Question: Please use sample script of 2PAM, and modify for 4PAM requirements clear all; close all; fs = 48000; % sampling frequency Ts = 1/fs; %
Please use sample script of 2PAM, and modify for 4PAM requirements




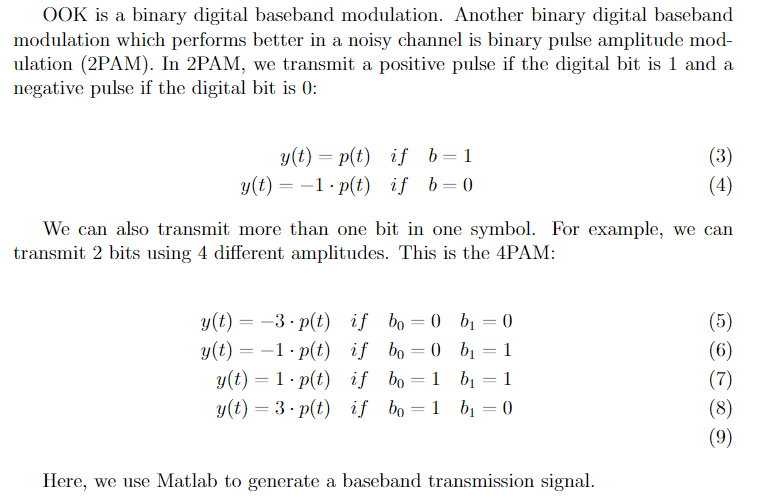
clear all;
close all;
fs = 48000; % sampling frequency
Ts = 1/fs; % sampling duration
symbolrate=1000; %transmitted pulses/second should be an integer divisor of fs
symbol_length = fs/symbolrate; % number of samples in one symbol
%
% Transmitter setup
%
% define the basic rectangular pulse shape
%
pulse = ones(1,symbol_length); % 1 pulse
textin = input('Enter ASCII text for transmission: ','s');
%textin
% Transform from ACSII text to a binary string
data_input = dec2bin(double(textin));%change textin which is 10# to 2#
[number,length_data] = size(data_input);
data0 = reshape(data_input',1,number*length_data);% change the data of matrix to row vector
[number, length_data] = size(data0);
for i = 1:length_data
data(i) = bin2dec(data0(i));
end
[number, length0] = size(data);
symbol = 2*data-1;
for i = 1: length0
for j=1:symbol_length
signal((i-1)*symbol_length + j) = symbol(i) * pulse(j);
end
end
index = 0: Ts: (length0*symbol_length-1)*Ts;
freq=fft(signal);
freq=fftshift(freq);
figure(1);
plot(index, signal);
axis([0 1.5*length0*symbol_length*Ts -2 2]);
xlabel('time');
ylabel('amplitude');
title('baseband transmission signal of 2PAM');
figure(2);
plot(abs(freq));
xlabel('frequency');
ylabel('magnitude');
title('spectrum of 2PAM signal');
In the Matlab program provided here, we use rectangular pulse shape and 2PAM to generate the transmitted signal. Furthermore, we also take a look at the spectrum of the signal. Please read and understand the M file, then modify the source code so we can: 1. Plot the spectrum in correct index. 2. include a random initial time delay at transmitter side; 3. use OOK and 4PAM as modulation scheme; 4. use Hamming pulse shape to generate the baseband transmitted signal, inves- tigate its spectrum, compare it to the spectrum of using rectangular pulse; 5. use Hanning pulse shape to generate the baseband transmitted signal, investi- gate its spectrum, compare it to the spectrum of using rectangular pulse; Figure 2 and Figure 3 demonstrate the time domain signal and frequency domain spectrum of a baseband transmission using 2-PAM and rectangular pulse shape. a clear all; close all; fs = 48000; % sampling frequency Ts = 1/fs; % sampling duration symbolrate=1000; %transmitted pulses/ second should be an integer divisor of fs symbol_length = fs/symbolrate; % number of samples in one symbol - % % Transmitter setup % % define the basic rectangular pulse shape % pulse = ones(1, symbol_length); % 1 pulse = textin = input('Enter ASCII text for transmission: ','S'); %textin % Transform from ACSII text to a binary string data input dec2bin (double(textin));%change textin which is 10# to 2# [number, length_data] = size (data_input); data0 reshape (data_input',1,number*length_data);% change the data of matrix to row vec [number, length_data] = size (data); for i 1:length_data data(i) = bin2dec (data0(i)); end = = = = + = [number, lengtho] = size (data); symbol = 2*data-1; for i 1: length for j=1: symbol_length signal((i-1)*symbol_length + j) = symbol(i) * pulse(j); end end index = 0: Ts: (length(*symbol_length-1) *Ts; freq=fft(signal); freq=fftshift(freq); figure(1); plot(index, signal); axis ([0 1.5*length0*symbol_length*Ts -2 2]); xlabel('time'); ylabel('amplitude'); title('basband transmission signal of 2PAM'); figure(2); plot(abs (freq)); xlabel('frequency'); ylabel('magnitude'); title('spectrum of 2PAM signal'); OOK is a binary digital baseband modulation. Another binary digital baseband modulation which performs better in a noisy channel is binary pulse amplitude mod- ulation (2PAM). In 2PAM, we transmit a positive pulse if the digital bit is 1 and a negative pulse if the digital bit is (: y(t) = p(t) if b= 1 y(t) = -1.p(t) ifb=0 (3) (4) We can also transmit more than one bit in one symbol. For example, we can transmit 2 bits using 4 different amplitudes. This is the 4PAM: - y(t) = -3.p(t) if bo=0 bj = 0 y(t) = -1.pt) if bo=0 b = 1 (( y(t) = 1.pt) if bo=1 b1 = 1 bi y(t) = 3 .pt) if bo=1 b = 0 (5) ( (6) (7) (8) (9) Here, we use Matlab to generate a baseband transmission signal. In the Matlab program provided here, we use rectangular pulse shape and 2PAM to generate the transmitted signal. Furthermore, we also take a look at the spectrum of the signal. Please read and understand the M file, then modify the source code so we can: 1. Plot the spectrum in correct index. 2. include a random initial time delay at transmitter side; 3. use OOK and 4PAM as modulation scheme; 4. use Hamming pulse shape to generate the baseband transmitted signal, inves- tigate its spectrum, compare it to the spectrum of using rectangular pulse; 5. use Hanning pulse shape to generate the baseband transmitted signal, investi- gate its spectrum, compare it to the spectrum of using rectangular pulse; Figure 2 and Figure 3 demonstrate the time domain signal and frequency domain spectrum of a baseband transmission using 2-PAM and rectangular pulse shape. a clear all; close all; fs = 48000; % sampling frequency Ts = 1/fs; % sampling duration symbolrate=1000; %transmitted pulses/ second should be an integer divisor of fs symbol_length = fs/symbolrate; % number of samples in one symbol - % % Transmitter setup % % define the basic rectangular pulse shape % pulse = ones(1, symbol_length); % 1 pulse = textin = input('Enter ASCII text for transmission: ','S'); %textin % Transform from ACSII text to a binary string data input dec2bin (double(textin));%change textin which is 10# to 2# [number, length_data] = size (data_input); data0 reshape (data_input',1,number*length_data);% change the data of matrix to row vec [number, length_data] = size (data); for i 1:length_data data(i) = bin2dec (data0(i)); end = = = = + = [number, lengtho] = size (data); symbol = 2*data-1; for i 1: length for j=1: symbol_length signal((i-1)*symbol_length + j) = symbol(i) * pulse(j); end end index = 0: Ts: (length(*symbol_length-1) *Ts; freq=fft(signal); freq=fftshift(freq); figure(1); plot(index, signal); axis ([0 1.5*length0*symbol_length*Ts -2 2]); xlabel('time'); ylabel('amplitude'); title('basband transmission signal of 2PAM'); figure(2); plot(abs (freq)); xlabel('frequency'); ylabel('magnitude'); title('spectrum of 2PAM signal'); OOK is a binary digital baseband modulation. Another binary digital baseband modulation which performs better in a noisy channel is binary pulse amplitude mod- ulation (2PAM). In 2PAM, we transmit a positive pulse if the digital bit is 1 and a negative pulse if the digital bit is (: y(t) = p(t) if b= 1 y(t) = -1.p(t) ifb=0 (3) (4) We can also transmit more than one bit in one symbol. For example, we can transmit 2 bits using 4 different amplitudes. This is the 4PAM: - y(t) = -3.p(t) if bo=0 bj = 0 y(t) = -1.pt) if bo=0 b = 1 (( y(t) = 1.pt) if bo=1 b1 = 1 bi y(t) = 3 .pt) if bo=1 b = 0 (5) ( (6) (7) (8) (9) Here, we use Matlab to generate a baseband transmission signal
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


