Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
please help, The step size h= the size of the up movement u= the probability of a up movement pr= he size of the down
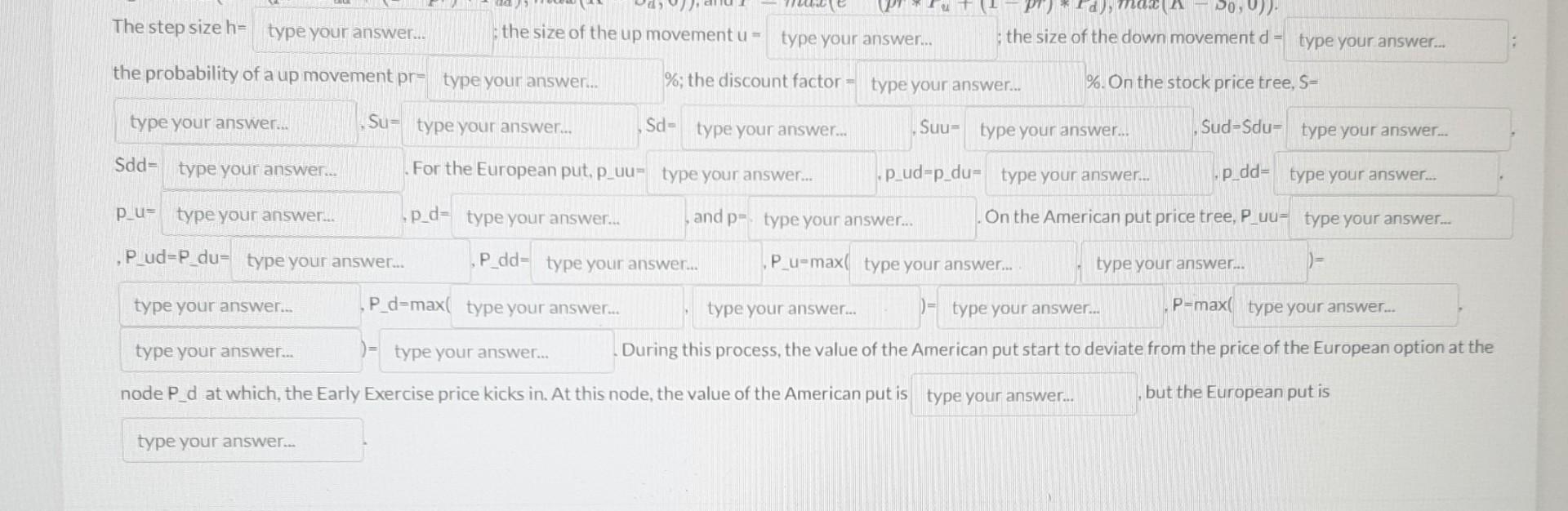
please help,
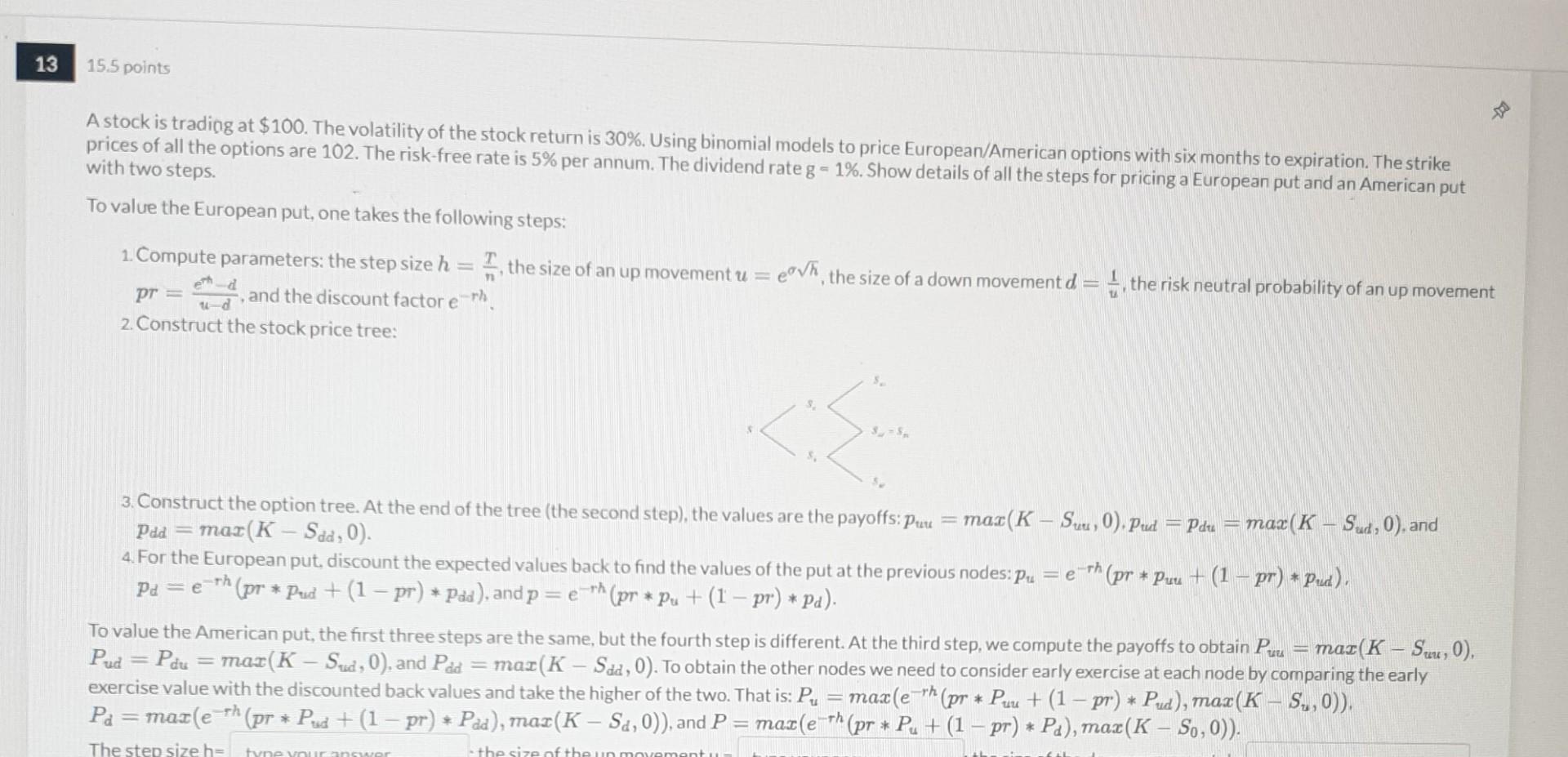
The step size h= the size of the up movement u= the probability of a up movement pr= he size of the down movement d= the probability of a up movement pr= .Su= %; the discount factor = %. On the stock price tree, S= Sdd = For the European put, p_uu= Sd= Sud =Sdu= P1= , pd= -p_ud=p_du= , p_dd = P_u = , and p= , P_ud=P_du= P_dd = , P_u=maxl type your answer... P_d =max( , P=max( During this process, the value of the American put start to deviate from the price of the European option at the node P_d at which, the Early Exercise price kicks in. At this node, the value of the American put is , but the European put is A stock is trading at $100. The volatility of the stock return is 30%. Using binomial models to price European/American options with six months to expiration. The strike prices of all the options are 102. The risk-free rate is 5% per annum. The dividend rate g=1%. Show details of all the steps for pricing a European put and an American put with two steps. To value the European put, one takes the following steps: 1. Compute parameters: the step size h=nT, the size of an up movement u=eh, the size of a down movement d=u1, the risk neutral probability of an up movement pr=udetd, and the discount factor erh. 2. Construct the stock price tree: 3. Construct the option tree. At the end of the tree (the second step), the values are the payoffs: puu=max(KSuu,0),pud=pdu=max(KSud,0), and pdd=max(KSdd,0). 4. For the European put, discount the expected values back to find the values of the put at the previous nodes: pu=erh(prpuu+(1pr)pud). pd=erh(prpud+(1pr)pdd),andp=erh(prpu+(1pr)pd). To value the American put, the first three steps are the same, but the fourth step is different. At the third step, we compute the payoffs to obtain Puu=max(KSuu,0), Pud=Pdu=max(KSud,0), and Pdd=max(KSdd,0). To obtain the other nodes we need to consider early exercise at each node by comparing the early exercise value with the discounted back values and take the higher of the two. That is: Pu=max(erh(prPuu+(1pr)Pud),max(KSu,0)). Pd=max(erh(prPud+(1pr)Pdd),max(KSd,0)), and P=max(eh(prPu+(1pr)Pd),max(KS0,0)). The step size h= the size of the up movement u= the probability of a up movement pr= he size of the down movement d= the probability of a up movement pr= .Su= %; the discount factor = %. On the stock price tree, S= Sdd = For the European put, p_uu= Sd= Sud =Sdu= P1= , pd= -p_ud=p_du= , p_dd = P_u = , and p= , P_ud=P_du= P_dd = , P_u=maxl type your answer... P_d =max( , P=max( During this process, the value of the American put start to deviate from the price of the European option at the node P_d at which, the Early Exercise price kicks in. At this node, the value of the American put is , but the European put is A stock is trading at $100. The volatility of the stock return is 30%. Using binomial models to price European/American options with six months to expiration. The strike prices of all the options are 102. The risk-free rate is 5% per annum. The dividend rate g=1%. Show details of all the steps for pricing a European put and an American put with two steps. To value the European put, one takes the following steps: 1. Compute parameters: the step size h=nT, the size of an up movement u=eh, the size of a down movement d=u1, the risk neutral probability of an up movement pr=udetd, and the discount factor erh. 2. Construct the stock price tree: 3. Construct the option tree. At the end of the tree (the second step), the values are the payoffs: puu=max(KSuu,0),pud=pdu=max(KSud,0), and pdd=max(KSdd,0). 4. For the European put, discount the expected values back to find the values of the put at the previous nodes: pu=erh(prpuu+(1pr)pud). pd=erh(prpud+(1pr)pdd),andp=erh(prpu+(1pr)pd). To value the American put, the first three steps are the same, but the fourth step is different. At the third step, we compute the payoffs to obtain Puu=max(KSuu,0), Pud=Pdu=max(KSud,0), and Pdd=max(KSdd,0). To obtain the other nodes we need to consider early exercise at each node by comparing the early exercise value with the discounted back values and take the higher of the two. That is: Pu=max(erh(prPuu+(1pr)Pud),max(KSu,0)). Pd=max(erh(prPud+(1pr)Pdd),max(KSd,0)), and P=max(eh(prPu+(1pr)Pd),max(KS0,0))Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


