plz

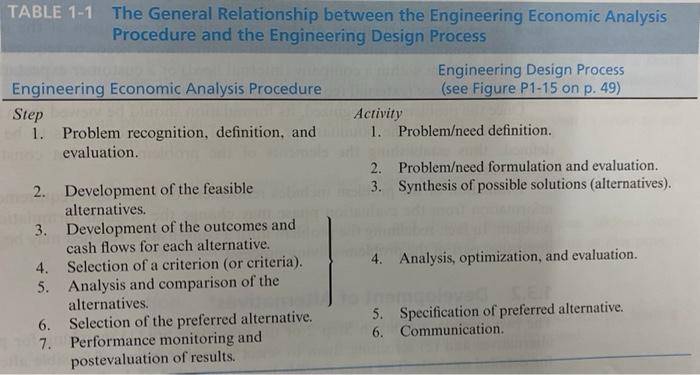
1-16. You have just moved to a new country to take up a two-year assignment. You need to buy a car and are deciding between a new one that costs $20,000 and a three-year-old one that costs $9,000. The used car has an odometer reading of 25,000 miles. You have $10,000 in savings, and can borrow the rest from your company, repaying them 110% after two years. The value of the new car will depreciate by 50% in two years, while that of the used car will depreciate by one-third. What should you do? Use the seven-step procedure from Table 1-1 to analyze your situation. Identify the principles that accompany each step. TABLE The General Relationship between the Engineering Economic Analysis Procedure and the Engineering Design Process Engineering Design Process Engineering Economic Analysis Procedure (see Figure P1-15 on p. 49) Step Activity 1. Problem recognition, definition, and 1. Problemeed definition. evaluation. 2. Problemeed formulation and evaluation. 2. Development of the feasible 3. Synthesis of possible solutions (alternatives). alternatives. 3. Development of the outcomes and cash flows for each alternative. 4. Selection of a criterion (or criteria). 4. Analysis, optimization, and evaluation. 5. Analysis and comparison of the alternatives. 6. Selection of the preferred alternative. 5. Specification of preferred alternative. 7. Performance monitoring and 6. Communication. postevaluation of results. 1/1 1-16. You have just moved to a new country to take up a two-year assignment. You need to buy a car and are deciding between a new one that costs $20,000 and a three-year-old one that costs $9,000. The used car has an odometer reading of 25,000 miles. You have $10,000 in savings, and can borrow the rest from your company, repaying them 110% after two years. The value of the new car will depreciate by 50% in two years, while that of the used car will depreciate by one-third. What should you do? Use the seven-step procedure from Table 1-1 to analyze your situation. Identify the principles that accompany each step. (1) cosa TABLE 1-1 The General Relationship between the Engineering Economic Analysis Procedure and the Engineering Design Process Engineering Design Process Engineering Economic Analysis Procedure (see Figure P1-15 on p. 49) Step Activity 1. Problem recognition, definition, and 1. Problemeed definition. evaluation 2. Problemeed formulation and evaluation. 2. Development of the feasible 3. Synthesis of possible solutions (alternatives). alternatives. 3. Development of the outcomes and cash flows for each alternative. 4. Selection of a criterion (or criteria). 4. Analysis, optimization, and evaluation. 5. Analysis and comparison of the alternatives. 6. Selection of the preferred alternative. 5. Specification of preferred alternative. 7. Performance monitoring and 6. Communication postevaluation of results