Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Please solve this problem using matplot and with open. DO NOT USE PANDAS Iterate data using loops and append each variable. See the grading notes
Please solve this problem using matplot and with open. DO NOT USE PANDAS
Iterate data using loops and append each variable.
See the grading notes and follow those directions. Do not use fancy functions not mentioned in grading notes.


Below are grading notes please follow these directions!
INPUT FILE
https://course.ccs.neu.edu/ds2000/homework/hw4ola_weather_feb.csv
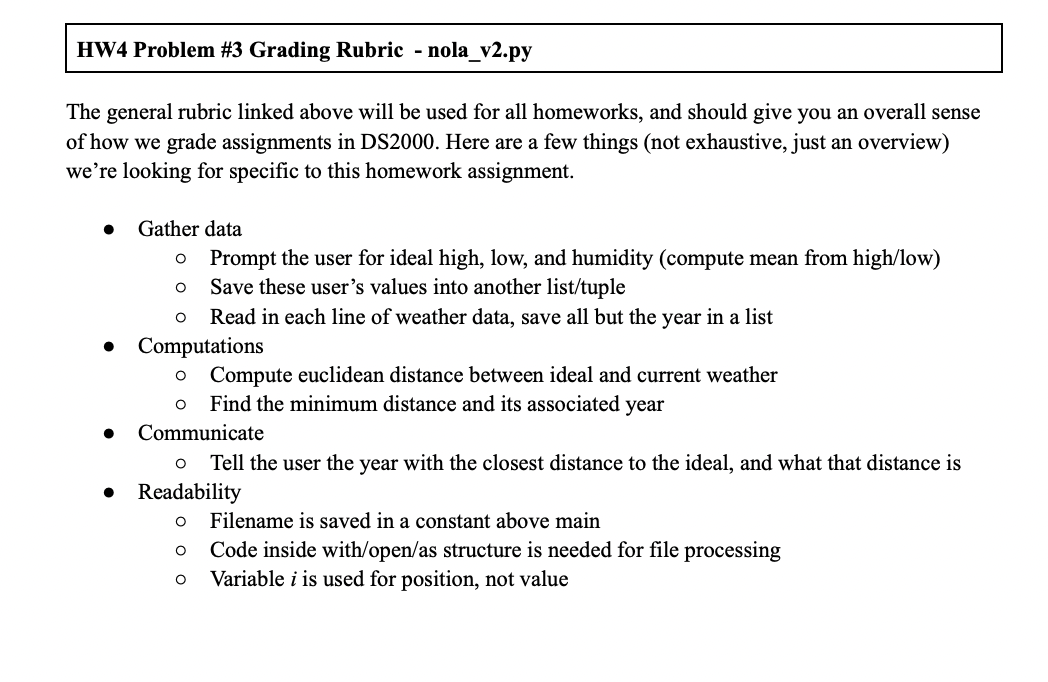
Filename: nola_v2.py Input files: nola weather feb, csv, same as for the previous problem Remember the Euclidean distance computation we used back in HW2? Back then, we computed the distance between two locations in physical space. Data scientists use distance measures for all kinds of things, not just physical distance, and for this problem we'll use it to compare days based on the weather. Given an ideal weather forecast, we'll find the year that was the closest to that ideal. First, prompt the user for their ideal weather conditions: ideal high temp, low temp, and humidity. Compute the mean from their high and low. Create a list with their ideal high_temp, low_temp, mean, humidity. Second, let's compare! We're using the same data file as for nola_v1, but we're reading it in differently. For each line in the file, create a list containing high_temp, low_temp, mean, humidity, in that order. Compute the Euclidean distance between the current year and the ideal weather. At the end, report back to the user the year with the weather that's closest to their ideal, and the distance. Euclidean Distance Note that your prompt the user for three things (low, high, humidity), but the list you create from their input will have length 4 (high, low, mean, humidity). Make sure the list you create from the file, for each year, is the same length and in the same order. Then you can apply the following: - Given two lists, 11 and 12, of length n, Euclidean distance is defined as: - sqrt((11[]12[])2+(11[1]12[1])2+(11[n1]12[n1])2) Note that 2-dimensional lists are not permitted on this homework. You can accomplish everything here with the lists and loops we've covered in class! For full credit under documentation, you must include at least one test case in a block comment at the top of your code. This doesn't have to include the actual closest year and its weather conditions! Something like this, but with your own example. Test case: Ideal: 70, 50, 56 Ideal list becomes: [70,50, 60, 56] Distance from here to 1937 71,48,59.5,55 (7071)2+(5048)2+(6059.5)2+(5655)02 =1+4+.25+1 And then sqrt(6.25)=2.5 Note that 2-dimensional lists are not permitted on this homework. You can accomplish everything her with the lists and loops we've covered in class! For full credit under documentation, you must include at least one test case in a block comment at th top of your code. This doesn't have to include the actual closest year and its weather conditions! Something like this, but with your own example. Test case: Ideal: 70, 50, 56 Ideal list becomes: [70, 50, 60, 56] Distance from here to 1937 71,48,59.5,55 (7071)2+(5048)2+(6059.5)2+(5655)2 =1+4+.25+1 And then sqrt (6.25)=2.5 Here's an example of what happens when I run my code (as always, yours doesn't need to look exactl the same, but the prompts DO need to be in the same order to make the autograder happy). The general rubric linked above will be used for all homeworks, and should give you an overall sense of how we grade assignments in DS2000. Here are a few things (not exhaustive, just an overview) we're looking for specific to this homework assignment. - Gather data - Prompt the user for ideal high, low, and humidity (compute mean from high/low) - Save these user's values into another list / tuple - Read in each line of weather data, save all but the year in a list - Computations - Compute euclidean distance between ideal and current weather - Find the minimum distance and its associated year - Communicate - Tell the user the year with the closest distance to the ideal, and what that distance is - Readability - Filename is saved in a constant above main - Code inside with/open/as structure is needed for file processing - Variable i is used for position, not value
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


