Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Please ignore the scribbles, I forgot to screenshot before inputing the wrong answers. And please note there are at least two duplicate parts due to
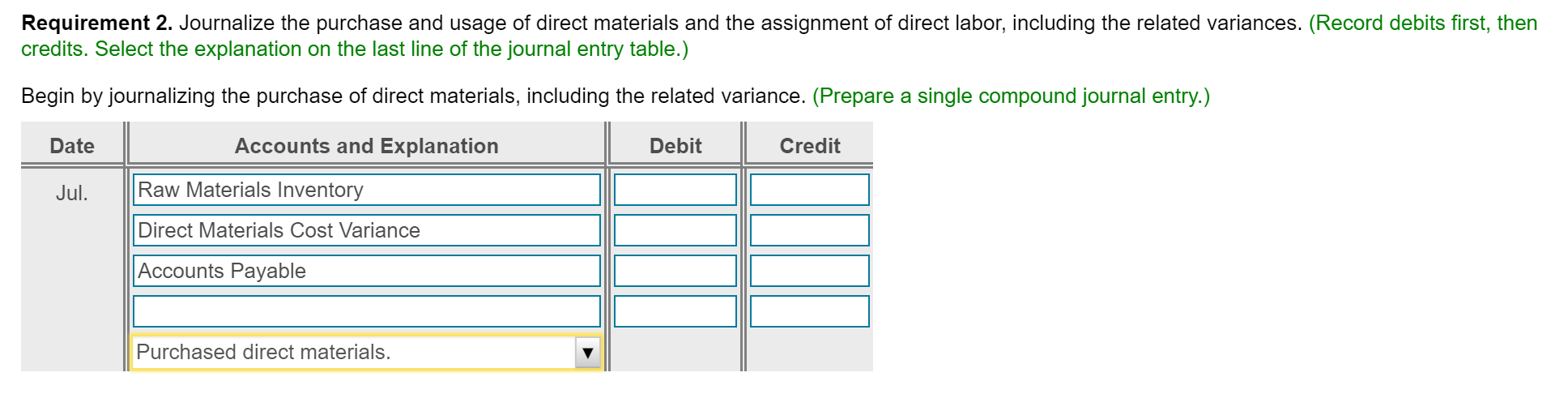
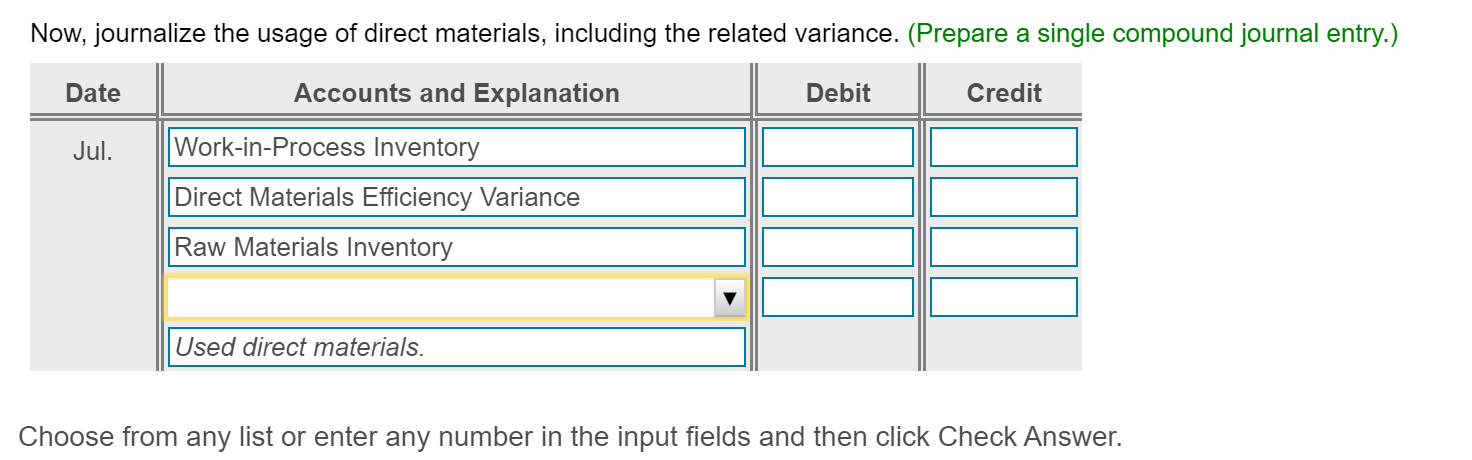
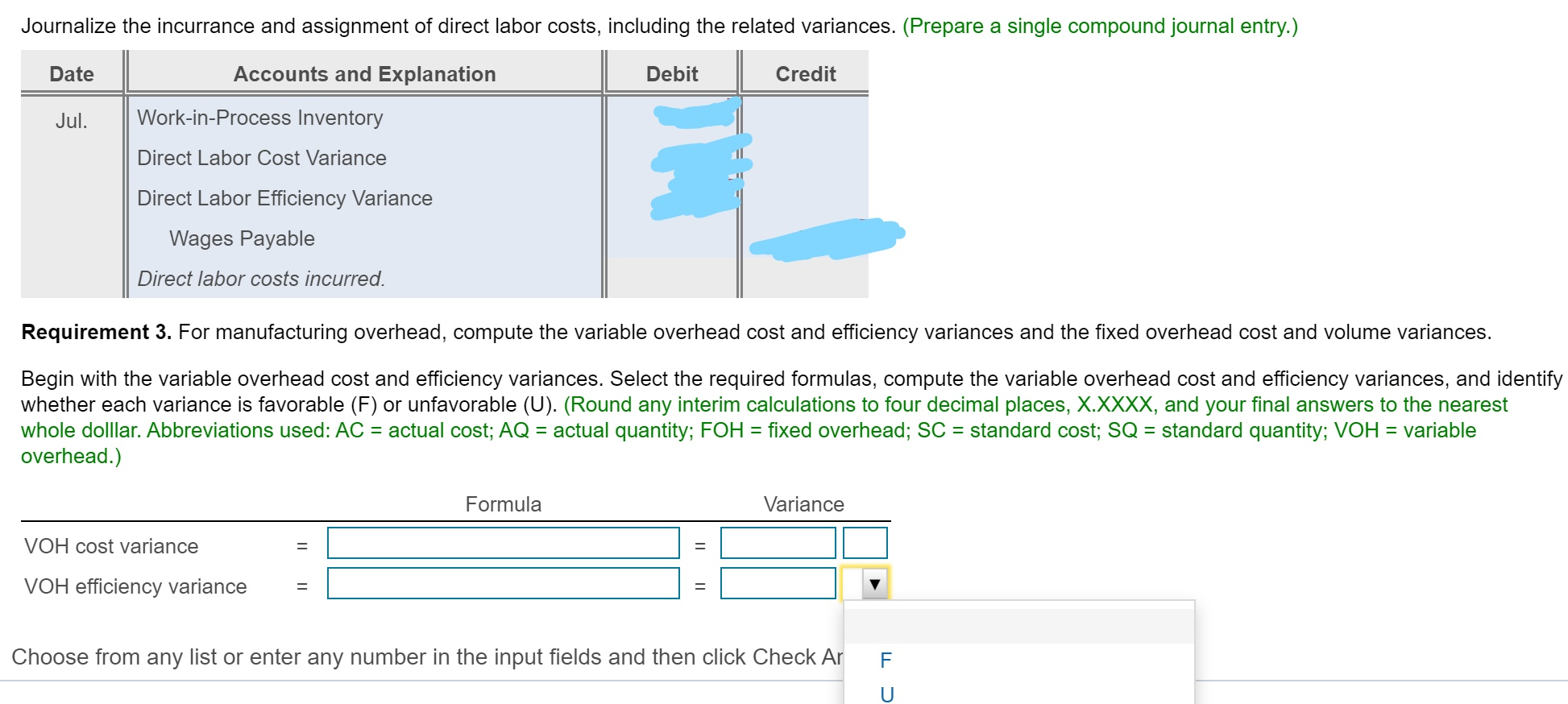
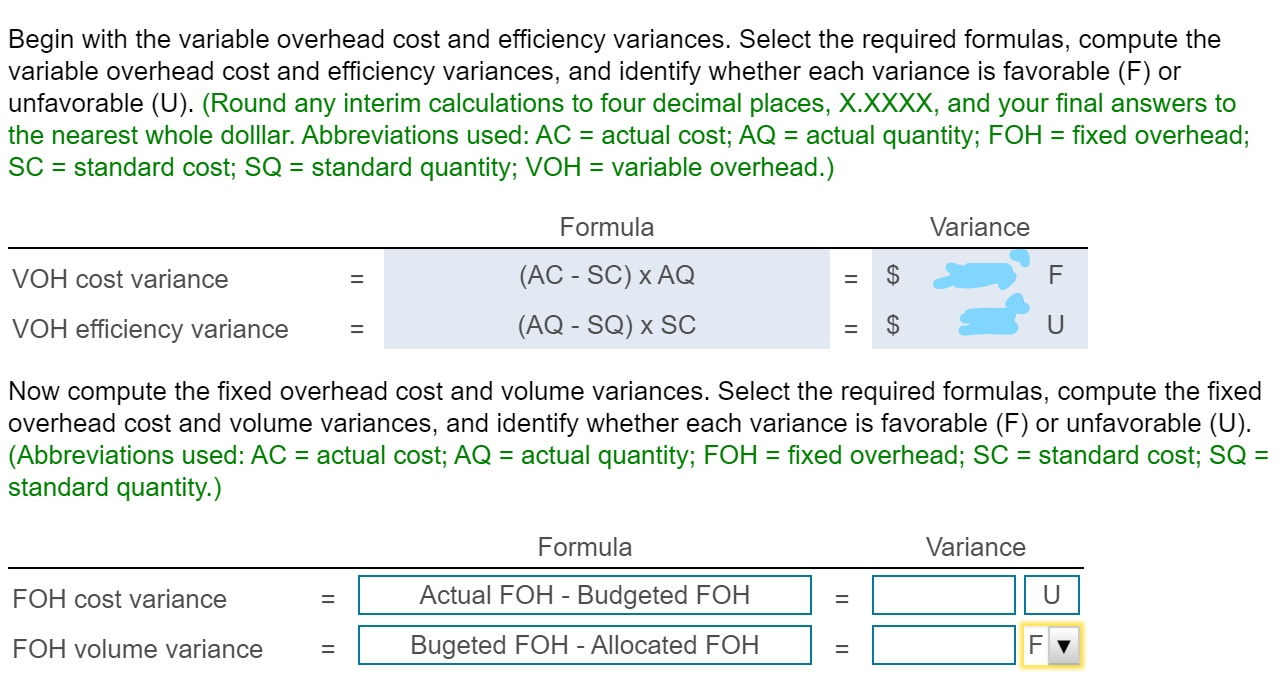

Please ignore the scribbles, I forgot to screenshot before inputing the wrong answers. And please note there are at least two duplicate parts due to screenshotting mistakes.Sorry, thank you.
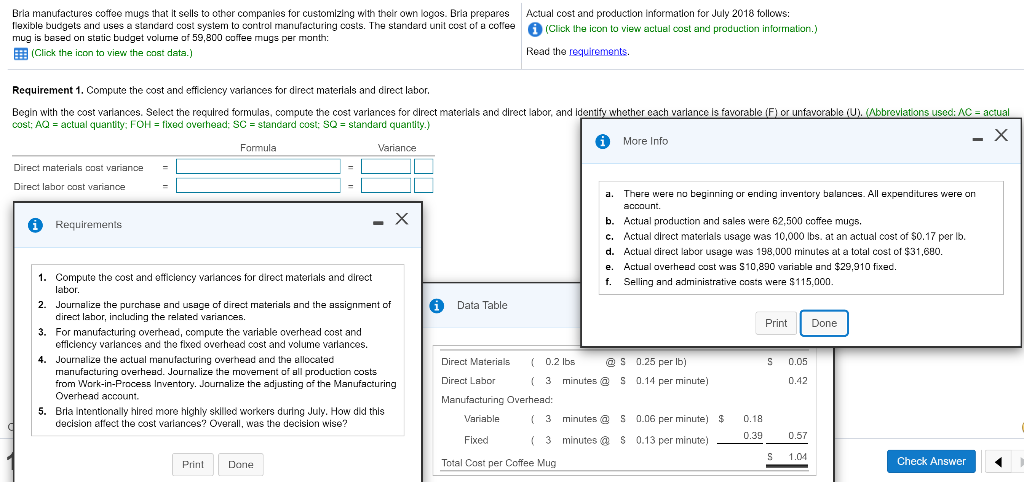
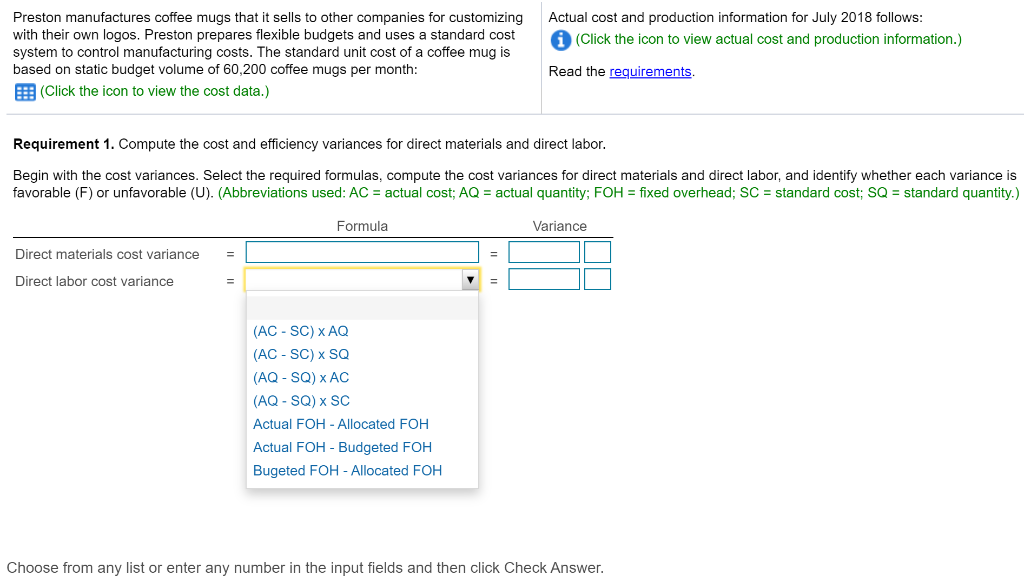
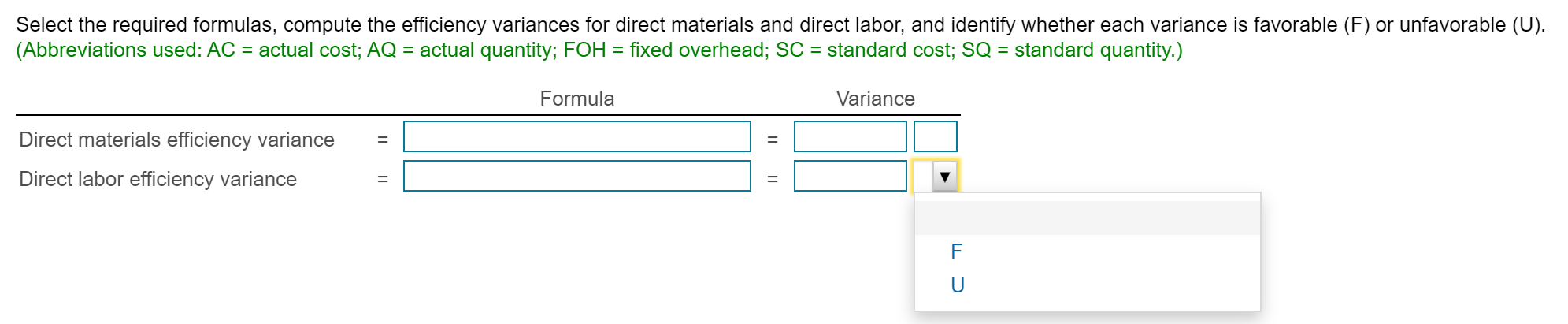
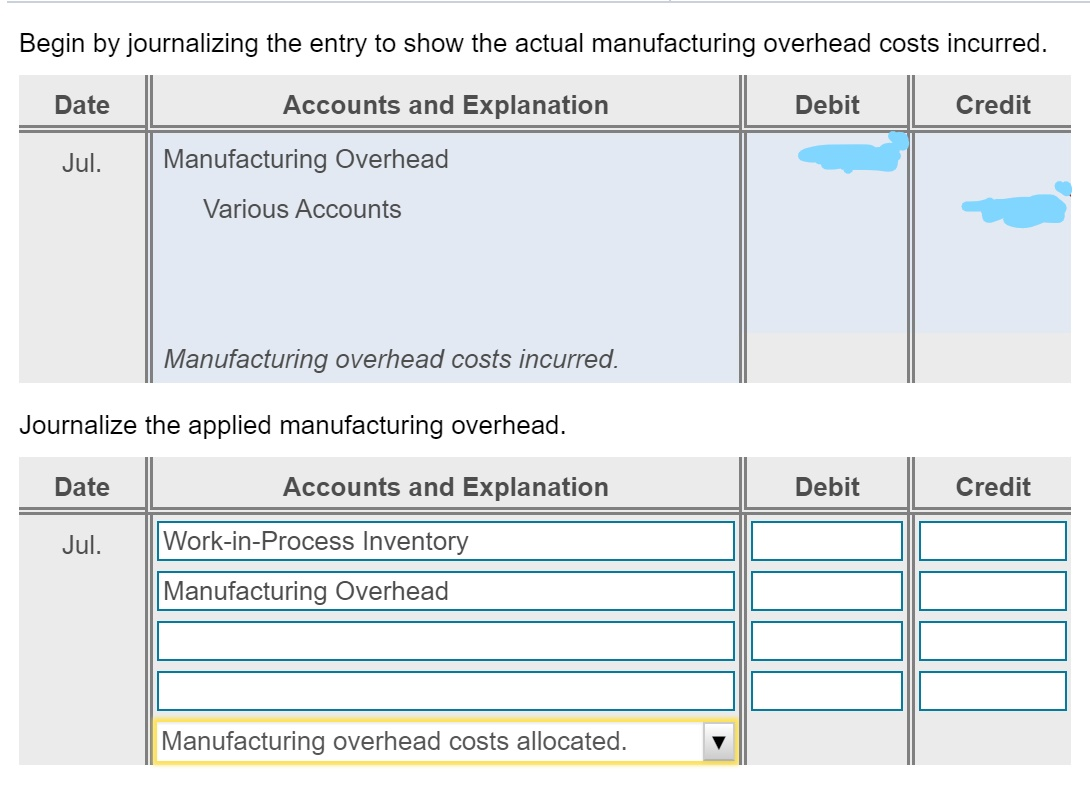
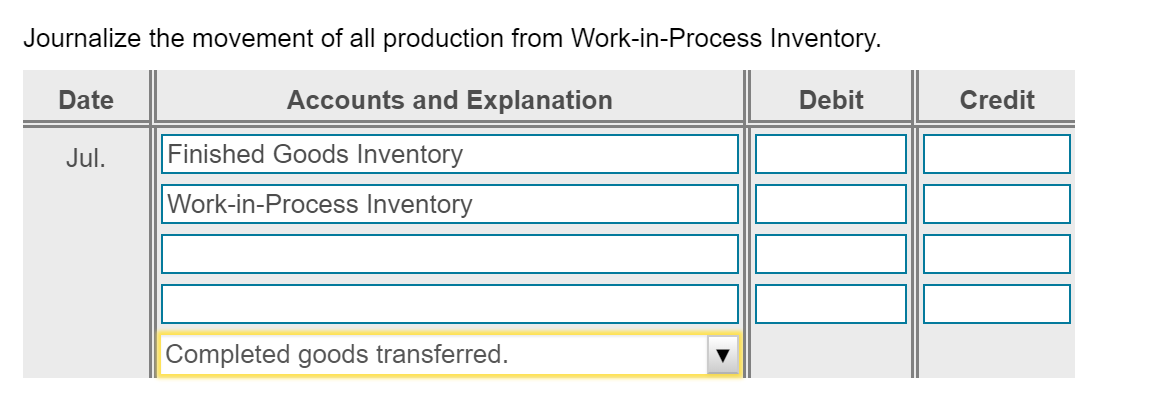
Bria manufactures coffee mugs that it sells to other companies for customizing with their own logos. Bria prepares Actual cost and production information for July 2018 follows: flexible budgets and uses a standard cost system to control manufacturing costs. The standard unit cost of a coffee (Click the icon to view actual cost and production information.) mug is based on static budget volume of 59,800 coffee mugs per month: (Click the icon to view the cost data.) Read the requirements. Requirement 1. Compute the cost and efficiency variances for direct materials and direct labor. Begin with the cost variances. Select the required formulas, compute the cost varlances for direct materials and direct labor, and identify whether each variance is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). (Abbreviations used: AC = actual cost; AQ = actual quantity: FOH = fixed overhead: SC = standard cost: SQ = standard quantity.) More Info - X Formula Variance Direct materials cost variance Direct labor cost variance a. Requirements - There were no beginning or ending inventory balances. All expenditures were on account. b. Actual production and sales were 62,500 coffee mugs, c. Actual direct materials usage was 10,000 lbs. at an actual cost of $0.17 per lb. d. Actual direct labor usage was 198.000 minutes at a total cost of $31,680. Actual overhead cost was $10,890 variable and $29,910 fixed. f. Selling and administrative costs were $115.000. e. i Data Table Print Done 1. Compute the cost and efficiency variances for direct materials and direct labor. 2. Journalize the purchase and usage of direct materials and the assignment of direct labor, including the related variances. 3. For manufacturing overhead, compute the variable overhead cost and efficiency varlances and the fixed overhead cost and volume varlances. 4. Journalize the actual manufacturing overhead and the allocated manufacturing overhead. Journalize the movement of all production costs from Work-in-Process Inventory. Journalize the adjusting of the Manufacturing Overhead account. 5. Brla intentionally hired more highly skilled workers during July. How did this decision affect the cost variances? Overall, was the decision wise? S 0.05 0.42 Direct Materials ( 0.2 lbs @S 0.25 per lb) Direct Labor (3 minutes @ S 0.14 per minute) Manufacturing Overhead: Variable (3 minutes @ S 0.06 per minute) $ 0.18 Fixed 0.39 (3 minutes @ $ 0.13 per minute) 0.57 S 1.04 Print Dane Total Cost per Coffee Mug Check Answer Actual cost and production information for July 2018 follows: (Click the icon to view actual cost and production information.) Preston manufactures coffee mugs that it sells to other companies for customizing with their own logos. Preston prepares flexible budgets and uses a standard cost system to control manufacturing costs. The standard unit cost of a coffee mug is based on static budget volume of 60,200 coffee mugs per month: (Click the icon to view the cost data.) Read the requirements. Requirement 1. Compute the cost and efficiency variances for direct materials and direct labor. Begin with the cost variances. Select the required formulas, compute the cost variances for direct materials and direct labor, and identify whether each variance is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). (Abbreviations used: AC = actual cost; AQ = actual quantity; FOH = fixed overhead; SC = standard cost; SQ = standard quantity.) Formula Variance Direct materials cost variance Direct labor cost variance (AC-SC) XAQ (AC-SC) SQ (AQ - SQ)X AC (AQ - SQ)X SC Actual FOH - Allocated FOH Actual FOH - Budgeted FOH Bugeted FOH - Allocated FOH Choose from any list or enter any number in the input fields and then click Check Answer. Select the required formulas, compute the efficiency variances for direct materials and direct labor, and identify whether each variance is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). (Abbreviations used: AC = actual cost; AQ = actual quantity; FOH = fixed overhead; SC = standard cost; SQ = standard quantity.) Formula Variance Direct materials efficiency variance Direct labor efficiency variance II II F U Requirement 2. Journalize the purchase and usage of direct materials and the assignment of direct labor, including the related variances. (Record debits first, then credits. Select the explanation on the last line of the journal entry table.) Begin by journalizing the purchase of direct materials, including the related variance. (Prepare a single compound journal entry.) Date Accounts and Explanation Debit Credit Jul. Raw Materials Inventory Direct Materials Cost Variance Accounts Payable Purchased direct materials. Now, journalize the usage of direct materials, including the related variance. (Prepare a single compound journal entry.) Date Accounts and Explanation Debit Credit Jul. Work-in-Process Inventory Direct Materials Efficiency Variance Raw Materials Inventory Used direct materials. Choose from any list or enter any number in the input fields and then click Check Answer. Journalize the incurrance and assignment of direct labor costs, including the related variances. (Prepare a single compound journal entry.) Date Accounts and Explanation Debit Credit Jul. Work-in-Process Inventory Direct Labor Cost Variance Direct Labor Efficiency Variance Wages Payable Direct labor costs incurred. Requirement 3. For manufacturing overhead, compute the variable overhead cost and efficiency variances and the fixed overhead cost and volume variances. Begin with the variable overhead cost and efficiency variances. Select the required formulas, compute the variable overhead cost and efficiency variances, and identify whether each variance is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). (Round any interim calculations to four decimal places, X.XXXX, and your final answers to the nearest whole dolllar. Abbreviations used: AC = actual cost; AQ = actual quantity; FOH = fixed overhead; SC = standard cost; SQ = standard quantity; VOH = variable overhead.) Formula Variance VOH cost variance VOH efficiency variance Choose from any list or enter any number in the input fields and then click Check Ar F U Begin with the variable overhead cost and efficiency variances. Select the required formulas, compute the variable overhead cost and efficiency variances, and identify whether each variance is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). (Round any interim calculations to four decimal places, X.XXXX, and your final answers to the nearest whole dolllar. Abbreviations used: AC = actual cost; AQ = actual quantity; FOH = fixed overhead; SC = standard cost; SQ = standard quantity; VOH = variable overhead.) Formula Variance VOH cost variance = $ F (AC - SC) XAQ (AQ - SQ) x SC VOH efficiency variance $ U Now compute the fixed overhead cost and volume variances. Select the required formulas, compute the fixed overhead cost and volume variances, and identify whether each variance is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). (Abbreviations used: AC = actual cost; AQ = actual quantity; FOH = fixed overhead; SC = standard cost; SQ = standard quantity.) Formula Variance FOH cost variance Actual FOH - Budgeted FOH U FOH volume variance Bugeted FOH - Allocated FOH F Begin by journalizing the entry to show the actual manufacturing overhead costs incurred. Date Debit Credit Jul. Accounts and Explanation Manufacturing Overhead Various Accounts Manufacturing overhead costs incurred. Journalize the applied manufacturing overhead. Date Accounts and Explanation Debit Credit Jul. Work-in-Process Inventory Manufacturing Overhead Manufacturing overhead costs allocated. Journalize the movement of all production from Work-in-Process Inventory. Date Accounts and Explanation Debit Credit Jul. Finished Goods Inventory Work-in-Process Inventory Completed goods transferred. Journalize the adjusting of the Manufacturing Overhead account. (Prepare a single compound journal entry.) Date Accounts and Explanation Debit Credit Jul. Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance Fixed Overhead Cost Variance Variable Overhead Cost Variance Fixed Overhead Volume Variance Manufacturing Overhead To adjust Manufacturing Overhead. Requirement 5. Preston intentionally hired more highly skilled workers during July. How did this decision affect the cost variances? Overall, was the decision wise? Hiring more-skilled, higher-paid labor led to an unfavorable direct labor cost variance. Given the unfavorable direct labor efficiency variance, it does not appear that these more-skilled workers performed efficiently. The overall net effect is unfavorable thus management's decision was unwise This question is complete. Move your cursor over or tap on the red arrows to see incorrect answersStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started