pls ans asap,,i will thumb up
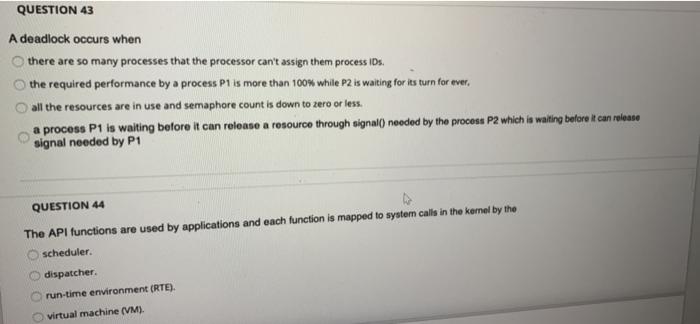
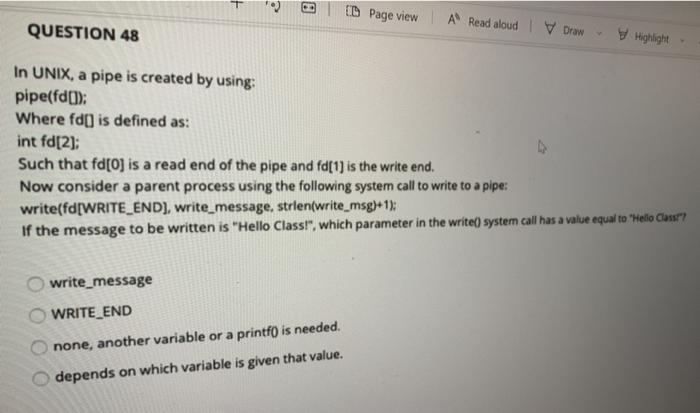
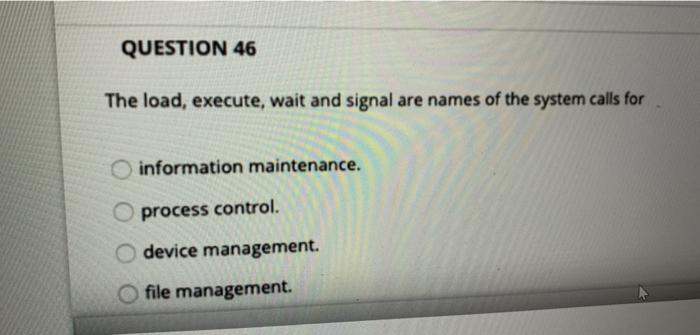
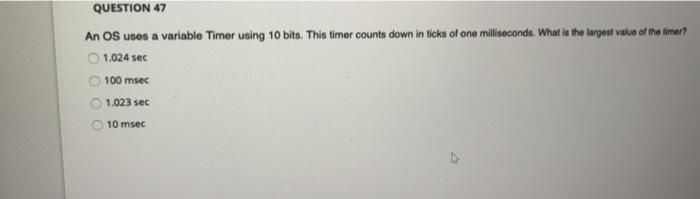
QUESTION 43 A deadlock occurs when there are so many processes that the processor can't assign them process IDs. the required performance by a process Pl is more than 100% while P2 is waiting for its turn for ever. all the resources are in use and semaphore count is down to zero or less. a process P1 is waiting before it can release a resource through signal() needed by the process P2 which is waiting before it can release signal needed by P1 QUESTION 44 The API functions are used by applications and each function is mapped to system calls in the kernel by the scheduler. dispatcher. run-time environment (RTE). virtual machine (VM). QUESTION 46 The load, execute, wait and signal are names of the system calls for information maintenance. process control. device management. file management. QUESTION 47 An Os usos a variable Timer using 10 bits. This timer counts down in ticks of one milliseconds. What is the largest value of the timer? 1.024 sec 100 msec 1.023 sec 10 msec D Page view A Read aloud Draw QUESTION 48 Highlight In UNIX, a pipe is created by using pipe(fd[); Where fd() is defined as: int fd[2]; Such that fd[O) is a read end of the pipe and fd[ 1) is the write end. Now consider a parent process using the following system call to write to a pipe: write(fd[WRITE_END], write_message, strlen(write_msg)+1); If the message to be written is "Hello Class!", which parameter in the write() system call has a value equal to "Hello Cass" write_message WRITE_END none, another variable or a printf() is needed. depends on which variable is given that value. QUESTION 49 Consider the POSIX-based Linux command for shared memory synchronization between a producer and consumer pair of processes fd shm_open(name, O_CREATO_RDWR, 0666) Where fd is a file descripter for a memory mapped file with permissions 0666. Let's analyze the permissions 0666. Each of these digta a Bototal de ranging from 0 to 7 (or, binary 000 to 111). The three bits can be written as b1b2b3, where 1 - 1 of read is permitted, 12 -1.fwrite a permitted and 13 1 means deletion is permitted. The right most digit (6 in this case) applies to a user process, the next applies to a group and the third opt applies to processes. In other words, 0666 means that the consumer process, the group of processes to which it belongs and all processes can read or write to the shared memory file, but no process can delete it. That is (0666-000 110 110 1101. Don't worry about the left most octaldigt which a Banyway How will this permission (0666) change if only the consumer process and the processes in the group were allowed read and write to the above command) 0066 0606 @ @ 0555 0055