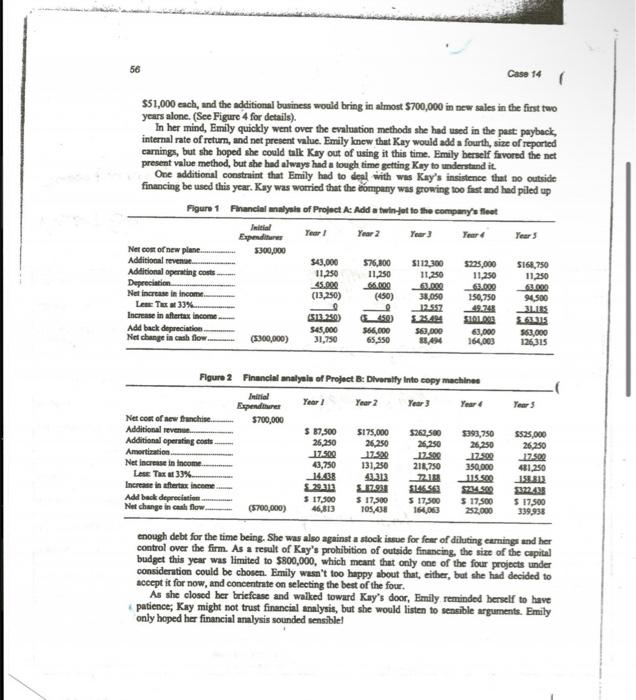
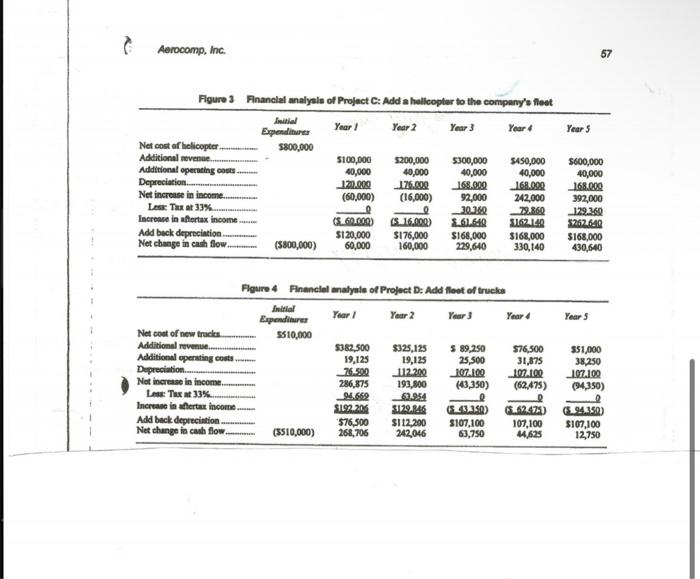
Please solve questions 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 on the last page. Thank you!

Aerocomp, Inc. As whe beadad soward her boss's office, Fmily Hamilton, ehief opernting officer for the Aerocomp CopporitionA. A proponal ot add a jet ob the conpeter services frm that opocialized in wirbome wupport-wiabed she could eomptay's ficet. The pinne wat only tict year old asd wat eonsidered a remember more of her thainisg in sood bey at 5300,000 . In retum, the financial theory that she had been plane woeld bring over 5600,000 in exposed to in colloge. Emily had just additional revenoe during the pert five completed sammarizaing the finuncial yews with oely about 556,000 in openting eontr. (See Figure 1 for projects that were open to Aeroconp during the coming year, and ahe wus B. A proposal to liveraity into copy faced with the tatik of rooommending machines. The finchise wat to eont which thould be seloctod. Whit 5700,000 , shich would be amortized concemed ber was the knowiledge that over a 40-year period. The new ber bos, Kay Manth, a "ntreet imert" chief executive, with no background in buiness wa expected to genernte over 51.4 million in tales over the nert five financial theory, would immediately yeers, end over $800,000 in aftertar favor the project that promised the C. emingn. (Soe Figare 2 for details.) highest gain in reported net ineoce. Emily luow that melectiag projocts parely. on that basis would be incorroct, bout she Wam't aure of her ability to esevince Kay, who tended to asuane finmeiern thought up fincy methods just to show how smart they were, As ahe prepared to enter Kxy's office, Emily polled her summary sheets from ber briefcase and quickly reviewed the details of the four projects, all of which sbe considered to be equally risky. D. A propoeal to begin operating a fleet of truck. Ten oould be bought for aely \$51,000 each, and the additional business would bring in almost $700,000 in ncw sales in the first two years alone. (See Figure 4 for details). In her mind, Emily quickly went over the evaluation methods she had used in the paet paybeck, internal rate of return, and net present value. Emily lonew that Kay would add a fourth, size of reported carnings, but she hoped sbe coald tall Kay out of using it this time. Emily berself fivored the net present value method, but ahe had always had a tough time getting Kry to understand it. One additional constraint that Emily had to deal with wes Kay's insistence that po outside financing be used this year. Kay was worried that the eompany was growing too fast and had piled up Figure 1 Fhancial malyain of Project Ac Add a twin-tot to the company's fleet enough debt for the time being. She was also against a stock issue for fenr of diluting earningr and her control over the firm. As a result of Kay's prohibition of outside financing, the size of the cupital budget this year was limited to $800,000, which meant that only one of the four projects under consideration could be ebosen. Emily wasn't too happy about that, either, but she had decided to aceept it for now, and concentrnte on selecting the best of the four. As she elosod ber briefcase and waiked toward Kay's door. Emily reminded berself to have patience, Kay might not trust financial analysis, but she would listen to sensible arguments. Emily only hoped her financial amalysis sounded sensiblel Aerocomp, inc. Fleure 3 Fnancial analyeis of Project C: Add a helleopter to the company's neet 1. Refer to Figures 1 through 4. Add up the total increase in after-tax income for each project. Given what you know about Kay Mash, to which project do you think she will be attracted? 2. Computer the Payback Period, Discounted Payback Period, Net Present Value, Internal Rate of Return (IRR), and Productivity Index of all four alternatives based on cash flow. User 10 percent for the cost of capital in your calculations. For the Payback Period and for the Discounted Payback Period, compute to the midyear points as discussed in class. 3. a. According to the payback method, which project should be selected? b. What is the chief disadvantage of this method? c. Why would anyone want to use this method? 4. a. According to the Discounted Payback method, which project should be selected? b. What is the chief disadvantage of this method? c. Why would anyone want to use this method? 5. a. According to the Net Present Value method, which project should be selected? b. What are the major advantages of the Net Present Value method? c. What are any disadvantages of the Net Present Value Method? d. If Kay had not put a limit on the size of the capital budget, under the NPV method which projects would have been accepted? 6. a. According to the IRR method, which project should be chosen? b. What is the major disadvantage of the IRR method that occurs when HIGH IRR projects are selected? c. Can you think of another disadvantage of the IRR method? (Hint: Look over the four alternatives and compare the sizes of the projects. Ask yourself whether you would prefer to make a large percent return on a small amount of money or a small percent gain on a large amount of money.) d. Do the NPV and IRR both reject the same projects - Why? 7. a. According to the Productivity Index, which project should be chosen? b. Explain why people use the Productivity Index. c. Explain why a Productivity index so closely correlates with the results of NPV. Aerocomp, Inc. As whe beadad soward her boss's office, Fmily Hamilton, ehief opernting officer for the Aerocomp CopporitionA. A proponal ot add a jet ob the conpeter services frm that opocialized in wirbome wupport-wiabed she could eomptay's ficet. The pinne wat only tict year old asd wat eonsidered a remember more of her thainisg in sood bey at 5300,000 . In retum, the financial theory that she had been plane woeld bring over 5600,000 in exposed to in colloge. Emily had just additional revenoe during the pert five completed sammarizaing the finuncial yews with oely about 556,000 in openting eontr. (See Figure 1 for projects that were open to Aeroconp during the coming year, and ahe wus B. A proposal to liveraity into copy faced with the tatik of rooommending machines. The finchise wat to eont which thould be seloctod. Whit 5700,000 , shich would be amortized concemed ber was the knowiledge that over a 40-year period. The new ber bos, Kay Manth, a "ntreet imert" chief executive, with no background in buiness wa expected to genernte over 51.4 million in tales over the nert five financial theory, would immediately yeers, end over $800,000 in aftertar favor the project that promised the C. emingn. (Soe Figare 2 for details.) highest gain in reported net ineoce. Emily luow that melectiag projocts parely. on that basis would be incorroct, bout she Wam't aure of her ability to esevince Kay, who tended to asuane finmeiern thought up fincy methods just to show how smart they were, As ahe prepared to enter Kxy's office, Emily polled her summary sheets from ber briefcase and quickly reviewed the details of the four projects, all of which sbe considered to be equally risky. D. A propoeal to begin operating a fleet of truck. Ten oould be bought for aely \$51,000 each, and the additional business would bring in almost $700,000 in ncw sales in the first two years alone. (See Figure 4 for details). In her mind, Emily quickly went over the evaluation methods she had used in the paet paybeck, internal rate of return, and net present value. Emily lonew that Kay would add a fourth, size of reported carnings, but she hoped sbe coald tall Kay out of using it this time. Emily berself fivored the net present value method, but ahe had always had a tough time getting Kry to understand it. One additional constraint that Emily had to deal with wes Kay's insistence that po outside financing be used this year. Kay was worried that the eompany was growing too fast and had piled up Figure 1 Fhancial malyain of Project Ac Add a twin-tot to the company's fleet enough debt for the time being. She was also against a stock issue for fenr of diluting earningr and her control over the firm. As a result of Kay's prohibition of outside financing, the size of the cupital budget this year was limited to $800,000, which meant that only one of the four projects under consideration could be ebosen. Emily wasn't too happy about that, either, but she had decided to aceept it for now, and concentrnte on selecting the best of the four. As she elosod ber briefcase and waiked toward Kay's door. Emily reminded berself to have patience, Kay might not trust financial analysis, but she would listen to sensible arguments. Emily only hoped her financial amalysis sounded sensiblel Aerocomp, inc. Fleure 3 Fnancial analyeis of Project C: Add a helleopter to the company's neet 1. Refer to Figures 1 through 4. Add up the total increase in after-tax income for each project. Given what you know about Kay Mash, to which project do you think she will be attracted? 2. Computer the Payback Period, Discounted Payback Period, Net Present Value, Internal Rate of Return (IRR), and Productivity Index of all four alternatives based on cash flow. User 10 percent for the cost of capital in your calculations. For the Payback Period and for the Discounted Payback Period, compute to the midyear points as discussed in class. 3. a. According to the payback method, which project should be selected? b. What is the chief disadvantage of this method? c. Why would anyone want to use this method? 4. a. According to the Discounted Payback method, which project should be selected? b. What is the chief disadvantage of this method? c. Why would anyone want to use this method? 5. a. According to the Net Present Value method, which project should be selected? b. What are the major advantages of the Net Present Value method? c. What are any disadvantages of the Net Present Value Method? d. If Kay had not put a limit on the size of the capital budget, under the NPV method which projects would have been accepted? 6. a. According to the IRR method, which project should be chosen? b. What is the major disadvantage of the IRR method that occurs when HIGH IRR projects are selected? c. Can you think of another disadvantage of the IRR method? (Hint: Look over the four alternatives and compare the sizes of the projects. Ask yourself whether you would prefer to make a large percent return on a small amount of money or a small percent gain on a large amount of money.) d. Do the NPV and IRR both reject the same projects - Why? 7. a. According to the Productivity Index, which project should be chosen? b. Explain why people use the Productivity Index. c. Explain why a Productivity index so closely correlates with the results of NPV