Question
Please READ THIS FIRST The financial characteristics of companies vary for many reasons. The two most prominent drivers are industry economics and firm strategy. Each
Please READ THIS FIRST
The financial characteristics of companies vary for many reasons. The two most prominent drivers are industry
economics and firm strategy.
Each industry has a financial norm around which companies within the industry tend to operate. An airline,
for example, would naturally be expected to have a high proportion of fixed assets (airplanes), while a consulting
firm would not. A steel manufacturer would be expected to have a lower gross margin than a pharmaceutical
manufacturer because commodities such as steel are subject to strong price competition, while highly
differentiated products like patented drugs enjoy much more pricing freedom. Because of each industrys
unique economic features, average financial statements will vary from one industry to the next.
Similarly, companies within industries have different financial characteristics, in part because of the diverse
strategies that can be employed. Executives choose strategies that will position their company favorably in the
competitive jockeying within an industry. Strategies typically entail making important choices in how a product
is made (e.g., capital intensive versus labor intensive), how it is marketed (e.g., direct sales versus the use of
distributors), and how the company is financed (e.g., the use of debt or equity). Strategies among companies in
the same industry can differ dramatically. Different strategies can produce striking differences in financial results
for firms in the same industry.
The following paragraphs describe pairs of participants in a number of different industries. Their strategies
and market niches provide clues as to the financial condition and performance that one would expect of them.
The companies common-sized financial statements and operating data, as of early 2016, are presented in a
standardized format in Exhibit 1. It is up to you to match the financial data with the company descriptions.
Also, try to explain the differences in financial results across industries.
Airlines
Companies A and B are airline companies. One firm is a major airline that flies both domestically and
internationally and offers additional services including travel packages and airplane repair. The company owns
a refinery to supply its own jet fuel as a hedge to fuel-price volatility. In 2008, this company merged with one
of the largest airline carriers in the United States.
The other company operates primarily in the United States, with some routes to the Caribbean and Latin
America. It is the leading low-cost carrier in the United States. One source of operating efficiency is the fact
that the company carries only three different aircraft in its fleet, making maintenance much simpler than for
legacy airlines that might need to service 20 or 30 different aircraft models. This companys growth has been
mostly organicit expands its routes by purchasing new aircraft and the rights to fly into new airports.
Beer
Of the beer companies, C and D, one is a national brewer of mass-market consumer beers sold under a
variety of brand names. This company operates an extensive network of breweries and distribution systems.
The firm also owns a number of beer-related businessessuch as snack-food and aluminum-container
manufacturing companiesand several major theme parks. Over the past 12 years, it has acquired several large
brewers from around the globe.
The other company is the largest craft brewer in the United States. Like most craft brewers, this company
produces higher-quality beers than the mass-market brands, but production is at a lower volume and the beers
carry premium prices. The firm is financially conservative.
Computers
Companies E and F sell computers and related equipment. One company sells high-performance
computing systems (supercomputers) to government agencies, universities, and commercial businesses. It
has experienced considerable growth due to an increasing customer base. The company is financially
conservative.
The other company sells personal computers as well as handheld devices and software. The firm has been
able to differentiate itself by using its own operating system for its computers and by creating new and
innovative designs for all its products. These products carry premium prices domestically and globally. The
company follows a vertical integration strategy starting with owning chip manufacturers and ending with
owning its own retail stores.
Hospitality
Companies G and H are both in the hospitality business. One company operates hotels and residential
complexes. Rather than owning the hotels, this firm chooses to manage or franchise its hotels. The company
receives its revenues each month based on long-term contracts with the hotel owners, who pay a percentage of
the hotel revenues as a management fee or franchise fee. Much of this companys growth is inorganicthe
company buys the rights to manage existing hotel chains and also the rights to use the hotels brand name. This
company has also pursued a strategy of repurchasing a significant percentage of the shares of its own common
stock.
The other company owns and operates several chains of upscale, full-service hotels and resorts. The firms
strategy is to maintain market presence by owning all of its properties, which contributes to the high recognition
of its industry-leading brands.
Newspapers
Companies I and J are newspaper companies. One company owns and operates two newspapers in the
southwestern United States. Due to the transition of customer preference from print to digital, the company
has begun offering marketing and digital-advertising services and acquiring firms in more profitable industries.
The company has introduced cost controls to address cost-structure issues such as personnel expenses.
Founded in 1851, the other company is renowned for its highly circulated newspaper offered both in print
and online formats. This paper is sold and distributed domestically as well as around the world. Because the
company is focused largely on one product, it has strong central controls that have allowed it to remain
profitable despite the fierce competition for subscribers and advertising revenues.
Pharmaceuticals
Companies K and L manufacture and market pharmaceuticals. One firm is a diversified company that sells
both human pharmaceuticals as well as health products for animals. This companys strategy is to stay ahead of
the competition by investing in the discovery and development of new and innovative drugs.
The other company focuses on generic pharmaceuticals and medical devices. Most of this companys
growth has been inorganicthe growth strategy has been to engage in highly leveraged acquisitions, and it has
participated in more than 100 during the past eight years. The goal of acquiring new businesses is to enhance
the value of the proven drugs in the companys portfolio rather than gamble on discoveries of new drugs for
the future.
Power
Companies M and N are in the power-generation industry. One company focuses on solar power. This
includes the manufacturing and selling of power systems as well as maintenance services for those systems.
The other company owns large, mostly coal-powered electric-power-generation plants in countries around
the world. Most of its revenues result from power-purchase agreements with a countrys government that buy
the power generated. Some of its U.S. assets include regulated public utilities.
Retail
Companies O and P are retailers. One is a leading e-commerce company that sells a broad range of
products, including media (books, music, and videos) and electronics, which together account for 92% of
revenues. One-third of revenues are international and 20% of sales come from third-party sellers (i.e., sellers
who transact through the companys website to sell their own products rather than those owned by the
company). A growing portion of operating profit comes from the companys cloud-computing business. With
its desire to focus on customer satisfaction, this company has invested considerably in improving its online
technologies.
The other company is a leading retailer in apparel and fashion accessories for men, women, and children.
The company sells mostly through its upscale brick-and-mortar department stores
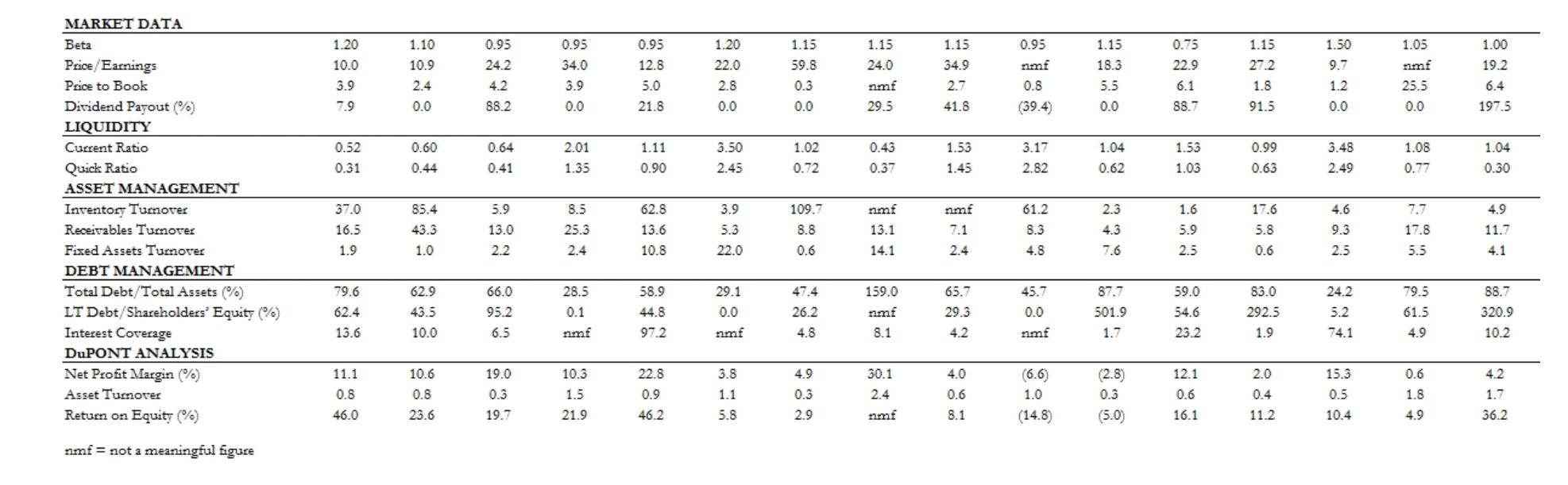

AFTER YOU READING Please fill the table
Review the Financial data for the various Industries in the Case Study. Identify the respective companies as described. Identify and explain the Key Ratio observations for each of the companies : (20 MARKS)
|
|
| OBSERVATIONS | OBSERVATIONS |
|
| AIRLINES
| COMPANY A: _____________
* * *
| COMPANY B: ________________ * * *
|
|
| COMPUTERS
| COMPANY E: _____________
* * *
| COMPANY F: _____________ * * *
|
|
| NEWSPAPERS
| COMPANY I: _____________
* * *
| COMPANY J: _____________ * * *
|
|
| POWER
| COMPANY M: _____________ * * * | COMPANY N: _____________ * * * |
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


