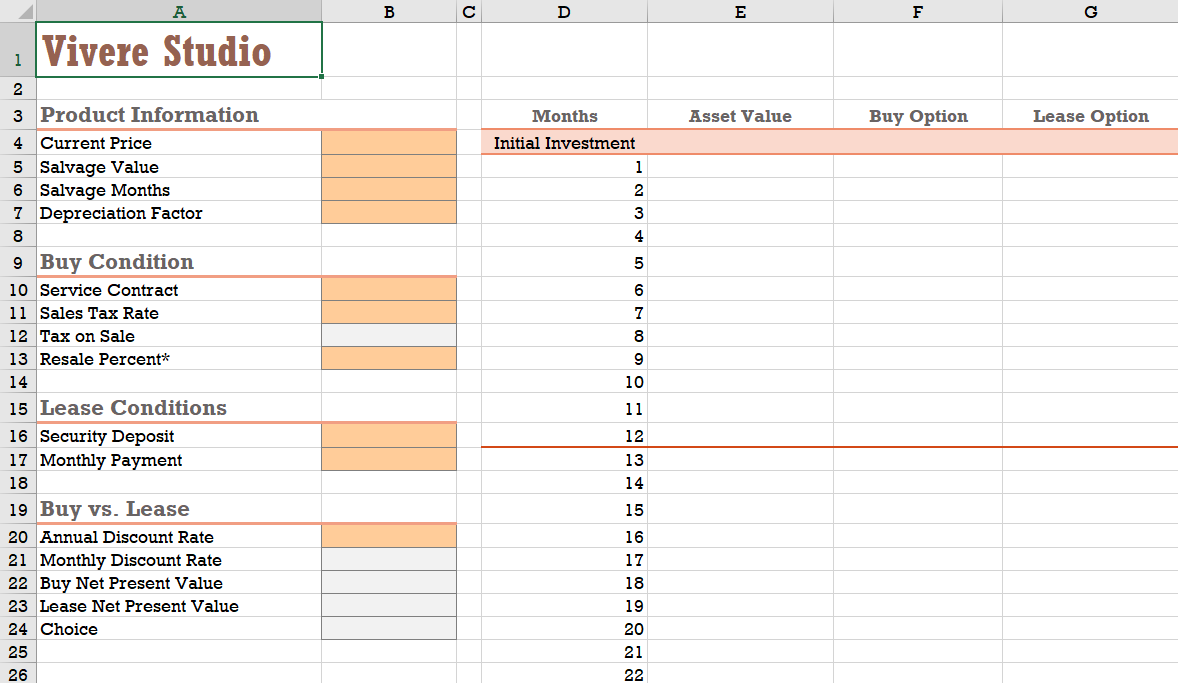
3. In the Buy vs. Lease worksheet, in cell B4, enter $23,000 as the current price of the digital equipment. 4. The digital equipment has a salvage value of $8,000 after 120 months, or 10 years. In the range B5:36, enter the salvage value and the salvage time (in months). 5. Digital equipment depreciates at reduced rate. In cell B7, enter 0.8 as the depreciation factor. 6. John decides to purchase an optional service maintenance contract that covers the next three years. In cell B10, enter $660 as the value of this contract. 7. In cell B11, enter 3.5% as the sales tax John will have to pay on the equipment. Enter this tax rate. In cell B12, enter a formula to calculate the tax on sale amount by multiplying the sales tax rate by the current price of the equipment. 8. In cell B13, enter 92% as the resale percent (which means that the store will agree to repurchase the digital equipment at 92% of its depreciated value after three years). 9. If John decides to lease this equipment, he will have to pay a $1,500 security deposit and a monthly payment of $320. Enter these values in the range B16:117. 10. In cell E4, enter a formula that shows the current value of the digital equipment entered in cell B4. 11. In the range E5:E40, calculate the value of the equipment as it depreciates each year. To calculate the depreciated values, subtract the depreciation amount from the value of the equipment in the previous month. To calculate the depreciation amount, use the DDB function for the double-declining method using the depreciation values entered in the range B4:37 and the corresponding period value in column D. 12. In cell F4, enter as a negative the cash flow the cost of purchasing the equipment plus the cost of the service contract in cell B10 and the cost of sales tax in B12. 13. For Month 1 through Month 36, John will not have to make any payments on the equipment. Enter 0 as the cash flow values in the range F5:F40. 14. After Month 36, John will sell the equipment back to the store. In cell F41, enter as a positive cash flow the final depreciated value of the equipment in cell E40 multiplied by the resale percentage in cell B13. 15. In cell G4, enter as a negative cash flow the cost of the security deposit on the digital equipment entered in cell B16. 16. In the range G5:G40, enter as a negative cash flow the monthly lease payments in cell B17. 17. After the term of the lease is over, John will return the digital equipment and receive his security deposit back. In cell G41, enter the value of the security deposit from cell B16 as a positive cash flow. 18. To calculate the time value of money, John will assume a 4.80 percent discount rate. Enter this value into cell B20. To express this as a monthly percentage, in cell B21, enter a formula to divide the value of cell B20 by 12. 19. In cell B22, enter a formula to calculate the net present value of buying the digital equipment by adding the initial investment in cell F4 to the present value of the cash flows in the range F5:F41. Use the NPV function with the monthly discount rate in cell B21 as the rate of return to calculate the present value of the cost of the buying the digital equipment for the next three years of use. 20. In cell B23, enter a formula to calculate the net present value of leasing by adding the initial investment from cell G4 to the present value of the cash flows in the range G5:G41. Again, use cell B21 as the discount rate, and calculate the present value of leasing the equipment for the next three years. 21. In cell B24, enter an IF function that displays the text BUY if the present value of buying the equipment is greater than the present value of leasing the equipment; otherwise display the text LEASE. 22. Save the workbook. 23. If the digital equipment depreciates more than expected, John will have to sell it back to the company for less money. Change the value depreciation factor in cell B7 to 1.5 (resulting in faster depreciation and a lower buy-back value). Determine whether your choice of buying versus leasing changes under this scenario. 24. Save the revised workbook as Vivere Studio 2, and then close it. B C D E F G Vivere Studio 1 Months Asset Value Buy Option Lease Option Initial Investment 1 2 3 4 5 2 3 Product Information 4 Current Price 5 Salvage Value 6 Salvage Months 7 Depreciation Factor 8 9 Buy Condition 10 Service Contract 11 Sales Tax Rate 12 Tax on Sale 13 Resale Percent* 14 15 Lease Conditions 16 Security Deposit 17 Monthly Payment 18 19 Buy vs. Lease 20 Annual Discount Rate 21 Monthly Discount Rate 22 Buy Net Present Value 23 Lease Net Present Value 24 Choice 25 26 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 c D E F G B 25 26 27 * Resale percent represents the percent of the 28 depreciated value of the asset. 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 End of Contract 3. In the Buy vs. Lease worksheet, in cell B4, enter $23,000 as the current price of the digital equipment. 4. The digital equipment has a salvage value of $8,000 after 120 months, or 10 years. In the range B5:36, enter the salvage value and the salvage time (in months). 5. Digital equipment depreciates at reduced rate. In cell B7, enter 0.8 as the depreciation factor. 6. John decides to purchase an optional service maintenance contract that covers the next three years. In cell B10, enter $660 as the value of this contract. 7. In cell B11, enter 3.5% as the sales tax John will have to pay on the equipment. Enter this tax rate. In cell B12, enter a formula to calculate the tax on sale amount by multiplying the sales tax rate by the current price of the equipment. 8. In cell B13, enter 92% as the resale percent (which means that the store will agree to repurchase the digital equipment at 92% of its depreciated value after three years). 9. If John decides to lease this equipment, he will have to pay a $1,500 security deposit and a monthly payment of $320. Enter these values in the range B16:117. 10. In cell E4, enter a formula that shows the current value of the digital equipment entered in cell B4. 11. In the range E5:E40, calculate the value of the equipment as it depreciates each year. To calculate the depreciated values, subtract the depreciation amount from the value of the equipment in the previous month. To calculate the depreciation amount, use the DDB function for the double-declining method using the depreciation values entered in the range B4:37 and the corresponding period value in column D. 12. In cell F4, enter as a negative the cash flow the cost of purchasing the equipment plus the cost of the service contract in cell B10 and the cost of sales tax in B12. 13. For Month 1 through Month 36, John will not have to make any payments on the equipment. Enter 0 as the cash flow values in the range F5:F40. 14. After Month 36, John will sell the equipment back to the store. In cell F41, enter as a positive cash flow the final depreciated value of the equipment in cell E40 multiplied by the resale percentage in cell B13. 15. In cell G4, enter as a negative cash flow the cost of the security deposit on the digital equipment entered in cell B16. 16. In the range G5:G40, enter as a negative cash flow the monthly lease payments in cell B17. 17. After the term of the lease is over, John will return the digital equipment and receive his security deposit back. In cell G41, enter the value of the security deposit from cell B16 as a positive cash flow. 18. To calculate the time value of money, John will assume a 4.80 percent discount rate. Enter this value into cell B20. To express this as a monthly percentage, in cell B21, enter a formula to divide the value of cell B20 by 12. 19. In cell B22, enter a formula to calculate the net present value of buying the digital equipment by adding the initial investment in cell F4 to the present value of the cash flows in the range F5:F41. Use the NPV function with the monthly discount rate in cell B21 as the rate of return to calculate the present value of the cost of the buying the digital equipment for the next three years of use. 20. In cell B23, enter a formula to calculate the net present value of leasing by adding the initial investment from cell G4 to the present value of the cash flows in the range G5:G41. Again, use cell B21 as the discount rate, and calculate the present value of leasing the equipment for the next three years. 21. In cell B24, enter an IF function that displays the text BUY if the present value of buying the equipment is greater than the present value of leasing the equipment; otherwise display the text LEASE. 22. Save the workbook. 23. If the digital equipment depreciates more than expected, John will have to sell it back to the company for less money. Change the value depreciation factor in cell B7 to 1.5 (resulting in faster depreciation and a lower buy-back value). Determine whether your choice of buying versus leasing changes under this scenario. 24. Save the revised workbook as Vivere Studio 2, and then close it. B C D E F G Vivere Studio 1 Months Asset Value Buy Option Lease Option Initial Investment 1 2 3 4 5 2 3 Product Information 4 Current Price 5 Salvage Value 6 Salvage Months 7 Depreciation Factor 8 9 Buy Condition 10 Service Contract 11 Sales Tax Rate 12 Tax on Sale 13 Resale Percent* 14 15 Lease Conditions 16 Security Deposit 17 Monthly Payment 18 19 Buy vs. Lease 20 Annual Discount Rate 21 Monthly Discount Rate 22 Buy Net Present Value 23 Lease Net Present Value 24 Choice 25 26 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 c D E F G B 25 26 27 * Resale percent represents the percent of the 28 depreciated value of the asset. 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 End of Contract










