please show calculations
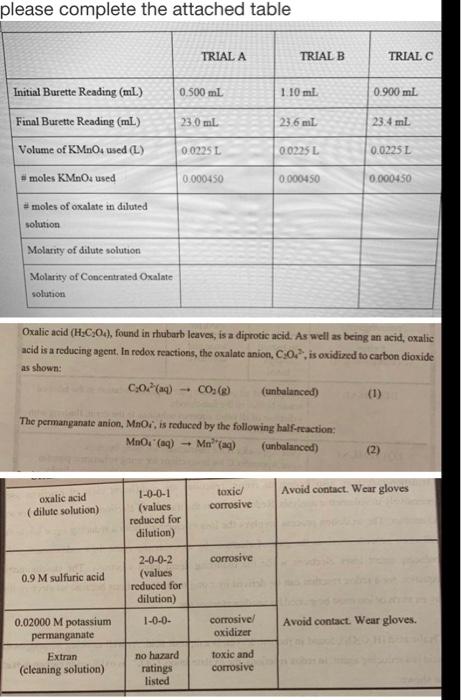
please complete the attached table TRIAL A TRIAL B TRIAL C Initial Burette Reading (ml) 0.500 ml 1.10 ml 0.900 ml. Final Burette Reading (mL) 23.0 ml 23.6 ml 23.4 ml Volume of KMnOs used (L) 0.0225L 00225L 0.0235 L 0.000450 0.000450 0.000450 moles KMnOs used #moles of oxalate in diluted solution Molarity of dilute solution Molarity of Concentrated Oxalate solution Oxalic acid (H2C_04), found in rhubarb leaves, is a diprotic acid. As well as being an acide oxalic acid is a reducing agent. In redox reactions, the oxalate anion, C 0.2, is oxidized to carbon dioxide as shown: 0,02(aq) -- CO. (unbalanced) (1) The permanganate anion, MnO, is reduced by the following half-reaction: MnO'(aq) - Mn"(aq) (unbalanced (2) toxic Avoid contact. Wear gloves axalic acid (dilute solution) corrosive 1-0-0-1 (values reduced for dilution) corrosive 0.9 M sulfuric acid 2-0-0-2 (values reduced for dilution) 1-0-0- corrosive/ oxidizer Avoid contact. Wear gloves. 0.02000 M potassium permanganate Extran (cleaning solution) no hazard ratings listed toxic and Corrosive 8:55 Given pongue skepo: Balance the other atoms tacept od # Sa (01) 2019 stero Balance the 'o' stoms Add hyp melecules 'o' deficient side. Add fem, deficient side Sa (01) 209 (9) Balance the elections had e's election deliciods sac) 249( AR This is belmeel exurlion mai (4) Selo: Balance He o atoms Add yo moleculer o deficet side MO (6) Mego shee Add thions, i deficient de tra, (a + 8 M (44) (et) + 40W shee @bdence the elections. Add e's, electrodeficient side. Mnd (1) +84 (+ 5 Meny + kolley This is belanced etuation you want and both equalize election, (xs) + (x3) To cg (1) + 10 2 m, () + 16 (1) + e. - - (+8406) ssa (et) + 2 1990, tet) + 16 (0) JOCS (9) 2015) Click on the oxalic acid bottle and use the arrow keys on your keyboard to draw up 25.00 mL of solution Click on the pipette and add the oxalic acid to the volumetric flask Repeat the previous two steps to add an additional 25.00 mL of oxalic acid to the volumetric flask Click on the deionized water bottle to fill the volumetric flask to the graduation Click on the volumetric flask and shake it Click on the pipette to draw up 25.00 mL of the dilute oxalic acid solution Click on the pipette to add the solution to the Erlenmeyer Click on the H.SO, bottle and use the arrow keys on your keyboard to adjust the volume in the beaker to 60 ml Click on the beaker to add the sulfuric acid to the Erlenmeyer flask Click on the Erlenmeyer to move it to the hot plate Click on the Erlenmeyer and choose to add the thermometer to the solution Tum on the hot plate by clicking the red button on the left - Heat the sample to a temperature of 60C Click on the Erlenmeyer flask to move it to stir plate under the burette Click on the KMnO bottle to add the potassium permanganate to the burette Click on the burette to record the initial volume Use the arrow keys on your keyboard to add a few drops of KMnOs into the Erlenmeyer flask from the burette. At this point, the colour will change and will require roughly 30 minutes of stirring before it returns clear. DO NOT add additional KMnO until it clears up or you will have to re-start Once the solution goes back to clear, continue the titration until you obtain a permanent purple colour Click on the burette to zoom in and read the final volume. Continue adding KMnO2 until the solution in the Erlenmeyer flask consistently remains a purple colour Titration is complete Repeat this entire procedure until you obtain two titrations within 0.1 mL of each other










