
 please write the formula which I could know how to get the answers. Ex: D16=E8*D2. thank you
please write the formula which I could know how to get the answers. Ex: D16=E8*D2. thank you
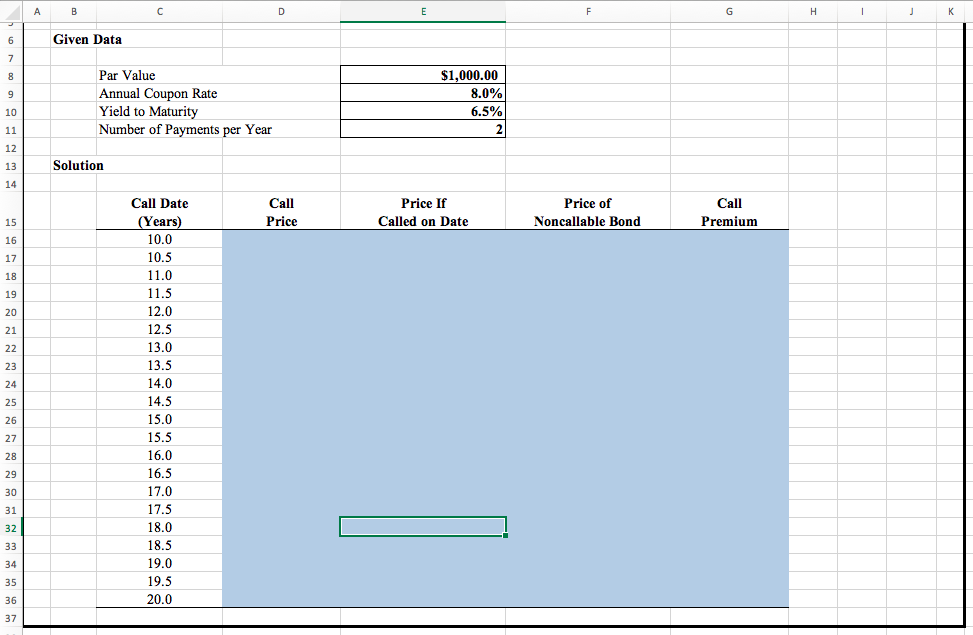
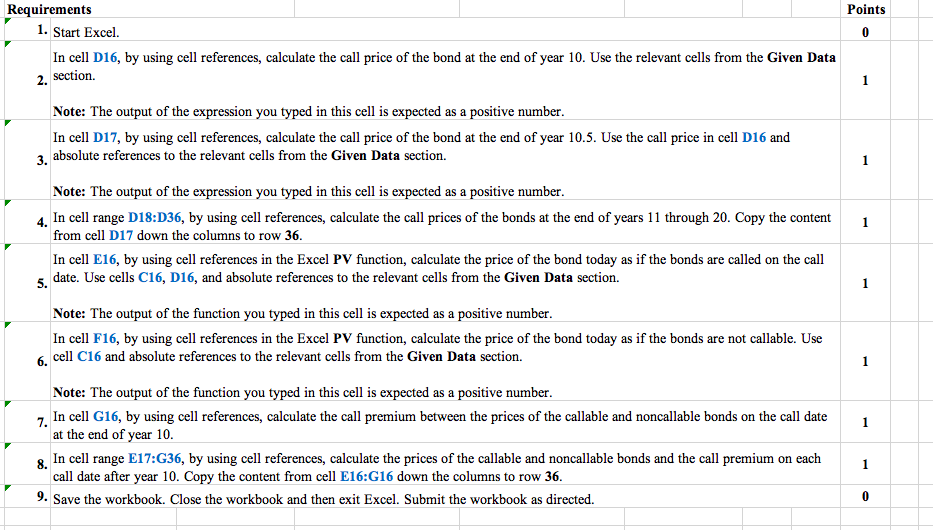
ADVANCED PROBLEM 6-2 FOR SPREADSHEET APPLICATION N w Callable bond and call premium. Edward has just purchased a callable bond and wants to determine the bond's potential payoff price if it is called at any time during its callable life. The callable bond is a twenty-year semiannual bond that an issuer can call starting at year ten. It is callable every six months on the coupon payment date. The call price is declining and starts out as one extra year's coupon (a full annual coupon payment). It reduces each period (every six months by 1/20th of the annual coupon payment) untilat the bond's maturitythere is no call premium price. If the original bond is an 8% bond (with 4% coupons paid semiannually), a par value of $1,000 and an original yield to maturity of 6.5%, what is the bond price today at each potential callable date (coupon payment date) given no change in its original yield to maturity? Edward wants to compare the callable bond price at each callable date with that of a noncallable bond that is identical in every way other than the call feature (same yield to maturity, same coupon rate, and same maturity date). The difference between the callable bond price and the noncallable bond price is the call premium if called on that date. Find the call premium for each potential call date. Given Data Par Value Annual Coupon Rate Yield to Maturity Number of Payments per Year $1,000.00 8.0% 6.5% Solution Call Price Price If Called on Date Price of Noncallable Bond Call Premium Call Date (Years) 10.0 10.5 11.0 11.5 12.0 12.5 13.0 13.5 14.0 14.5 15.0 15.5 16.0 16.5 17.0 17.5 18.0 18.5 19.0 19.5 20.0 Points Requirements 1. Start Excel. In cell D16, by using cell references, calculate the call price of the bond at the end of year 10. Use the relevant cells from the Given Data 2. section. Note: The output of the expression you typed in this cell is expected as a positive number. In cell 017, by using cell references, calculate the call price of the bond at the end of year 10.5. Use the call price in cell D16 and 3. absolute references to the relevant cells from the Given Data section. Note: The output of the expression you typed in this cell is expected as a positive number. In cell range D18:D36, by using cell references, calculate the call prices of the bonds at the end of years 11 through 20. Copy the content from cell D17 down the columns to row 36 In cell E16, by using cell references in the Excel PV function, calculate the price of the bond today as if the bonds are called on the call date. Use cells C16, D16, and absolute references to the relevant cells from the Given Data section. Note: The output of the function you typed in this cell is expected as a positive number. In cell F16, by using cell references in the Excel PV function, calculate the price of the bond today as if the bonds are not callable. Use 6. cell C16 and absolute references to the relevant cells from the Given Data section. Note: The output of the function you typed in this cell is expected as a positive number. 7. In cell G16, by using cell references, calculate the call premium between the prices of the callable and noncallable bonds on the call date at the end of year 10. 8. In cell range E17:G36, by using cell references, calculate the prices of the callable and noncallable bonds and the call premium on each call date after year 10. Copy the content from cell E16:G16 down the columns to row 36. 9. Save the workbook. Close the workbook and then exit Excel. Submit the workbook as directed. ADVANCED PROBLEM 6-2 FOR SPREADSHEET APPLICATION N w Callable bond and call premium. Edward has just purchased a callable bond and wants to determine the bond's potential payoff price if it is called at any time during its callable life. The callable bond is a twenty-year semiannual bond that an issuer can call starting at year ten. It is callable every six months on the coupon payment date. The call price is declining and starts out as one extra year's coupon (a full annual coupon payment). It reduces each period (every six months by 1/20th of the annual coupon payment) untilat the bond's maturitythere is no call premium price. If the original bond is an 8% bond (with 4% coupons paid semiannually), a par value of $1,000 and an original yield to maturity of 6.5%, what is the bond price today at each potential callable date (coupon payment date) given no change in its original yield to maturity? Edward wants to compare the callable bond price at each callable date with that of a noncallable bond that is identical in every way other than the call feature (same yield to maturity, same coupon rate, and same maturity date). The difference between the callable bond price and the noncallable bond price is the call premium if called on that date. Find the call premium for each potential call date. Given Data Par Value Annual Coupon Rate Yield to Maturity Number of Payments per Year $1,000.00 8.0% 6.5% Solution Call Price Price If Called on Date Price of Noncallable Bond Call Premium Call Date (Years) 10.0 10.5 11.0 11.5 12.0 12.5 13.0 13.5 14.0 14.5 15.0 15.5 16.0 16.5 17.0 17.5 18.0 18.5 19.0 19.5 20.0 Points Requirements 1. Start Excel. In cell D16, by using cell references, calculate the call price of the bond at the end of year 10. Use the relevant cells from the Given Data 2. section. Note: The output of the expression you typed in this cell is expected as a positive number. In cell 017, by using cell references, calculate the call price of the bond at the end of year 10.5. Use the call price in cell D16 and 3. absolute references to the relevant cells from the Given Data section. Note: The output of the expression you typed in this cell is expected as a positive number. In cell range D18:D36, by using cell references, calculate the call prices of the bonds at the end of years 11 through 20. Copy the content from cell D17 down the columns to row 36 In cell E16, by using cell references in the Excel PV function, calculate the price of the bond today as if the bonds are called on the call date. Use cells C16, D16, and absolute references to the relevant cells from the Given Data section. Note: The output of the function you typed in this cell is expected as a positive number. In cell F16, by using cell references in the Excel PV function, calculate the price of the bond today as if the bonds are not callable. Use 6. cell C16 and absolute references to the relevant cells from the Given Data section. Note: The output of the function you typed in this cell is expected as a positive number. 7. In cell G16, by using cell references, calculate the call premium between the prices of the callable and noncallable bonds on the call date at the end of year 10. 8. In cell range E17:G36, by using cell references, calculate the prices of the callable and noncallable bonds and the call premium on each call date after year 10. Copy the content from cell E16:G16 down the columns to row 36. 9. Save the workbook. Close the workbook and then exit Excel. Submit the workbook as directed


 please write the formula which I could know how to get the answers. Ex: D16=E8*D2. thank you
please write the formula which I could know how to get the answers. Ex: D16=E8*D2. thank you 





