Please use matlab and explain your answer.

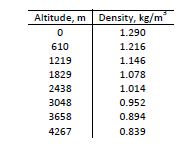 The starting altitude from the time of the jump is 4000 m.
The starting altitude from the time of the jump is 4000 m.
During his or her vertical descent, a skydiver will also usually be travelling a horizontally. This horizontal velocity is met with air resistance, just as the vertical velocity is. To be more explicit, there is a horizontal speed during every segment of the sky dive, during free-fall, and while under canopy. Account for horizontal speed for every segment with the following project steps. Air Craft Speed and Horizontal Movement For skydiving, the aircraft typically flies up to 140 km/h (90 mph) at the time of the jump. What is the initial horizontal velocity of the skydiver? Assume it flies in the positive direction and be sure to include it in your model. Now model the effects of air resistance in the horizontal direction. Model this air resistance similarly to how it was modeled in the vertical direction (use the same Newtonian Friction formula with the same parameters as was used in the vertical direction). To (1) Does gravity act in the horizontal direction? (2) What should the magnitude of the drag be (positive or negative)? Calculate and record the horizontal distance, velocity, and acceleration. During a skydive, there may be moderate to severe wind. This wind may be moving in the same direction as the parachutist or not. Assume the wind is blowing at a constant 7 m/s in the same direction that the aircraft is flying. Since the velocity in the Newtonian drag formula is the velocity relative to the frictional medium, calculate the velocity relative to the medium as [velocity] - [wind speed], for use as velocity in the drag formula. To consider: how would the magnitude of the drag term change if the wind were blowing in the opposite direction? In addition to your plot from Task 5 create 1 figure with 3 subplots showing the altitude of the parachutist (y-axis) vs horizontal position (x-axis), vs horizontal velocity, and v horizontal acceleration. Include all necessary labeling. Determine from the simulation the following questions: How far does the skydiver travel forward during free-fall? How far does the skydiver travel during canopy flight? During his or her vertical descent, a skydiver will also usually be travelling a horizontally. This horizontal velocity is met with air resistance, just as the vertical velocity is. To be more explicit, there is a horizontal speed during every segment of the sky dive, during free-fall, and while under canopy. Account for horizontal speed for every segment with the following project steps. Air Craft Speed and Horizontal Movement For skydiving, the aircraft typically flies up to 140 km/h (90 mph) at the time of the jump. What is the initial horizontal velocity of the skydiver? Assume it flies in the positive direction and be sure to include it in your model. Now model the effects of air resistance in the horizontal direction. Model this air resistance similarly to how it was modeled in the vertical direction (use the same Newtonian Friction formula with the same parameters as was used in the vertical direction). To (1) Does gravity act in the horizontal direction? (2) What should the magnitude of the drag be (positive or negative)? Calculate and record the horizontal distance, velocity, and acceleration. During a skydive, there may be moderate to severe wind. This wind may be moving in the same direction as the parachutist or not. Assume the wind is blowing at a constant 7 m/s in the same direction that the aircraft is flying. Since the velocity in the Newtonian drag formula is the velocity relative to the frictional medium, calculate the velocity relative to the medium as [velocity] - [wind speed], for use as velocity in the drag formula. To consider: how would the magnitude of the drag term change if the wind were blowing in the opposite direction? In addition to your plot from Task 5 create 1 figure with 3 subplots showing the altitude of the parachutist (y-axis) vs horizontal position (x-axis), vs horizontal velocity, and v horizontal acceleration. Include all necessary labeling. Determine from the simulation the following questions: How far does the skydiver travel forward during free-fall? How far does the skydiver travel during canopy flight

 The starting altitude from the time of the jump is 4000 m.
The starting altitude from the time of the jump is 4000 m.





