please help with whatever uou can. i am so confused !!
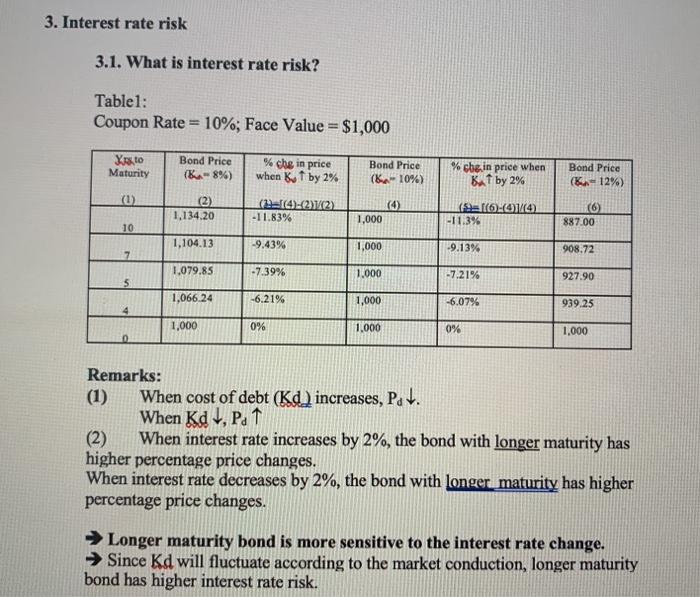
Bond Price, YTM and Returns 1. Reproduce the bond prices (Pd) in Table.1 on page 4 of Handout #1? Show your detail calculation for at least one premium bond, one discount bond and one par bond. 2. Calculate the percentage change in bond price when Kd increases from 8% to 10%. Show your work. 3. Calculate the percentage change in bond price when Kd decreases from 12% to 10%. Show your work. (Your answers here should be different from the number in Table 1 in Handout #1. Column 5 in Table 1 in Handout 1 is the percentage price change when kd increases from 10% to 12%.) 4. Based on your answers in question2 and 3, how does bond price reacted to the increase or decrease in Kd? Which terms (more than one) on bond contract will influence the change in bond price when Kd changes. 5. What is interest rate risk? 6. Use Excel spread sheet to find the YTM on Bond issued by General Electric Capital Corp. Bonds data is on lecture notes p.3. The data is on 10/10/2007. Therefore, the bond maturing in Sept. 2017 is approximately a 10-year bond. To make it simpler, assume that the bond pays coupon annually. Price of the bond are quoted as percentage of par value. A quoted price of 102.63 is 102.63% of par value. If par value (face value) of the bond is $1,000, the market price of the bond is $1,026.30. The assigned videos 9,10, and 11 last week are related to this exercise. 7. Please note that YTM is observed Kd. 3. Interest rate risk 3.1. What is interest rate risk? Table1: Coupon Rate = 10%; Face Value = $1,000 Maturity Bond Price (8%) % che in price when K by 2% Bond Price (ko 10%) % cbe in price when But by 2% Bond Price (12%) (1) (2) 1,134,20 (12-14)-(272) -11.83% 1,000 (16 (114 -11.3% (6) 887.00 10 1,104.13 -9.43% 1,000 -9.13% 908.72 7 1.079.85 -7.39% 1.000 -7.21% 927.90 5 1,066.24 -6.21% 1,000 -6.07% 939.25 1,000 0% 1.000 0% 1.000 Remarks: (1) When cost of debt (Kd) increases, Pdt. When Kd, P. 1 (2) When interest rate increases by 2%, the bond with longer maturity has higher percentage price changes. When interest rate decreases by 2%, the bond with longer maturity has higher percentage price changes. Longer maturity bond is more sensitive to the interest rate change. Since Kd will fluctuate according to the market conduction, longer maturity bond has higher interest rate risk. Bond Price, YTM and Returns 1. Reproduce the bond prices (Pd) in Table.1 on page 4 of Handout #1? Show your detail calculation for at least one premium bond, one discount bond and one par bond. 2. Calculate the percentage change in bond price when Kd increases from 8% to 10%. Show your work. 3. Calculate the percentage change in bond price when Kd decreases from 12% to 10%. Show your work. (Your answers here should be different from the number in Table 1 in Handout #1. Column 5 in Table 1 in Handout 1 is the percentage price change when kd increases from 10% to 12%.) 4. Based on your answers in question2 and 3, how does bond price reacted to the increase or decrease in Kd? Which terms (more than one) on bond contract will influence the change in bond price when Kd changes. 5. What is interest rate risk? 6. Use Excel spread sheet to find the YTM on Bond issued by General Electric Capital Corp. Bonds data is on lecture notes p.3. The data is on 10/10/2007. Therefore, the bond maturing in Sept. 2017 is approximately a 10-year bond. To make it simpler, assume that the bond pays coupon annually. Price of the bond are quoted as percentage of par value. A quoted price of 102.63 is 102.63% of par value. If par value (face value) of the bond is $1,000, the market price of the bond is $1,026.30. The assigned videos 9,10, and 11 last week are related to this exercise. 7. Please note that YTM is observed Kd. 3. Interest rate risk 3.1. What is interest rate risk? Table1: Coupon Rate = 10%; Face Value = $1,000 Maturity Bond Price (8%) % che in price when K by 2% Bond Price (ko 10%) % cbe in price when But by 2% Bond Price (12%) (1) (2) 1,134,20 (12-14)-(272) -11.83% 1,000 (16 (114 -11.3% (6) 887.00 10 1,104.13 -9.43% 1,000 -9.13% 908.72 7 1.079.85 -7.39% 1.000 -7.21% 927.90 5 1,066.24 -6.21% 1,000 -6.07% 939.25 1,000 0% 1.000 0% 1.000 Remarks: (1) When cost of debt (Kd) increases, Pdt. When Kd, P. 1 (2) When interest rate increases by 2%, the bond with longer maturity has higher percentage price changes. When interest rate decreases by 2%, the bond with longer maturity has higher percentage price changes. Longer maturity bond is more sensitive to the interest rate change. Since Kd will fluctuate according to the market conduction, longer maturity bond has higher interest rate risk

 please help with whatever uou can. i am so confused !!
please help with whatever uou can. i am so confused !!





