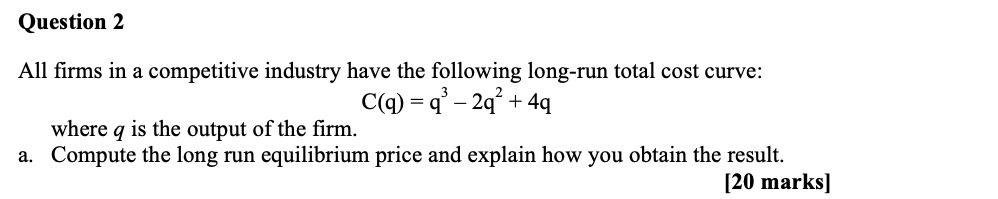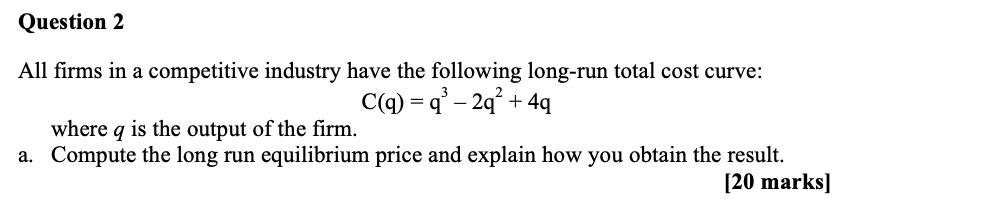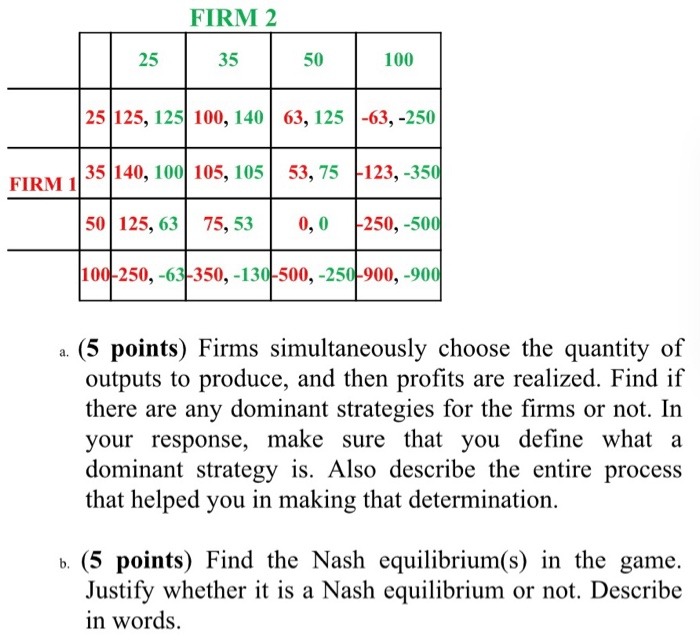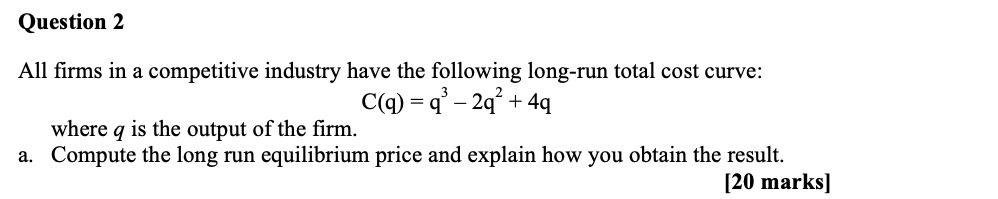
Please solve the following queations.
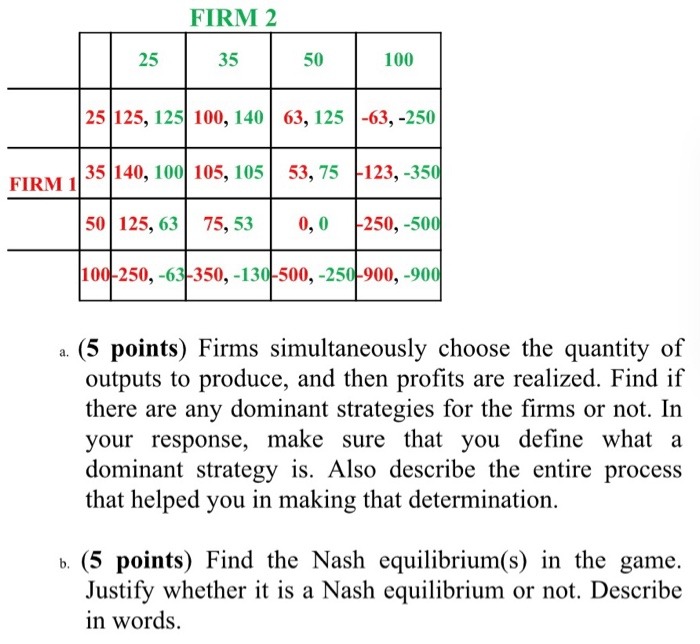
Question 1 (a) Right before Christmas, the price of Christmas trees went up by 30%, while the quantity of Christmas trees sold increased by 80%. Do these figures imply an upward sloping demand curve for Christmas trees? Explain with a diagram. (10 marks) (b) The Kowloon Motor Bus (KMB) Company Limited has done a research on the price elasticity of demand for bus service. The following table shows that the price elasticity of demand varies in different timeslots of a day Timeslots Price elasticity of demand 7:00 a.m. - 10:00 a.m 0.5 10:00 a.m. - 5:00 p.m. 1.5 5:00 p.m. - 8:00 p.m. 0.7 8:00 p.m. - 12:00 mid-night 2.0 Explain the meaning of those numbers of price elasticity of demand, and why the demand for bus service has different levels of price elasticity of demand during different timeslots? (10 marks) (c) Suppose the Hong Kong government imposes a price ceiling above the equilibrium price of flour. How does this price ceiling affect the price and the quantity sold of flour? Explain. (5 marks) Question 2 (a) John buys a T-shirt for $100 and his consumer surplus is $0. What is John's maximum willingness to pay for the T-shirt? Show the steps of your calculation. (5 marks) (b) Suppose Hong Kong is experiencing an economic recession. Explain with a diagram how the decrease in household income affects the equilibrium price, equilibrium quantity, consumer surplus, producer surplus, total surplus, and deadweight loss in the market for computers. (13 marks) (c) Marginal cost curve always cuts the lowest point of the average total cost curve. Do you agree? Explain. (7 marks) Question 3 (a) Explain the three conditions held at the long-run equilibrium in a perfectly competitive market with a diagram. (10 marks) (b) If a firm makes zero economic profit, it will exit the market in the long run. Do you agree? Explain. (7 marks) (c) What makes a firm become a natural monopolist, and how does it become a barrier to entry of new firms? Explain. (8 marks)Question 2 All rms in a competitive industry have the following long-run total cost curve: C(q) = cf' 2q2 + 4q where q is the output of the rm. 3. Compute the long run equilibrium price and explain how you obtain the result. [20 marks] FIRM 2 25 35 50 100 25 125, 125 100, 140 63, 125 -63, -250 FIRM 1 35 140, 100 105, 105 53, 75 123, -350 50 125, 63 75, 53 0,0 -250, -500 100-250, -63-350, -130-500, -250-900, -900 a. (5 points) Firms simultaneously choose the quantity of outputs to produce, and then profits are realized. Find if there are any dominant strategies for the firms or not. In your response, make sure that you define what a dominant strategy is. Also describe the entire process that helped you in making that determination. b. (5 points) Find the Nash equilibrium(s) in the game. Justify whether it is a Nash equilibrium or not. Describe in words