please questions 1 till 5 as soon as possible.
please as soon as possible thank you
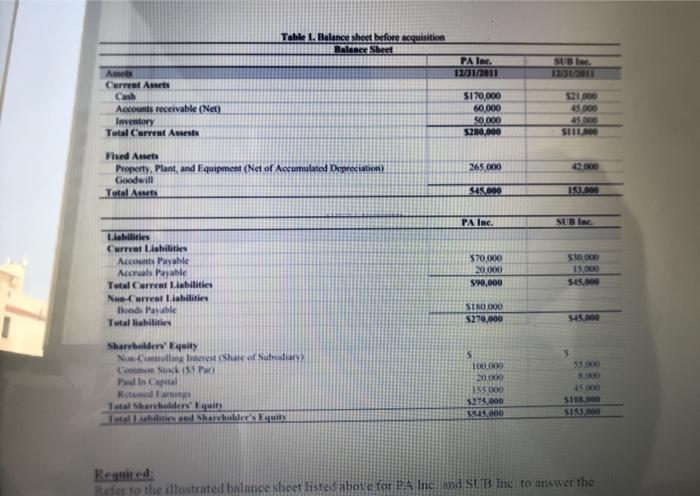
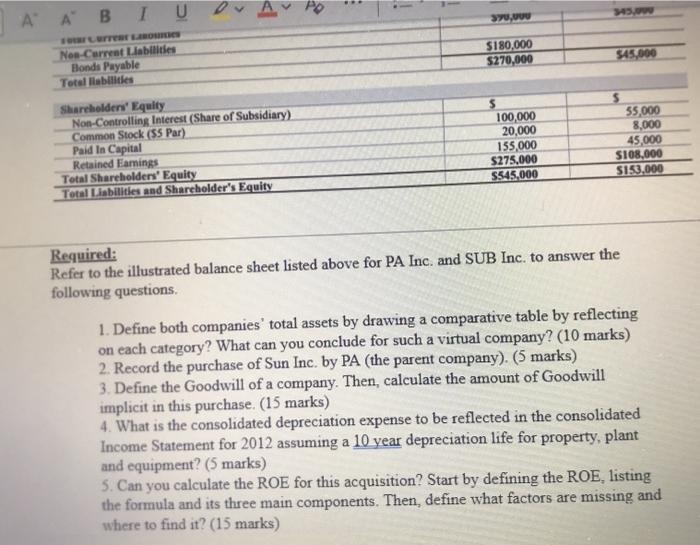
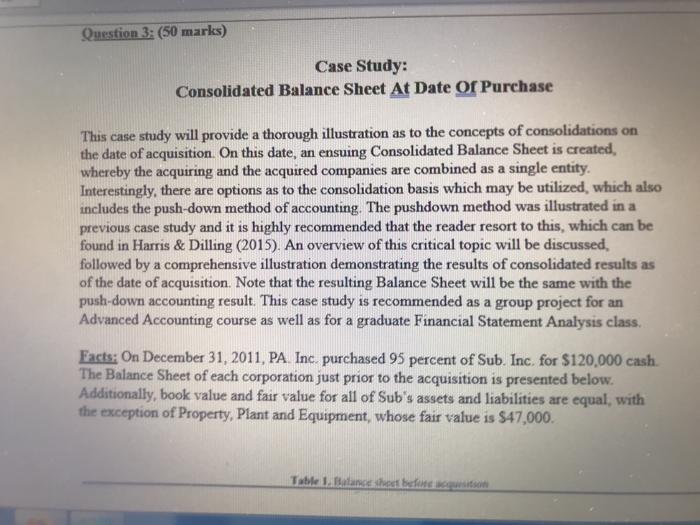
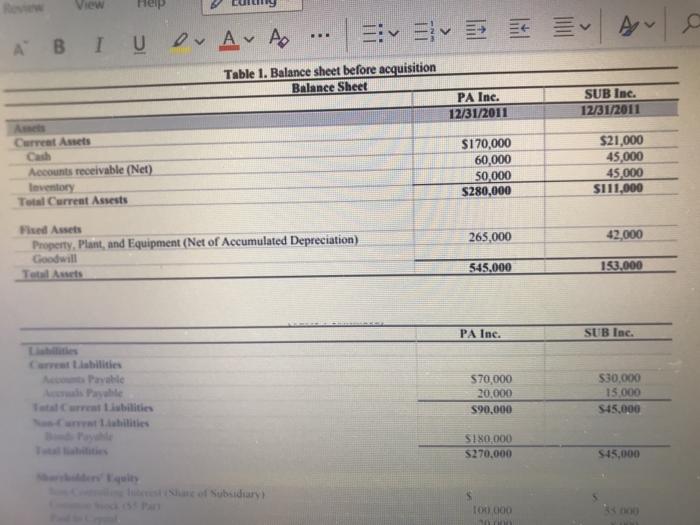
Case Study: Consolidated Balance Sheet At Date Of Purchase This case study will provide a thorough illustration as to the concepts of consolidations on the date of acquisition. On this date, an ensuing Consolidated Balance Sheet is created, whereby the acquiring and the acquired companies are combined as a single entity. Interestingly, there are options as to the consolidation basis which may be utilized, which also includes the push- down method of accounting. The pushdown method was illustrated in a previous case study and it is highly recommended that the reader resort to this, which can be found in Harris & Dilling (2015). An overview of this critical topic will be discussed, followed by a comprehensive illustration demonstrating the results of consolidated results as of the date of acquisition. Note that the resulting Balance Sheet will be the same with the push-down accounting result. This case study is recommended as a group project for an Advanced Accounting course as well as for a graduate Financial Statement Analysis class. Facts: On December 31, 2011. PA. Inc. purchased 95 percent of Sub. Inc. for $120,000 cash. The Balance Sheet of each corporation just prior to the acquisition is presented below. Additionally, book value and fair value for all of Sub's assets and liabilities are equal, with the exception of Property. Plant and Equpment, whose fair value is $47,000. Table Balance lieet Plas 12/31/2011 Ats Curel Acts Net S1900 O OY SO 5210, Trail Table 1. Balance sheet before acquisition Balance Sheet PA Inc. 12/31/2011 SUBI 12/31/2011 Carreal Arts Cash Accounts receivable (Net) Inventory Total Current Assets $170.000 60.000 50 000 S280,000 35.00 SIITTO 265,000 Fhed Amets Property, Plant, and Equipment (Net of Accumulated Depreciation Goodwill Total Assets 345.000 1600 PA Inc. SUBlac Les Curret Liabilities Accounts Payable Accruals Payable Total Current Liabilities Neo-Curral Liabilities Bends Payable Total liabilities 570.000 20.000 590.000 510 000 15 000 $45.000 SIROOO $270.000 $45.000 Shareholders' Equity NoControllen Interest (Shale of No Comis $5.000 5 100.000 20.000 ISS000 $275.000 SI5.000 Red Earning Total Shareholders guits Total blend Shareholders Equity 45 000 SION SI. Required Refer to the illustrated balance sheet listed above for PA Inc and SUB Ine to answer the Retained Earnings Total Shareholders' Equity Tots Liabilities and Shareholders Equity 20,000 155.000 $275.000 5545.000 SIDO Required: Refer to the illustrated balance sheet listed above for PA Inc. and SUB Inc. to answer the following questions. 1. Define both companies' total assets by drawing a comparative table by reflecting on each category? What can you conclude for such a virtual company? (10 marks) 2. Record the purchase of Sun Inc. by PA (the parent company). (5 marks) 3. Define the Goodwill of a company. Then, calculate the amount of Goodwill implicit in this purchase. (15 marks) 4. What is the consolidated depreciation expense to be reflected in the consolidated Income Statement for 2012 assuming a 10 year depreciation life for property.plant and equipment? (5 marks) 5. Can you calculate the ROE for this acquisition? Start by defining the ROE, listing the formula and its three main components. Then, define what factors are missing and where to find it? (15 marks) Question 3: (50 marks) Case Study: Consolidated Balance Sheet At Date Of Purchase This case study will provide a thorough illustration as to the concepts of consolidations on the date of acquisition. On this date, an ensuing Consolidated Balance Sheet is created, whereby the acquiring and the acquired companies are combined as a single entity. Interestingly, there are options as to the consolidation basis which may be utilized, which also includes the push-down method of accounting. The pushdown method was illustrated in a previous case study and it is highly recommended that the reader resort to this, which can be found in Harris & Dilling (2015). An overview of this critical topic will be discussed, followed by a comprehensive illustration demonstrating the results of consolidated results as of the date of acquisition. Note that the resulting Balance Sheet will be the same with the push-down accounting result. This case study is recommended as a group project for an Advanced Accounting course as well as for a graduate Financial Statement Analysis class Facts: On December 31, 2011, PA Inc. purchased 95 percent of Sub Inc, for $120,000 cash. The Balance Sheet of each corporation just prior to the acquisition is presented below. Additionally, book value and fair value for all of Sub's assets and liabilities are equal, with the exception of Property, Plant and Equipment, whose fair value is $47,000. Table 1. Balance Sched button Help v EvEA AR BI U or A A Table 1. Balance sheet before acquisition Balance Sheet PA Inc. 12/31/2011 SUB Inc. 12/31/2011 Current Assets Accounts receivable (Net) Inventory Total Current Assets $170,000 60,000 50,000 $280,000 $21,000 45,000 45,000 S111,000 265,000 42,000 Fixed Assets Property. Plant, and Equipment (Net of Accumulated Depreciation) Goodwill Total Arts 545.000 133.000 PA Inc. SUB Inc. Pavlic Pa Total Current Lisbilities $70,000 20.000 $90.000 $30,000 15.000 $45.000 S180.000 $270,000 $45.000 of Subsidiary TO) 000 sy, Lurrar LOMICS Neo-Carrear Liabilities Honda Payable Total liabilities $180,000 $270,000 $45,000 Shareholders' Equity Non-Controlling Interest (Share of Subsidiary) Common Stock (55 Par) Paid In Capital Retained Earnings Total Shareholders' Equity Total Liabilities and Shareholder's Equity 100,000 20,000 155,000 $275,000 S545,000 55,000 8,000 45,000 S108,000 S153,000 Required: Refer to the illustrated balance sheet listed above for PA Inc. and SUB Inc. to answer the following questions 1. Define both companies' total assets by drawing a comparative table by reflecting on each category? What can you conclude for such a virtual company? (10 marks) 2. Record the purchase of Sun Inc. by PA (the parent company). (5 marks) 3. Define the Goodwill of a company. Then, calculate the amount of Goodwill implicit in this purchase. (15 marks) 4. What is the consolidated depreciation expense to be reflected in the consolidated Income Statement for 2012 assuming a 10 year depreciation life for property, plant and equipment? (5 marks) 5. Can you calculate the ROE for this acquisition? Start by defining the ROE, listing the formula and its three main components. Then, define what factors are missing and where to find it? (15 marks)

 please questions 1 till 5 as soon as possible.
please questions 1 till 5 as soon as possible.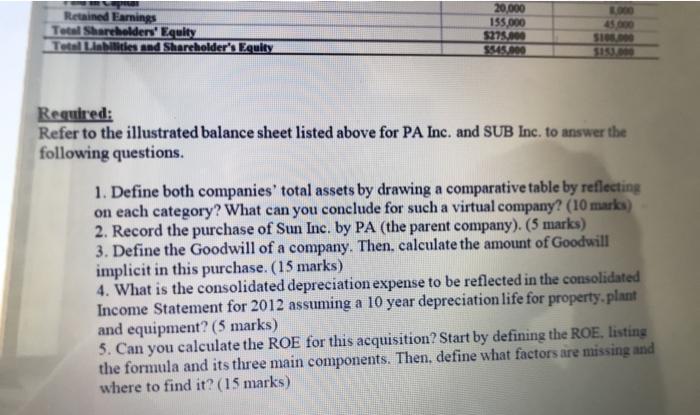
 please as soon as possible thank you
please as soon as possible thank you 





