Please show in similar format. Thank you!

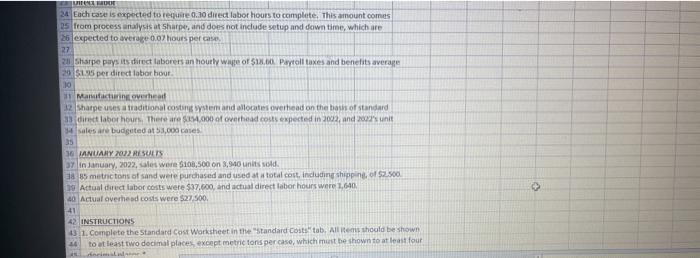
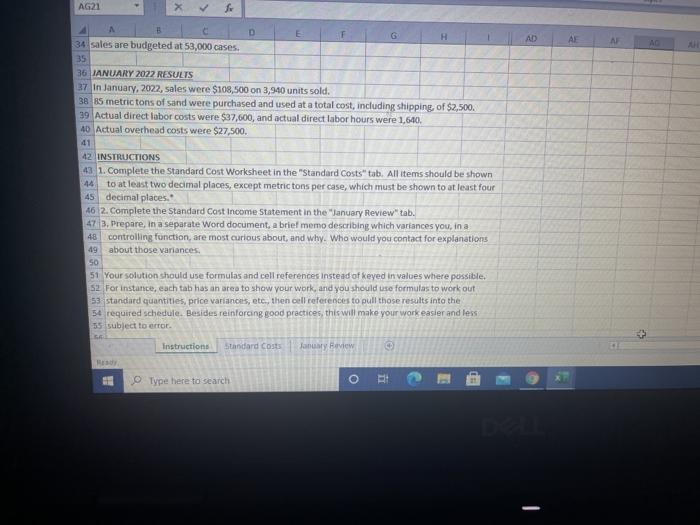
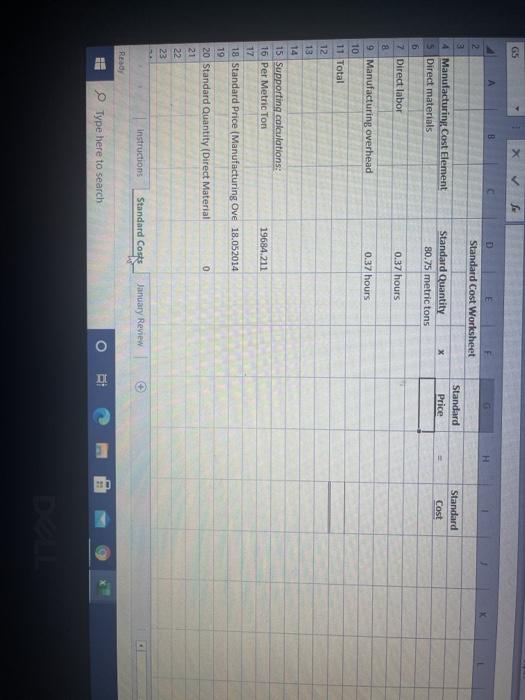
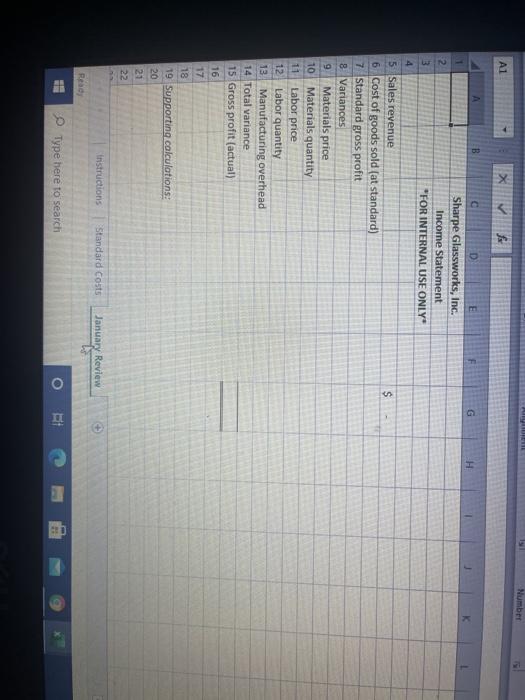
7 You work in the corporate controller's office for Sharpe Glassworks, Inc. Sharpe manufactures 12 Bounce beer bottles for smaller breweries who lack the scale or vertical integration to make their own. The bottles are sold to brewers by the case, at prices generally tanging between $25 and $28 10 per case, and there are 100 bottles to a case 11 12 STANDARD COSTING 13. Direct materials 14 Sand makes up about 85% of the weight of the finished product, and is the only material 15 treated as a direct material. All other materials are treated as indirect, and thus part of 16 manufacturing overhead. There are 18.700 grams of sand in one finished goods unit (case). 17 but not all sand purchased makes it into the finished product. Waste and scrap in the normal 10 manufacturing process results in approximately 5% of the sand purchased being lost 19 20 Sand is purchased by the metric ton (one million grams. The cost from Sharpe's main 3 supplier h $9.95 per metric ton, shipped locally at a cost to Shape of 517.rper matricton. 23 Direct labor 24 Each case is expected to requue 0.30 direct labor hours to complete. This amount comes 25 from process analysis at Sharpe, and does not include setup and down time, which are 26 expected to average 0.07 hours percise EUR 24 Each case is expected to reuse 0.10 direct labor hours to complete. This amount comes 05 from process analysis at Sharpe, and does not include setup and down time, which are 26 expected to average 0.02 hours per case 27 2 Sharpe pays its direct laborers an hourly we of $12.00 Payroll taxes and benefits average 20 $0.95 per direct labor hour 10 11 March 32 Sharpe uses a traditional costing system and allocates overhead on the basis of standard 33 direct labor hours. There are $144,000 of overhead costs expected in 2002, and unit 4 sales are budgeted at 53.000 cases 35 36 IANUARY RESULTS in January, 2022, les were $10.500 on 3,940 units sold 38 85 mettons of sand were purchased and used a total cost indluding shipping, of 2.500 19 Actual direct labor costs were $37.000, and actual direct labor hours were 1,640 40 Actual overhead costs were $27.500. 42. INSTRUCTIONS 13.1. Complete the Standard Cost Worksheet in the standard Coststab, All items should be shown 1 to at least two decimal places, exopt metric tons per caso, which must be shown to at least four AG21 f AD AE AB A 34 sales are budgeted at 53,000 cases. 35 36. JANUARY 2022 RESULTS 37 in January, 2022, sales were $108,500 on 3,940 units sold. 38 85 metric tons of sand were purchased and used at a total cost, including shipping, of $2,500. 39 Actual direct labor costs were $37,600, and actual direct labor hours were 1,640 40 Actual overhead costs were $27,500 41 42 INSTRUCTIONS 43 1. Complete the Standard Cost Worksheet in the "Standard Costs" tab. All items should be shown to at least two decimal places, except metric tons per case, which must be shown to at least four 45 decimal places. A6 2. Complete the Standard Cost Income Statement in the "January Review"tab 47 3. Prepare, in a separate Word document, a brief memo describing which variances you, in a 48 controlling function, are most curious about, and why. Who would you contact for explanations 49 about those variances 50 51 Your solution should use formulas and cell references instead of keyed in values where possible. 52 For instance, each tab has an area to show your work, and you should use formulas to work out 53 Standard quantities, price variances, etc., then cell references to pull those results into the 54 required schedule. Besides reinforcing good practices, this will make your work easier and less 55 subject to error Instructions Standard Costs January Review BE Type here to search O H D Standard Cost Worksheet 2 3 4 Manufacturing Cost Element 5 Direct materials Standard x Standard Quantity 80.75 metric tons Price Standard Cost 0.37 hours 0.37 hours 7 Direct labor 8 9 Manufacturing overhead 10 11 Total 12 13 14 15 Supporting calculations: 15 Per Metric Ton 19684.211 17 18 Standard Price (Manufacturing Ove 18.052014 19 20 Standard Quantity (Direct Material 0 21 22 23 instructions Standard Costs January Review Read Type here to search DE Number A1 G H K $ B D E 1 Sharpe Glassworks, Inc. 2 Income Statement 3 "FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY 4 5 Sales revenue 6. Cost of goods sold (at standard) 7 Standard gross profit 8 Variances 9 Materials price 10 Materials quantity 11 Labor price 12 Labor quantity 13. Manufacturing overhead 14 Total variance 15 Gross profit (actual) 16 17 18 19 Supporting calculations: 20 21 22 tristructions Standard Costs January Review Ready Type here to search RI 7 You work in the corporate controller's office for Sharpe Glassworks, Inc. Sharpe manufactures 12 Bounce beer bottles for smaller breweries who lack the scale or vertical integration to make their own. The bottles are sold to brewers by the case, at prices generally tanging between $25 and $28 10 per case, and there are 100 bottles to a case 11 12 STANDARD COSTING 13. Direct materials 14 Sand makes up about 85% of the weight of the finished product, and is the only material 15 treated as a direct material. All other materials are treated as indirect, and thus part of 16 manufacturing overhead. There are 18.700 grams of sand in one finished goods unit (case). 17 but not all sand purchased makes it into the finished product. Waste and scrap in the normal 10 manufacturing process results in approximately 5% of the sand purchased being lost 19 20 Sand is purchased by the metric ton (one million grams. The cost from Sharpe's main 3 supplier h $9.95 per metric ton, shipped locally at a cost to Shape of 517.rper matricton. 23 Direct labor 24 Each case is expected to requue 0.30 direct labor hours to complete. This amount comes 25 from process analysis at Sharpe, and does not include setup and down time, which are 26 expected to average 0.07 hours percise EUR 24 Each case is expected to reuse 0.10 direct labor hours to complete. This amount comes 05 from process analysis at Sharpe, and does not include setup and down time, which are 26 expected to average 0.02 hours per case 27 2 Sharpe pays its direct laborers an hourly we of $12.00 Payroll taxes and benefits average 20 $0.95 per direct labor hour 10 11 March 32 Sharpe uses a traditional costing system and allocates overhead on the basis of standard 33 direct labor hours. There are $144,000 of overhead costs expected in 2002, and unit 4 sales are budgeted at 53.000 cases 35 36 IANUARY RESULTS in January, 2022, les were $10.500 on 3,940 units sold 38 85 mettons of sand were purchased and used a total cost indluding shipping, of 2.500 19 Actual direct labor costs were $37.000, and actual direct labor hours were 1,640 40 Actual overhead costs were $27.500. 42. INSTRUCTIONS 13.1. Complete the Standard Cost Worksheet in the standard Coststab, All items should be shown 1 to at least two decimal places, exopt metric tons per caso, which must be shown to at least four AG21 f AD AE AB A 34 sales are budgeted at 53,000 cases. 35 36. JANUARY 2022 RESULTS 37 in January, 2022, sales were $108,500 on 3,940 units sold. 38 85 metric tons of sand were purchased and used at a total cost, including shipping, of $2,500. 39 Actual direct labor costs were $37,600, and actual direct labor hours were 1,640 40 Actual overhead costs were $27,500 41 42 INSTRUCTIONS 43 1. Complete the Standard Cost Worksheet in the "Standard Costs" tab. All items should be shown to at least two decimal places, except metric tons per case, which must be shown to at least four 45 decimal places. A6 2. Complete the Standard Cost Income Statement in the "January Review"tab 47 3. Prepare, in a separate Word document, a brief memo describing which variances you, in a 48 controlling function, are most curious about, and why. Who would you contact for explanations 49 about those variances 50 51 Your solution should use formulas and cell references instead of keyed in values where possible. 52 For instance, each tab has an area to show your work, and you should use formulas to work out 53 Standard quantities, price variances, etc., then cell references to pull those results into the 54 required schedule. Besides reinforcing good practices, this will make your work easier and less 55 subject to error Instructions Standard Costs January Review BE Type here to search O H D Standard Cost Worksheet 2 3 4 Manufacturing Cost Element 5 Direct materials Standard x Standard Quantity 80.75 metric tons Price Standard Cost 0.37 hours 0.37 hours 7 Direct labor 8 9 Manufacturing overhead 10 11 Total 12 13 14 15 Supporting calculations: 15 Per Metric Ton 19684.211 17 18 Standard Price (Manufacturing Ove 18.052014 19 20 Standard Quantity (Direct Material 0 21 22 23 instructions Standard Costs January Review Read Type here to search DE Number A1 G H K $ B D E 1 Sharpe Glassworks, Inc. 2 Income Statement 3 "FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY 4 5 Sales revenue 6. Cost of goods sold (at standard) 7 Standard gross profit 8 Variances 9 Materials price 10 Materials quantity 11 Labor price 12 Labor quantity 13. Manufacturing overhead 14 Total variance 15 Gross profit (actual) 16 17 18 19 Supporting calculations: 20 21 22 tristructions Standard Costs January Review Ready Type here to search RI