Pls help with exercise 3.25 and 3.26.

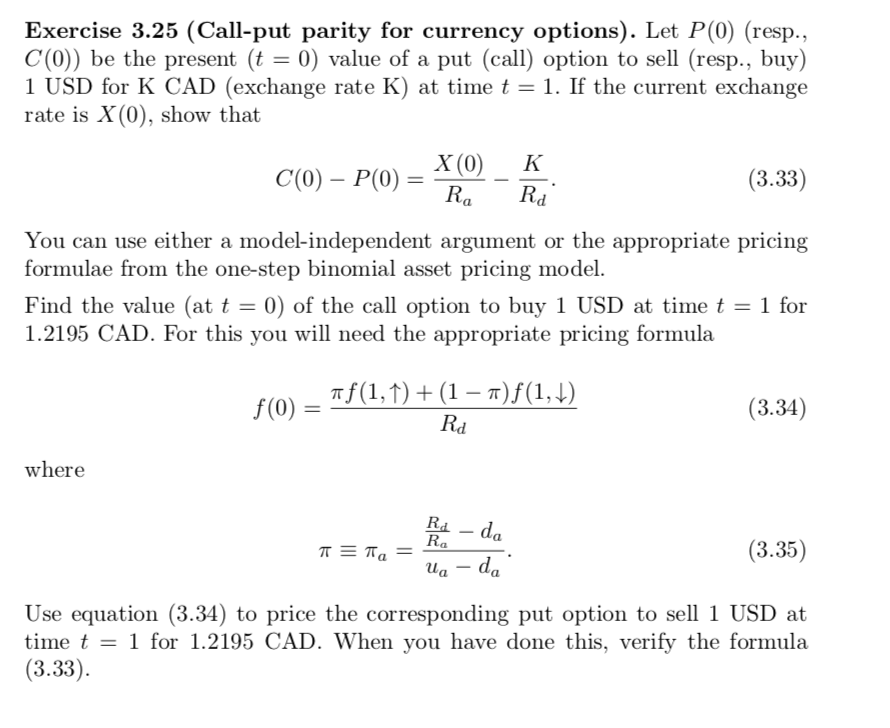

3.5 Exercises 63 For Exercises 3.25 and 3.26 you should use the following informa- tion. The two currency problems below are modelled in a one-step binomial asset pricing model. X(0), X(1,1) and X(1,1) will refer to USD/CAD exchange rates (directly quoted), and J(0), J(1,1) and J(1, 1) will refer to JPY/CAD exchange rates (directly quoted). JPY is the abbreviation for the Japanese yen. Write Rd (resp., Ra, R;), for the values at t = 1 in CAD (resp., USD, JPY), of one CAD (USD, JPY). The 30-day annual interest rates for the various currencies are 5.12%, 5.74% and 0.65%, respectively. So Rd = 1 + 0.0512 12 1.004267, Ra 1.004783 and R; ~ 1.000542. Suppose X(0) and J(0) were 1.2195 (about 82 cents), and 0.011377 (about 88 JPY to CAD). Take X(1,1). = 1.2821 and J(1,1) 0.012599. We shall take X(1, 1) = 1.1905, which corresponds to 84 cents. We shall also use the notation = X(1, 1) = UqX(0), X(1, 1) = deX(0), J(1, 1) = u;J(0), J(1, 1) = d;J(0). Exercise 3.25 (Call-put parity for currency options). Let P(0) (resp., C(0)) be the present (t = 0) value of a put (call) option to sell (resp., buy) 1 USD for K CAD (exchange rate K) at time t = 1. If the current exchange rate is X(0), show that C(0) P(0) = X (0) K Rd (3.33) a You can use either a model-independent argument or the appropriate pricing formulae from the one-step binomial asset pricing model. Find the value (at t = 0) of the call option to buy 1 USD at time t = 1 for 1.2195 CAD. For this you will need the appropriate pricing formula f(0) Af(1,1) + (1 7)f(1,1) Rd (3.34) where Ri - da Ra (3.35) ua da Use equation (3.34) to price the corresponding put option to sell 1 USD at time t = 1 for 1.2195 CAD. When you have done this, verify the formula (3.33). Exercise 3.26. 1. Let Ta (the American 7) be given by (3.35), and 7; (the Japanese a) be given the same formula but with all a replaced by j. Define the two Arrow-Debreu securities for the up and down states at t = 1. Give the price at t = 0) of the up Arrow-Debreu security using (a) the American exchange rates and (b) the Japanese exchange rates. Deduce that Ta = Tij. 2. Use 1. to show that J(1) = 0.011111. 3. Use (assume valid) the interest parity formula to compute the t = 1 forward exchange rates for USD/CAD, JPY/CAD and USD/JPY. 4. Canadian Corporation (CC) owns factories in both Japan and in the United States. Today (t = 0) the treasurer of CC goes to merchant bank XYZ to buy an option giving her the right to sell 10 million JPY for 93,688 USD at t = 1. By this she hopes to transfer cash from Japanese operations to the U.S. at about the forward rate. Show that the value of this option at t = 1 is (in CAD) (-10,000,000J(1) + 93,688X(1)]. Find the value of this option in CAD at t = 0. 3.5 Exercises 63 For Exercises 3.25 and 3.26 you should use the following informa- tion. The two currency problems below are modelled in a one-step binomial asset pricing model. X(0), X(1,1) and X(1,1) will refer to USD/CAD exchange rates (directly quoted), and J(0), J(1,1) and J(1, 1) will refer to JPY/CAD exchange rates (directly quoted). JPY is the abbreviation for the Japanese yen. Write Rd (resp., Ra, R;), for the values at t = 1 in CAD (resp., USD, JPY), of one CAD (USD, JPY). The 30-day annual interest rates for the various currencies are 5.12%, 5.74% and 0.65%, respectively. So Rd = 1 + 0.0512 12 1.004267, Ra 1.004783 and R; ~ 1.000542. Suppose X(0) and J(0) were 1.2195 (about 82 cents), and 0.011377 (about 88 JPY to CAD). Take X(1,1). = 1.2821 and J(1,1) 0.012599. We shall take X(1, 1) = 1.1905, which corresponds to 84 cents. We shall also use the notation = X(1, 1) = UqX(0), X(1, 1) = deX(0), J(1, 1) = u;J(0), J(1, 1) = d;J(0). Exercise 3.25 (Call-put parity for currency options). Let P(0) (resp., C(0)) be the present (t = 0) value of a put (call) option to sell (resp., buy) 1 USD for K CAD (exchange rate K) at time t = 1. If the current exchange rate is X(0), show that C(0) P(0) = X (0) K Rd (3.33) a You can use either a model-independent argument or the appropriate pricing formulae from the one-step binomial asset pricing model. Find the value (at t = 0) of the call option to buy 1 USD at time t = 1 for 1.2195 CAD. For this you will need the appropriate pricing formula f(0) Af(1,1) + (1 7)f(1,1) Rd (3.34) where Ri - da Ra (3.35) ua da Use equation (3.34) to price the corresponding put option to sell 1 USD at time t = 1 for 1.2195 CAD. When you have done this, verify the formula (3.33). Exercise 3.26. 1. Let Ta (the American 7) be given by (3.35), and 7; (the Japanese a) be given the same formula but with all a replaced by j. Define the two Arrow-Debreu securities for the up and down states at t = 1. Give the price at t = 0) of the up Arrow-Debreu security using (a) the American exchange rates and (b) the Japanese exchange rates. Deduce that Ta = Tij. 2. Use 1. to show that J(1) = 0.011111. 3. Use (assume valid) the interest parity formula to compute the t = 1 forward exchange rates for USD/CAD, JPY/CAD and USD/JPY. 4. Canadian Corporation (CC) owns factories in both Japan and in the United States. Today (t = 0) the treasurer of CC goes to merchant bank XYZ to buy an option giving her the right to sell 10 million JPY for 93,688 USD at t = 1. By this she hopes to transfer cash from Japanese operations to the U.S. at about the forward rate. Show that the value of this option at t = 1 is (in CAD) (-10,000,000J(1) + 93,688X(1)]. Find the value of this option in CAD at t = 0









