Please help work through these two problems and explain, thank you!
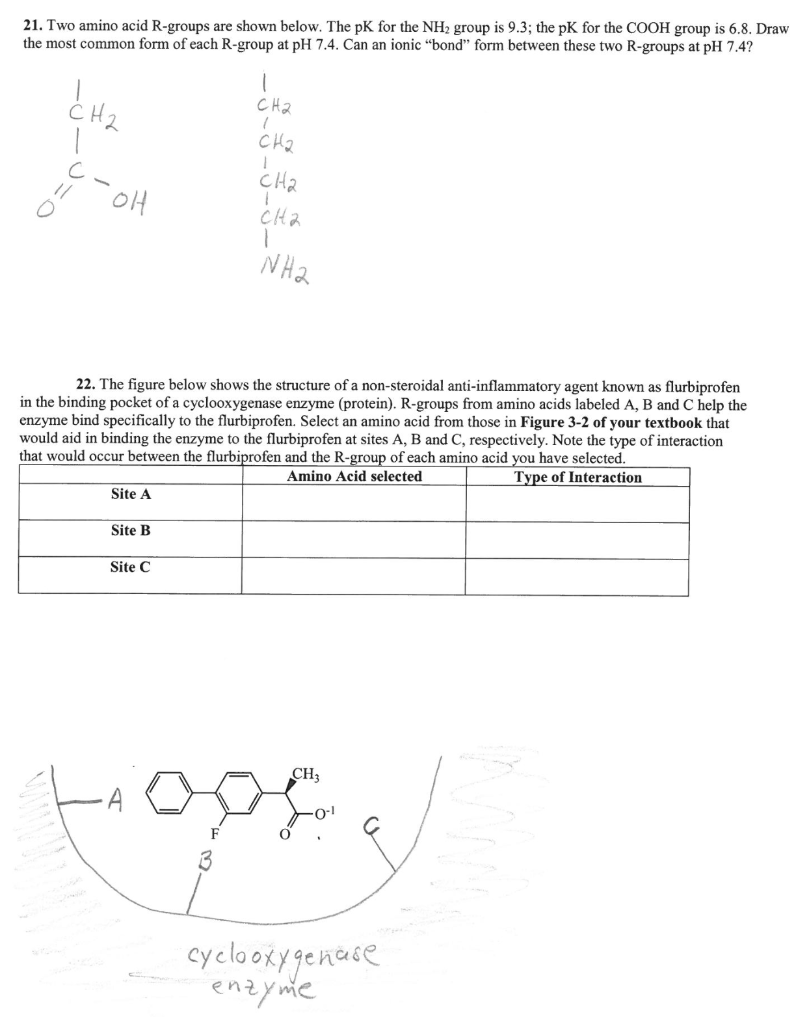
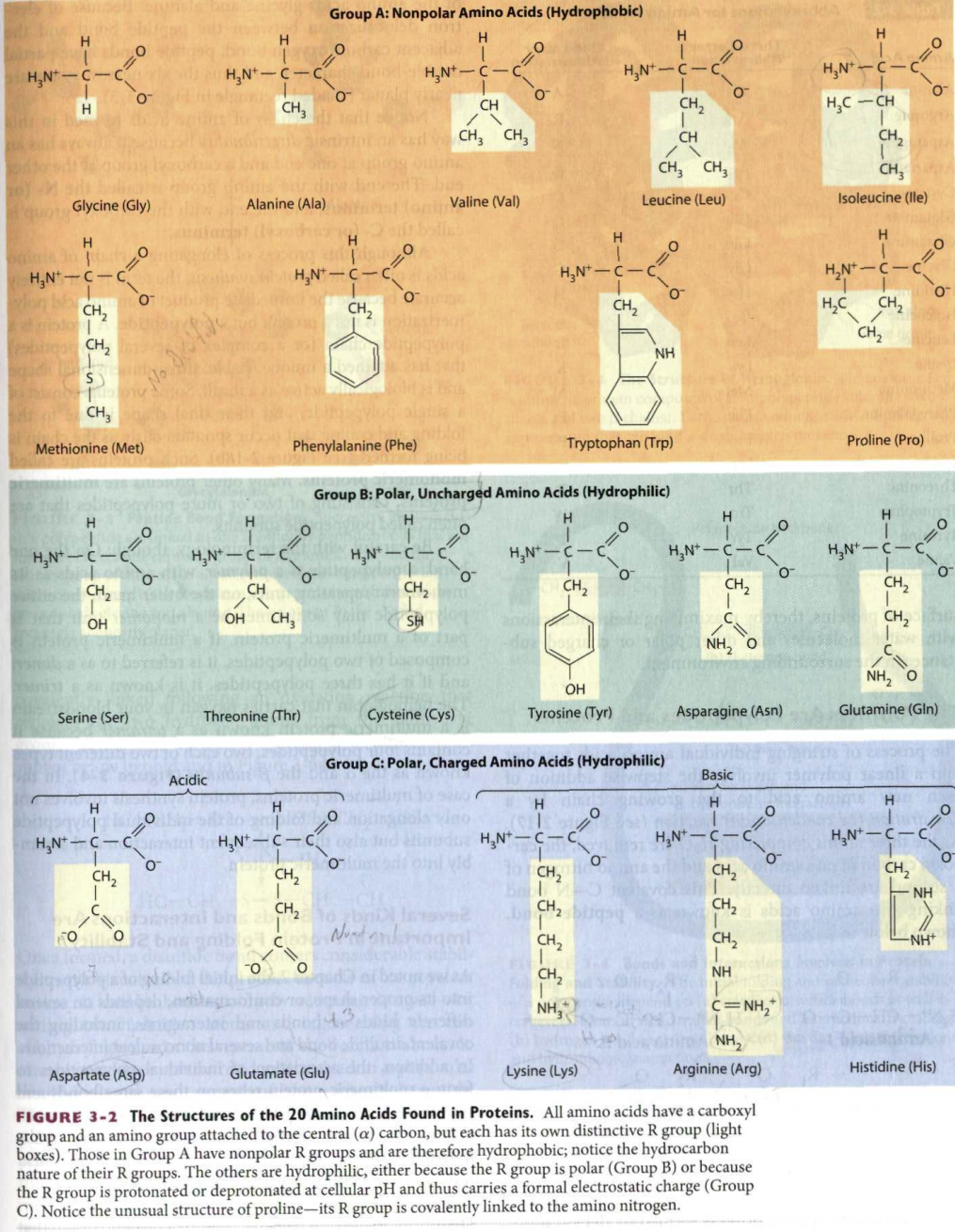
21. Two amino acid R-groups are shown below. The pK for the NH2 group is 9.3; the PK for the COOH group is 6.8. Draw the most common form of each R-group at pH 7.4. Can an ionic "bond" form between these two R-groups at pH 7.4? CH2 1 CH2 1 Cha 1 c- Cha OH cha NH2 22. The figure below shows the structure of a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent known as flurbiprofen in the binding pocket of a cyclooxygenase enzyme (protein). R-groups from amino acids labeled A, B and C help the enzyme bind specifically to the flurbiprofen. Select an amino acid from those in Figure 3-2 of your textbook that would aid in binding the enzyme to the flurbiprofen at sites A, B and C, respectively. Note the type of interaction that would occur between the flurbiprofen and the R-group of each amino acid you have selected. Amino Acid selected Type of Interaction Site A Site B Site C CH tools cyclooxygenase enzyme C=0 Group A: Nonpolar Amino Acids (Hydrophobic) H H H H H o o o TO HNT H2N-C-C H2N-C-C HN HN-C-C CH o- 0 0 0 0 H CH CH - CH CH CH CH, CH CH, 1 2 CH, Isoleucine (lle) Alanine (Ala) Glycine (Gly) Valine (Val) Leucine (Leu) H H H H O HN-C-C H2N-C-C HN 51 HN-C-C 0 0 0 0 CH2 CH2 CH 1 CH, HC CH CH, go S . Methionine (Met) Phenylalanine (Phe) Tryptophan (Trp) Proline (Pro) Group B: Polar, Uncharged Amino Acids (Hydrophilic) H H H H H H 0 0 O o F HAN C-6 H,N HEN-C- H2N-C- H2N-C-C =0 HN+ -c-c o 0 0 09 O CH, CH CH CH2 CH2 CH2 OH SH OH C CH2 NH2 o NH, o OH Tyrosine (Tyr) Serine (Ser) Threonine (Thr) Cysteine (Cys) Asparagine (Asn) Glutamine (Gln) Group C: Polar, Charged Amino Acids (Hydrophilic) Acidic Basic H H 0 0 HN C- H2N-C-C C-C HNT HEN H2N-C-C CH2 0 0 0 0 O CH2 CH CH 1 NH CH2 CH, $_$_$_I_ FO 0 Nund on our CH2 -NH O CH2 NH NH3 C=NH, NH, Arginine (Arg) Aspartate (Asp) Glutamate (Glu) Lysine (Lys) Histidine (His) FIGURE 3-2 The Structures of the 20 Amino Acids Found in Proteins. All amino acids have a carboxyl group and an amino group attached to the central (a) carbon, but each has its own distinctive R group (light boxes). Those in Group A have nonpolar R groups and are therefore hydrophobic; notice the hydrocarbon nature of their R groups. The others are hydrophilic, either because the R group is polar (Group B) or because the R group is protonated or deprotonated at cellular pH and thus carries a formal electrostatic charge (Group C). Notice the unusual structure of proline-its R group is covalently linked to the amino nitrogen








