Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Plz find L, D, heigh of the leg. Show all work plz You are to do a preliminary design for a horizontal gravity decanter. After


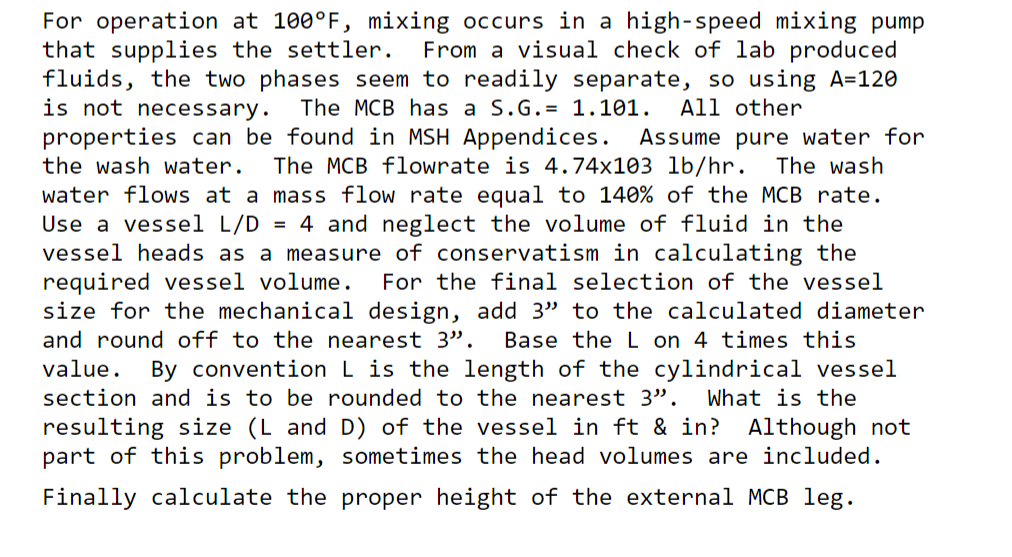
Plz find L, D, heigh of the leg. Show all work plz
You are to do a preliminary design for a horizontal gravity decanter. After being prepared in a reaction, impurities in crude mono-chlorobenzene (MCB) need to be removed by washing with water. Unlike the decanter described in MSH, your vessel will operate 100% filled with liquid. Company experience has indicated that some changes to the equation for separation (MSH eq. 2.15) are warranted. The new form is Avhu t = PA P The value of the constant A depends on how well the feed is mixed upstream of the separator 80 two phase pipeline flow or static mixing 90 in-line mechanical mixers or centrifugal pumps 100 high speed pumps or high shear mixers 120 chemical reaction products or bulk condensation products known to separate slowly Your company has determined that as vessel height gets larger, separation times increase. The reason for this is that coalesced drops must rise (or sink) further in larger vessels. To account for this a height (in meters) is included in the modified equation. This height is taken to be the total height of the less dense (top) layer in the separator. In this design the MCB (heavier) layer level is expected to be about 40% of the total. Some of the MCB droplets may need to travel 60% of the depths to reach the interface between layers. Thus 60% of the vessel diameter becomes the h value to use. For operation at 100F, mixing occurs in a high-speed mixing pump that supplies the settler. From a visual check of lab produced fluids, the two phases seem to readily separate, so using A=120 is not necessary. The MCB has a S.G.= 1.101. All other properties can be found in MSH Appendices. Assume pure water for the wash water. The MCB flowrate is 4.74x103 lb/hr. The wash water flows at a mass flow rate equal to 140% of the MCB rate. Use a vessel L/D = 4 and neglect the volume of fluid in the vessel heads as a measure of conservatism in calculating the required vessel volume. For the final selection of the vessel size for the mechanical design, add 3 to the calculated diameter and round off to the nearest 3". Base the L on 4 times this value. By convention L is the length of the cylindrical vessel section and is to be rounded to the nearest 3". What is the resulting size (L and D) of the vessel in ft & in? Although not part of this problem, sometimes the head volumes are included. Finally calculate the proper height of the external MCB leg. You are to do a preliminary design for a horizontal gravity decanter. After being prepared in a reaction, impurities in crude mono-chlorobenzene (MCB) need to be removed by washing with water. Unlike the decanter described in MSH, your vessel will operate 100% filled with liquid. Company experience has indicated that some changes to the equation for separation (MSH eq. 2.15) are warranted. The new form is Avhu t = PA P The value of the constant A depends on how well the feed is mixed upstream of the separator 80 two phase pipeline flow or static mixing 90 in-line mechanical mixers or centrifugal pumps 100 high speed pumps or high shear mixers 120 chemical reaction products or bulk condensation products known to separate slowly Your company has determined that as vessel height gets larger, separation times increase. The reason for this is that coalesced drops must rise (or sink) further in larger vessels. To account for this a height (in meters) is included in the modified equation. This height is taken to be the total height of the less dense (top) layer in the separator. In this design the MCB (heavier) layer level is expected to be about 40% of the total. Some of the MCB droplets may need to travel 60% of the depths to reach the interface between layers. Thus 60% of the vessel diameter becomes the h value to use. For operation at 100F, mixing occurs in a high-speed mixing pump that supplies the settler. From a visual check of lab produced fluids, the two phases seem to readily separate, so using A=120 is not necessary. The MCB has a S.G.= 1.101. All other properties can be found in MSH Appendices. Assume pure water for the wash water. The MCB flowrate is 4.74x103 lb/hr. The wash water flows at a mass flow rate equal to 140% of the MCB rate. Use a vessel L/D = 4 and neglect the volume of fluid in the vessel heads as a measure of conservatism in calculating the required vessel volume. For the final selection of the vessel size for the mechanical design, add 3 to the calculated diameter and round off to the nearest 3". Base the L on 4 times this value. By convention L is the length of the cylindrical vessel section and is to be rounded to the nearest 3". What is the resulting size (L and D) of the vessel in ft & in? Although not part of this problem, sometimes the head volumes are included. Finally calculate the proper height of the external MCB legStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


