Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
PLEASE PREPARE JOURNAL ENTRIES FOR ACCOUNTING. WORK IS ALREADY DONE PLEASE SEE ATTACHMENTS. JOURNAL REQUIREMENTS ARE 1) Record the use of direct materials with price
PLEASE PREPARE JOURNAL ENTRIES FOR ACCOUNTING. WORK IS ALREADY DONE PLEASE SEE ATTACHMENTS. JOURNAL REQUIREMENTS ARE 
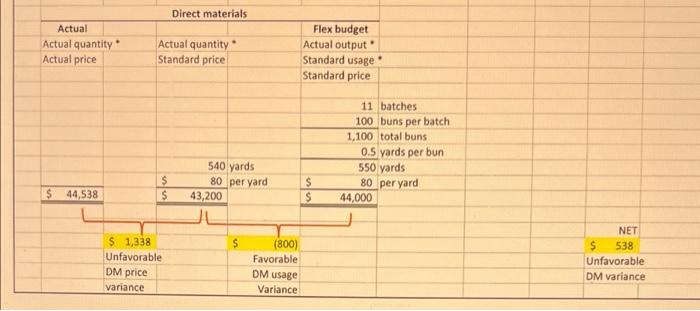
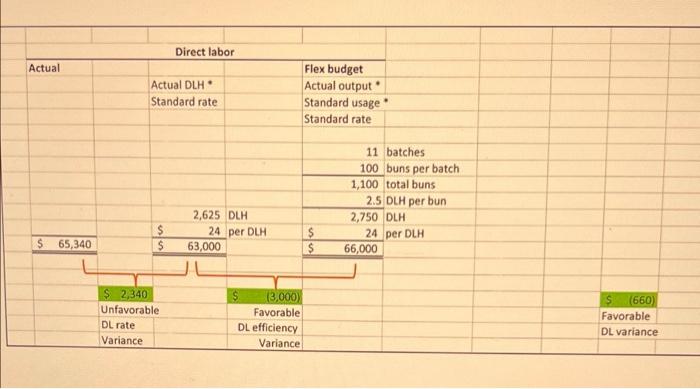
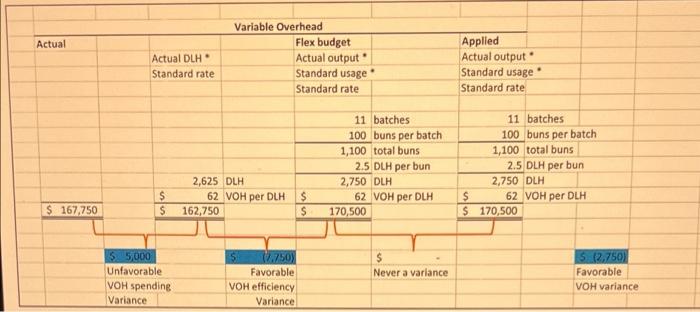
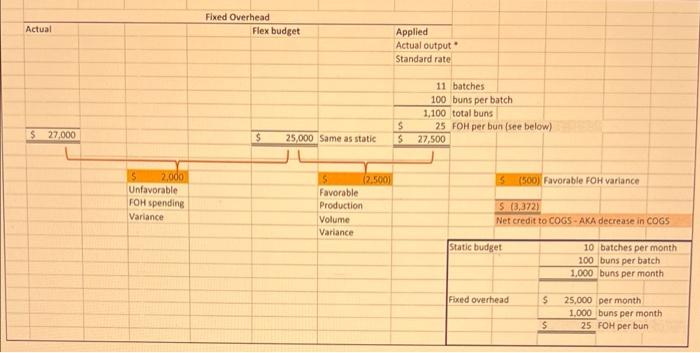
You have a business manufacturing man-buns for hipster wannabes. You produce these buns in batches of 100. Each bun has the following manufacturing standards (h.e., budgets): Direct materials 0.5 yards of $80.00 per yard material Direct labor 2.5 Direct $24.00 per Direct Labor Labor Hours Hour Variable Overhead $62.00 per DLH Fixed Overhead $25,000 per month Original (Static) budget 10 batches per month There is no beginning or ending inventory for Materials, WIP and Finished Goods. You buy what you need and sell all that you make. During March 2022 you made 11 batches of buns (100 buns in each batch) and spent/used/incurred the following: Yards of material 540 yards $44,538 in total Direct labor 2,625 DLH $65,340 in total Variable overhead $167,750 in total Fixed overhead $27,000 in total REQUIRED: a) Prepare an analysis of actual direct production costs for March compared to Budget-adjusted- for-output (Flex Budget). Identify the usage/efficiency, price/rate, spending, and production volume variances. b) Ferd is responsible for buying your direct materials. Did he do a "good" job in March? Why? c) Franny is in charge of the use of the direct materials. Did she do a "good" job in March with regards to material usage? Why? d) Floosy is in charge of the use of direct labor. Did she do a "good" job in March with regards to labor usage/efficiency? Why? e) Futz sets hourly wage rates for the direct labor. Did he do a "good" job in March? Why? f) Noxon is responsible for spending on both variable and fixed overhead. Did he do a good job in March? b) If you close all of the variances to COGS, what will be the net change in COGS? . . . Prepare the journal entries to record the activities discussed above: Record the use of direct materials with price and usage variances Record the incurrence of direct labor with rate and efficiency variances Record the incurrence of variable and fixed overhead with spending, efficiency, and production volume variances Record the transfer of COGM to FG Inventory Record the transfer of goods sold from FG Inventory to COGS Close all variances to COGS Post these entries to T-accounts and come to ending balances: Assume all overhead spending comes from cash Remember that there is no beginning or ending inventory for WIP and FG . . . Direct materials . Actual Actual quantity Actual price Actual quantity Standard price Flex budget Actual output Standard usage Standard price 11 batches 100 buns per batch 1,100 total buns 0.5 yards per bun 550 yards 80 per yard 44,000 540 yards 80 per yard 43,200 $ $ $ 44,538 S S $ $ 1,338 Unfavorable DM price variance (800) Favorable NET s 538 Unfavorable DM variance DM usage Variance Direct labor Actual Actual DLH Standard rate Flex budget Actual output Standard usage Standard rate 11 batches 100 buns per batch 1,100 total buns 2.5 DLH per bun 2,750 DLH 24 per DLH 66,000 2,625 DLH 24 per DLH 63,000 $ $ $ 65,340 $ $ $ 2.340 Unfavorable DL rate Variance (3,000 Favorable DL efficiency Variance S (660) Favorable DL variance Actual Actual DLH Standard rate Variable Overhead Flex budget Actual output Standard usage Standard rate Applied Actual output Standard usage . Standard rate 11 batches 100 buns per batch 1,100 total buns 2.5 DLH per bun 2,750 DLH 62 VOH per DLH 170,500 11 batches 100 buns per batch 1,100 total buns 2.5 DLH per bun 2,750 DLH $ 62 VOH per DLH $ 170,500 $ $ 2,625 DLH 62 VOH per DLH 162,750 $ S $ 167,750 55,000 Unfavorable VOH spending Variance $ Never a variance 10.750 Favorable VOH efficiency Variance 5 (2,750) Favorable VOH variance Fixed Overhead Flex budget Actual Applied Actual output Standard rate 11 batches 100 buns per batch 1,100 total buns 25 FOH per bun (see below) 27,500 $ 27,000 $ S s 25,000 Same as static 5 (500) Favorable FOH variance 2,000 Unfavorable FOH spending Variance $ (2,500) Favorable Production Volume Variance $ (3,372) Net credit to COGS - AKA decrease in COGS Static budget 10 batches per month 200 buns per batch 1.000 buns per month Fixed overhead $ 25,000 per month 1.000 buns per month 25 FOH per bun $ 1) Record the use of direct materials with price and usage variances
2) Record the incurrence of direct labor with rate and efficiency variances
3) Record the incurrence of variable and fixed overhead with spending, efficiency, and production volume variances
4) Record the transfer of COGM (cost of goods manufactured) to FG inventory
5) Record the transfer of goods sold from FG inventory to COGS
6) Close all variances to COGS
POST THESE TO T-ACCOUNTS AND COME TO ENDING BALANCES
1) Assume all overhead spending comes from cash
2) Remember that there is no beginning or ending inventory for WIP and FG
PLEASE NOTE ANSWERS ARE THERE JUST NEED JOURNAL ENTRIES
THANKS 






Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


