Question: Please really need help with this java code! Thank you ' HERE IS A LINK WHERE YOU CAN FIND THE STD.JAR LIBRARIES. ITS UNDER THE
Please really need help with this java code! Thank you
'

HERE IS A LINK WHERE YOU CAN FIND THE STD.JAR LIBRARIES. ITS UNDER THE NAME 'Linux-based Virtual Machine' AND SAYS IO LIBRARIES.
https://www.swamiiyer.net/cs210/course_info.html
CODE TEMPLATE
package edu.umb.cs210.p2; import stdlib.StdOut; import stdlib.StdRandom; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.NoSuchElementException; // Deque implementation using a linked list. public class LinkedDeque- implements Iterable
- { ... // Helper doubly-linked list class. private class Node { private Item item; // This Node's value private Node next; // The next Node private Node prev; // The previous Node } // Construct an empty deque. public LinkedDeque() { f... } // Is the deque empty? public boolean isEmpty() { ... } // The number of items on the deque. public int size() { ... } // Add item to the front of the deque. public void addFirst(Item item) { ... } // Add item to the end of the deque. public void addLast(Item item) { ... } // Remove and return item from the front of the deque. public Item removeFirst() { ... } // Remove and return item from the end of the deque. public Item removeLast() { ... } // An iterator over items in the queue in order from front to end. public Iterator
- iterator() { ... } // An iterator, doesn't implement remove() since it's optional. private class DequeIterator implements Iterator
- { ... // DequeIterator constructor DequeIterator() { ... } public boolean hasNext() { ... } public void remove() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } public Item next() { ... } } // A string representation of the deque. public String toString() { StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(); for (Item item : this) { s.append(item + " "); } if (s.length() deque = new LinkedDeque
(); String quote = "There is grandeur in this view of life, with its " + "several powers, having been originally breathed into a few " + "forms or into one; and that, whilst this planet has gone " + "cycling on according to the fixed law of gravity, from so " + "simple a beginning endless forms most beautiful and most " + "wonderful have been, and are being, evolved. ~ " + "Charles Darwin, The Origin of Species"; int r = StdRandom.uniform(0, quote.length()); for (int i = quote.substring(0, r).length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { deque.addFirst(quote.charAt(i)); } for (int i = 0; i Problem 1. (Deque) Create a generic iterable data type LinkedDeque - that uses a linked list to implement the following deque API: Method LinkedDeque () boolean isEmpty() int size void addFirst (Item item) void addLast(Item item) Description constructs an empty deque returns true if the deque empty, and false otherwise returns the number of items on the deque adds item to the front of the deque adds item to the end of the deque removes and returns the item from the front of the deque removes and returns the item from the end of the deque returns an iterator over items in the deque in order from front to end returns a string representation of the deque It em removeFirst() Item removeLast() Iterator
- iterator) String toString() Hints ** Use a doubly-linked list Node to implement the API, where each node stores a generic item, and pointers next and prev to the next and previous nodes first last nullitem 17 . tem 2 . em. 2 . items mull Problems ** Instance variables my Size of the deque, int n ~ Pointer to the head of the deque, Node first w Pointer to the tail of the deque, Node last LinkedDeque) my Initialize instance variables to appropriate values > boolean is Empty + Return whether the deque is empty or not m int size) my Return the size of the deque void addFirst (Item item) my Add the given item at the head end of the deque * Increment n by one > void addLast (Item item) my Add the given item at the tail end of the deque my Increment n by one Item removeFirst my Remove and return the item at the head end of the deque my Decrement n by one My Item removeLast() M Remove and return the item at the tail end of the deque my Decrement n by one Iterator
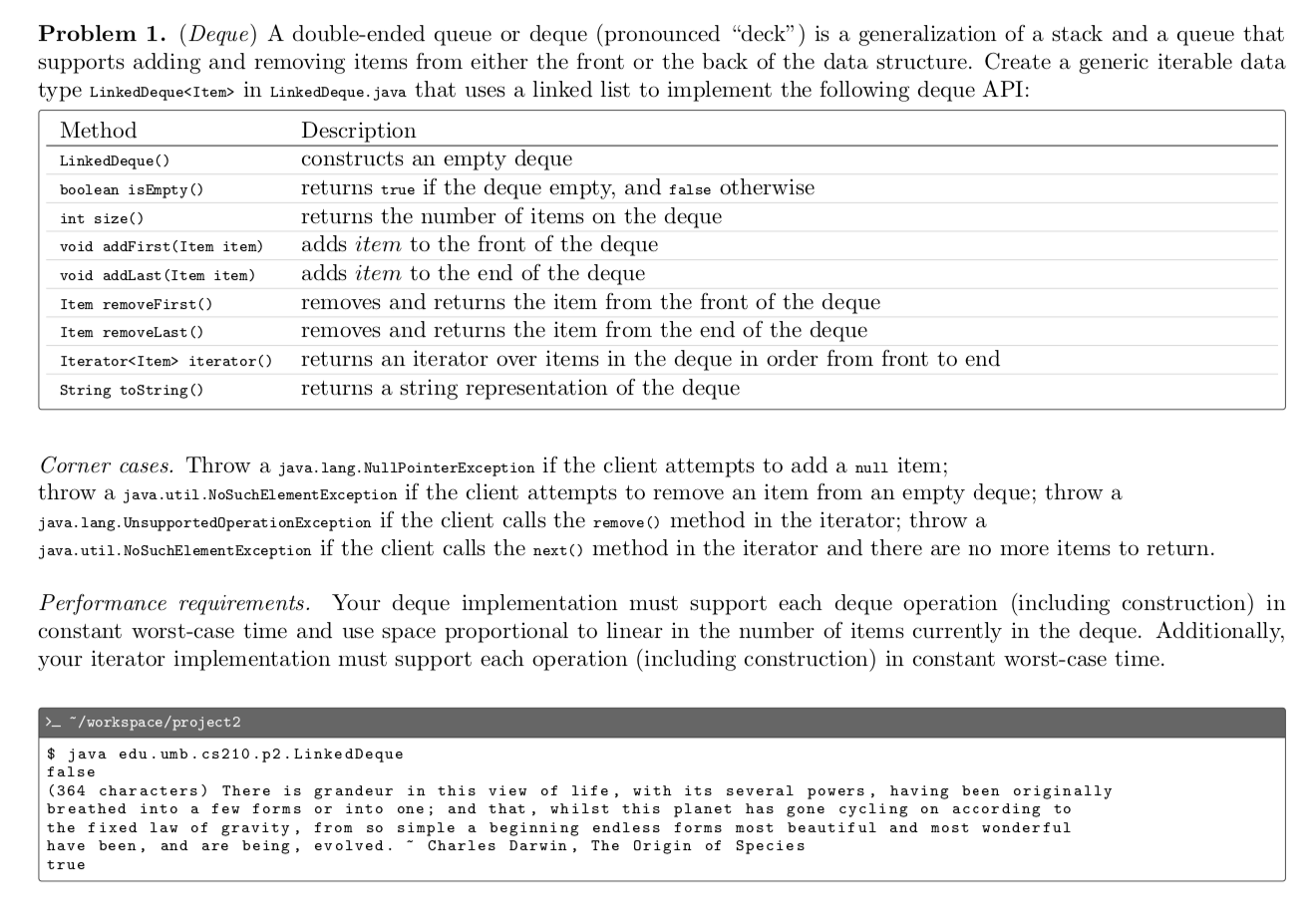
- iterator() Return an object of type DequeIterator DequeIterator : Instance variable Pointer to current node in the iterator, Node current DequeIterator : Deque Iterator() my Initialize instance variable appropriately DequeIterator :: boolean has Next() my Return whether the iterator has more items to iterate or not DequeIterator :: Item next() Return the item in current and advance current to the next node Problem 1. (Deque) A double-ended queue or deque (pronounced "deck) is a generalization of a stack and a queue that supports adding and removing items from either the front or the back of the data structure. Create a generic iterable data type LinkedDeque
- in LinkedDeque.java that uses a linked list to implement the following deque API: Method LinkedDeque() boolean is Empty() int size() void addFirst(Item item) Description constructs an empty deque returns true if the deque empty, and false otherwise returns the number of items on the deque adds item to the front of the deque adds item to the end of the deque removes and returns the item from the front of the deque removes and returns the item from the end of the deque returns an iterator over items in the deque in order from front to end returns a string representation of the deque void addLast (Item item) Item removeFirst() Item removeLast() Iterator
- iterator() String toString() Corner cases. Throw a java.lang.NullPointerException if the client attempts to add a null item; throw a java.util.NoSuchElement Exception if the client attempts to remove an item from an empty deque; throw a java.lang. UnsupportedOperationException if the client calls the remove() method in the iterator; throw a java.util. NoSuchElementException if the client calls the next() method in the iterator and there are no more items to return. Performance requirements. Your deque implementation must support each deque operation (including construction) in constant worst-case time and use space proportional to linear in the number of items currently in the deque. Additionally, your iterator implementation must support each operation (including construction in constant worst-case time. >_*/workspace/project2 $ java edu . umb. cs210.p2.LinkedDeque false (364 characters) There is grandeur in this view of life, with its several powers, having been originally breathed into a few forms or into one; and that, whilst this planet has gone cycling on according to the fixed law of gravity, from so simple a beginning endless forms most beautiful and most wonderful have been, and are being, evolved. - Charles Darwin, The Origin of Species true Problem 1. (Deque) Create a generic iterable data type LinkedDeque
- that uses a linked list to implement the following deque API: Method LinkedDeque () boolean isEmpty() int size void addFirst (Item item) void addLast(Item item) Description constructs an empty deque returns true if the deque empty, and false otherwise returns the number of items on the deque adds item to the front of the deque adds item to the end of the deque removes and returns the item from the front of the deque removes and returns the item from the end of the deque returns an iterator over items in the deque in order from front to end returns a string representation of the deque It em removeFirst() Item removeLast() Iterator
- iterator) String toString() Hints ** Use a doubly-linked list Node to implement the API, where each node stores a generic item, and pointers next and prev to the next and previous nodes first last nullitem 17 . tem 2 . em. 2 . items mull Problems ** Instance variables my Size of the deque, int n ~ Pointer to the head of the deque, Node first w Pointer to the tail of the deque, Node last LinkedDeque) my Initialize instance variables to appropriate values > boolean is Empty + Return whether the deque is empty or not m int size) my Return the size of the deque void addFirst (Item item) my Add the given item at the head end of the deque * Increment n by one > void addLast (Item item) my Add the given item at the tail end of the deque my Increment n by one Item removeFirst my Remove and return the item at the head end of the deque my Decrement n by one My Item removeLast() M Remove and return the item at the tail end of the deque my Decrement n by one Iterator
- iterator() Return an object of type DequeIterator DequeIterator : Instance variable Pointer to current node in the iterator, Node current DequeIterator : Deque Iterator() my Initialize instance variable appropriately DequeIterator :: boolean has Next() my Return whether the iterator has more items to iterate or not DequeIterator :: Item next() Return the item in current and advance current to the next node Problem 1. (Deque) A double-ended queue or deque (pronounced "deck) is a generalization of a stack and a queue that supports adding and removing items from either the front or the back of the data structure. Create a generic iterable data type LinkedDeque
- in LinkedDeque.java that uses a linked list to implement the following deque API: Method LinkedDeque() boolean is Empty() int size() void addFirst(Item item) Description constructs an empty deque returns true if the deque empty, and false otherwise returns the number of items on the deque adds item to the front of the deque adds item to the end of the deque removes and returns the item from the front of the deque removes and returns the item from the end of the deque returns an iterator over items in the deque in order from front to end returns a string representation of the deque void addLast (Item item) Item removeFirst() Item removeLast() Iterator
- iterator() String toString() Corner cases. Throw a java.lang.NullPointerException if the client attempts to add a null item; throw a java.util.NoSuchElement Exception if the client attempts to remove an item from an empty deque; throw a java.lang. UnsupportedOperationException if the client calls the remove() method in the iterator; throw a java.util. NoSuchElementException if the client calls the next() method in the iterator and there are no more items to return. Performance requirements. Your deque implementation must support each deque operation (including construction) in constant worst-case time and use space proportional to linear in the number of items currently in the deque. Additionally, your iterator implementation must support each operation (including construction in constant worst-case time. >_*/workspace/project2 $ java edu . umb. cs210.p2.LinkedDeque false (364 characters) There is grandeur in this view of life, with its several powers, having been originally breathed into a few forms or into one; and that, whilst this planet has gone cycling on according to the fixed law of gravity, from so simple a beginning endless forms most beautiful and most wonderful have been, and are being, evolved. - Charles Darwin, The Origin of Species true
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


