
 Please show all work in a readable manner thanks for your time in advance.
Please show all work in a readable manner thanks for your time in advance.
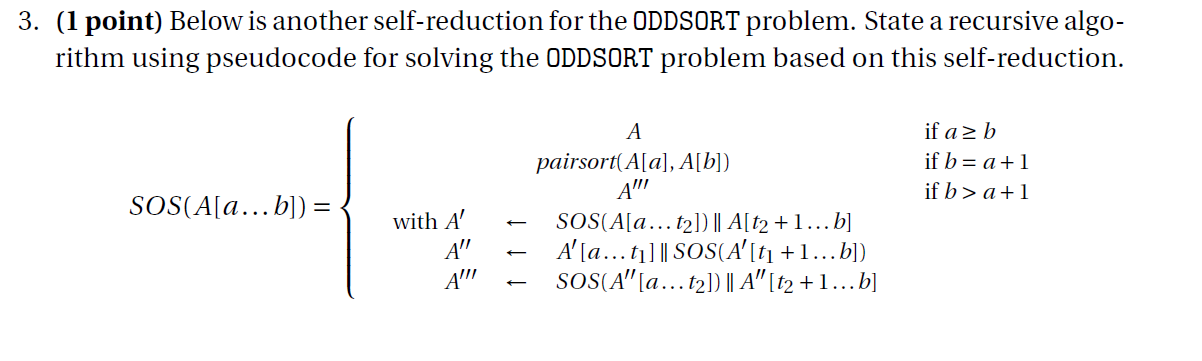
. a || denotes the concatenation of lists a and B (in this order); denotes the empty string; . len(s) > 0 denotes the length (number of characters) on string s; minx(A[a ... b]) denotes the index (in range [a ... b]) of the minimum odd element from list A[a... b]; t = a +[(b-a)/3] and t2 = b-[(b-a)/37 denote the indices at one third and two thirds the way from a to b, respectively; pairsort(X,Y) denotes either Y || X (if X and Y are both odd and X > Y) or X || Y (other- wise). Consider the problem of sorting the odd elements in a list of integers while keeping the even ones unchanged in their original places. Sort the odd elements in a list (ODDSORT) Input: A[1...n] a list of integers. Output: List A[1... N] such that A[i] = A[i] if A[i] is even, and A[i] S A[j] for all 1 sis jsn such that A[i] and A[j] are both odd. 3. (1 point) Below is another self-reduction for the ODDSORT problem. State a recursive algo- rithm using pseudocode for solving the ODDSORT problem based on this self-reduction. if a 2b if b= a +1 if b > a+1 SOS(A[a... b]) = with A pairsort(A[a], A[b]) A" SOS(A[a ... t2] || A[t2 +1... b] A [a ... t1] || SOS(A'[t +1... b]) SOS(A (a ... t2]) || A" [t2 +1... b] A' A'NI 4. (2+2 points) Using the same reduction as in the previous question, state a recurrence T'(n) that expresses the worst case running time of the recursive algorithm. From this recurrence, find a tight (Big-Theta) expression for T'(n). Hint: the Master Theorem may be the easiest solution here. . a || denotes the concatenation of lists a and B (in this order); denotes the empty string; . len(s) > 0 denotes the length (number of characters) on string s; minx(A[a ... b]) denotes the index (in range [a ... b]) of the minimum odd element from list A[a... b]; t = a +[(b-a)/3] and t2 = b-[(b-a)/37 denote the indices at one third and two thirds the way from a to b, respectively; pairsort(X,Y) denotes either Y || X (if X and Y are both odd and X > Y) or X || Y (other- wise). Consider the problem of sorting the odd elements in a list of integers while keeping the even ones unchanged in their original places. Sort the odd elements in a list (ODDSORT) Input: A[1...n] a list of integers. Output: List A[1... N] such that A[i] = A[i] if A[i] is even, and A[i] S A[j] for all 1 sis jsn such that A[i] and A[j] are both odd. 3. (1 point) Below is another self-reduction for the ODDSORT problem. State a recursive algo- rithm using pseudocode for solving the ODDSORT problem based on this self-reduction. if a 2b if b= a +1 if b > a+1 SOS(A[a... b]) = with A pairsort(A[a], A[b]) A" SOS(A[a ... t2] || A[t2 +1... b] A [a ... t1] || SOS(A'[t +1... b]) SOS(A (a ... t2]) || A" [t2 +1... b] A' A'NI 4. (2+2 points) Using the same reduction as in the previous question, state a recurrence T'(n) that expresses the worst case running time of the recursive algorithm. From this recurrence, find a tight (Big-Theta) expression for T'(n). Hint: the Master Theorem may be the easiest solution here


 Please show all work in a readable manner thanks for your time in advance.
Please show all work in a readable manner thanks for your time in advance. 





