Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
please post the whole answer otherwise part cuts out and cant see the numbers Check my work mode: This shows what is correct or incorrect
please post the whole answer otherwise part cuts out and cant see the numbers 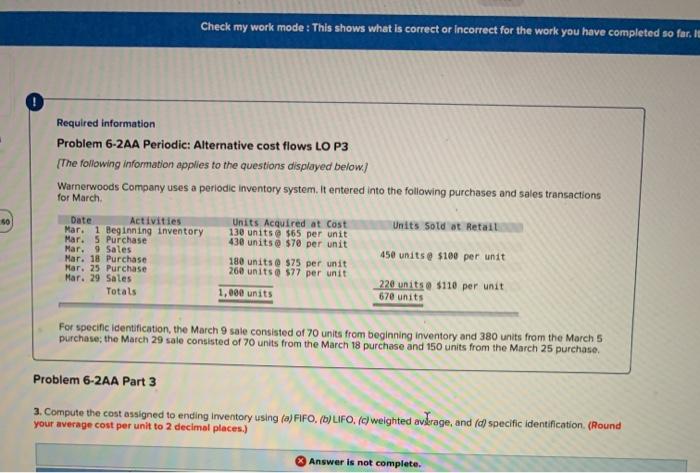
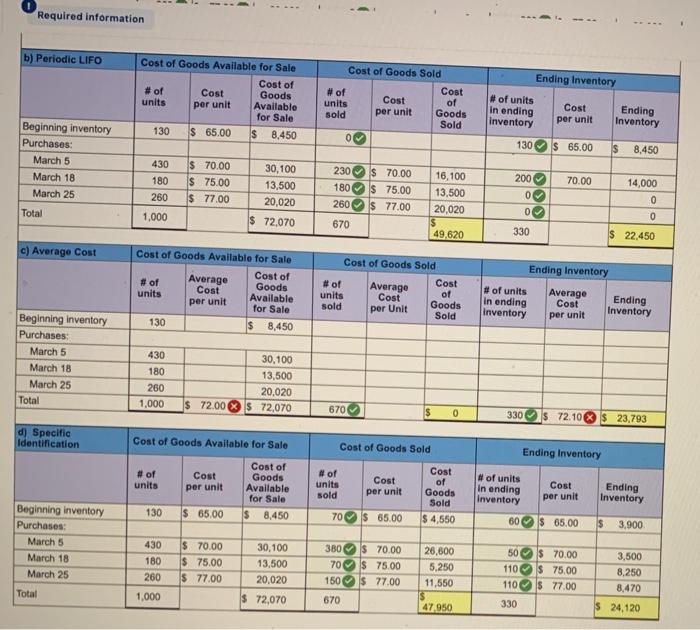
Check my work mode: This shows what is correct or incorrect for the work you have completed so far. In ! Required information Problem 6-2AA Periodic: Alternative cost flows LO P3 [The following information applies to the questions displayed below) Warnerwoods Company uses a periodic inventory system. It entered into the following purchases and sales transactions for March 50 Units sold at Retail Date Activities Mar. 1 Beginning inventory Mar. 5 Purchase Mar. 9 Sales Mar. 18 Purchase Mar. 25 Purchase Mar. 29 Sales Totals Units Acquired at Cost 130 units@ $65 per unit 430 units @ $70 per unit 180 units @ $75 per unit 260 units@ $77 per unit 450 units@ $100 per unit 1,000 units 220 unitse $110 per unit 670 units For specific identification, the March 9 sale consisted of 70 units from beginning inventory and 380 units from the March 5 purchase the March 29 sale consisted of 70 units from the March 18 purchase and 150 units from the March 25 purchase Problem 6-2AA Part 3 2. Compute the cost assigned to ending Inventory using (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO. (c) weighted average, and (d) specific identification (Round your average cost per unit to 2 decimal places.) Answer is not complete. Required information b) Periodic LIFO Cost of Goods Available for Sale Cost of #of Cost Goods units Available for Sale 130 $ 65,00 $ 8.450 Cost of Goods Sold # of Cost units Cost of sold per unit Goods Sold 0 per unit Ending Inventory # of units Cost Ending In ending Inventory Inventory per unit 130$ 65.00 S 8,450 Beginning inventory Purchases: March 5 March 18 March 25 430 180 260 $ 70.00 $ 75,00 $ 77.00 70.00 30,100 13,500 20,020 230 180 260 $ 70,00 $ 75.00 $ 77.00 14,000 16,100 13,500 20.020 200 0 0 0 Total 1,000 0 $ 72,070 670 49,620 330 22.450 c) Average Cost Ending Inventory Cost of Goods Available for Sale Average # of Cost of Goods Cost units Available for Sale 130 $ 8,450 Cost of Goods Sold # of Average Cost units Cost of sold Goods per Unit Sold per unit #of units in ending Inventory Average Cost Ending Inventory per unit Beginning inventory Purchases: March 5 March 18 March 25 Total 430 180 260 1,000 30,100 13,500 20.020 $ 72,070 $ 72.00 670 $ 0 330 $ 72.10 $ 23,793 d) Specific Identification Cost of Goods Available for Sale Cost of Goods Sold Ending Inventory # of units Cost per unit Cost of Goods Available for Sale $ 8,450 # of units sold Cost per unit Cost of Goods Sold $ 4,550 # of units In ending Inventory Cost per unit Ending Inventory 130 $ 65.00 70 $ 65.00 60 $ 65.00 $ 3,900 Beginning inventory Purchases: March 5 March 18 March 25 430 180 260 $ 70.00 $ 75.00 $ 77.00 30,100 13,500 20.020 380$ 70.00 70 $ 75.00 150 $ 77.00 OO 26,600 5,250 11,550 110 50$ 70.00 $ 75,00 110 $ 77.00 330 3,500 8,250 8,470 $ 24,120 Total 1,000 $ 72,070 670 47.950 

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


