Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
PLEASE INCLUDE SCREENSHOTS FROM VIRTUALBOX & MININET TO HELP ME UNDERSTAND! 2.3 Q3: Effects of Multiplexing Next, assume multiple hosts connected to sl want to
PLEASE INCLUDE SCREENSHOTS FROM VIRTUALBOX & MININET TO HELP ME UNDERSTAND!
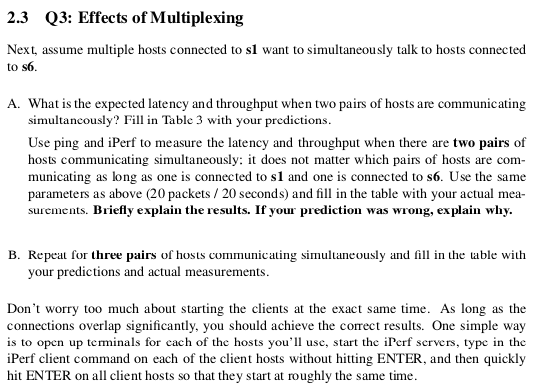
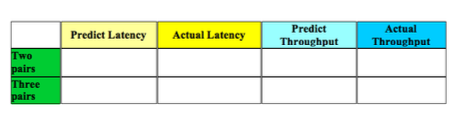
2.3 Q3: Effects of Multiplexing Next, assume multiple hosts connected to sl want to simultaneously talk to hosts connected to s6. A. What is the expected latency and throughput when two pairs of hosts are communicating simultancously? Fill in Table 3 with your predictions. Use ping and iPerf to measure the latency and throughput when there are two pairs of hosts communicating simultaneously: it does not matter which pairs of hosts are com municating as long as one is connected to s1 and one is connected to s6. Use the same parameters as above (20 packets / 20 seconds) and fill in the table with your actual mea surements. Briefly explain the results. If your prediction was wrong, explain why. B. Repeat for three pairs of hosts communicating simultaneously and fill in the able with your predictions and actual measurements. Don't worry too much about starting the clients at the exact same time. As long as the connections overlap significantly, you should achieve the correct results. One simple way is to open up teminals for each of the hosts you'll use, start the iPerf servers, type in the iPerf client command on each of the client hosts without hitting ENTER, and then quickly hit ENTER on all client hosts so that they start at roughly the same time 2.3 Q3: Effects of Multiplexing Next, assume multiple hosts connected to sl want to simultaneously talk to hosts connected to s6. A. What is the expected latency and throughput when two pairs of hosts are communicating simultancously? Fill in Table 3 with your predictions. Use ping and iPerf to measure the latency and throughput when there are two pairs of hosts communicating simultaneously: it does not matter which pairs of hosts are com municating as long as one is connected to s1 and one is connected to s6. Use the same parameters as above (20 packets / 20 seconds) and fill in the table with your actual mea surements. Briefly explain the results. If your prediction was wrong, explain why. B. Repeat for three pairs of hosts communicating simultaneously and fill in the able with your predictions and actual measurements. Don't worry too much about starting the clients at the exact same time. As long as the connections overlap significantly, you should achieve the correct results. One simple way is to open up teminals for each of the hosts you'll use, start the iPerf servers, type in the iPerf client command on each of the client hosts without hitting ENTER, and then quickly hit ENTER on all client hosts so that they start at roughly the same timeStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


