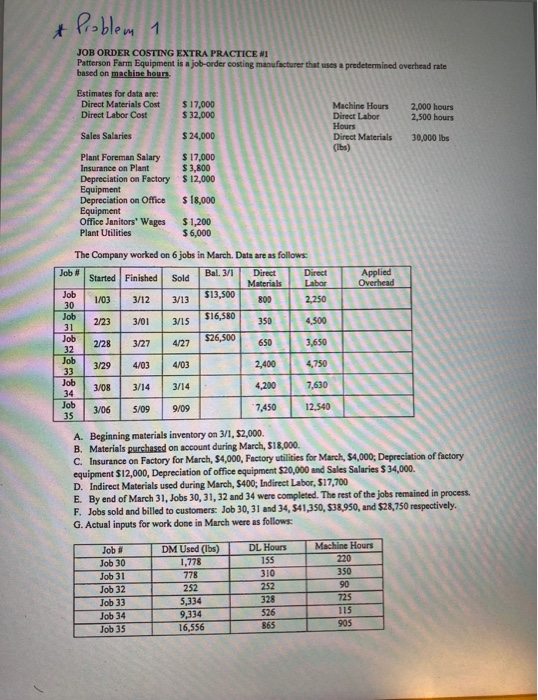
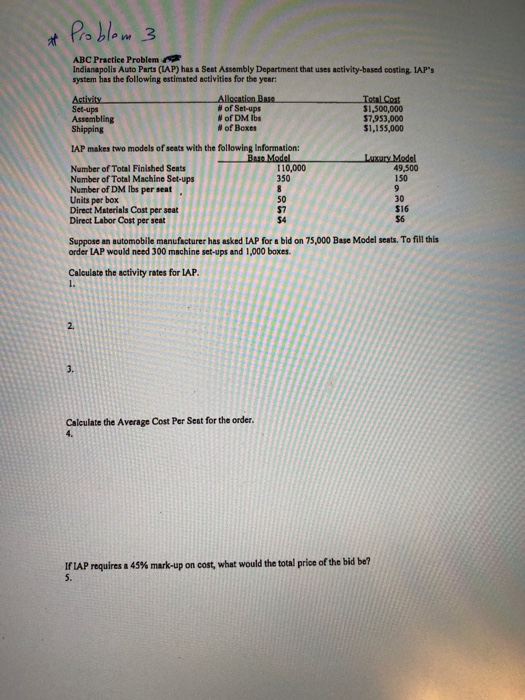
Poblem 1 JOB ORDER COSTING EXTRA PRACTICE #1 Patterson Farm Equipment is a job-order costing manufacturer that uses a predetermined overhead rate based on machine hours. Estimates for data are: Direct Materials Cost $17,000 $32,000 Machine Hours Direct Labor Hours Direct Materials (Ibs) 2,000 hours Direct Labor Cost 2,500 hours Sales Salaries $24,000 30,000 lbs $17,000 $3,800 $12,000 Plant Foreman Salary Insurance on Plant Depreciation on Factory Equipment Depreciation on Office Equipment Office Janitors' Wages Plant Utilities $18,000 $1,200 $6,000 The Company worked on 6 jobs in March. Data are as follows Direct Labor Job Bal. 3/1 Direct Applied Overhead Started Finished Sold Materials $13,500 Job 2,250 1/03 3/12 3/13 800 30 $16,580 Job 350 4,500 2/23 3/01 3/15 31 $26,500 Job 3,650 2/28 3/27 4/27 650 32 Job 2,400 4,750 4/03 3/29 4/03 33 Job 7,630 4,200 3/14 3/14 3/08 34 Job 35 12,540 7,450 9/09 3/06 5/09 A. Beginning materials inventory on 3/1, $2,000 B. Materials purchased on account during March, $18,000 C. Insurance on Factory for March, $4,000, Factory utilities for March, $4,000, Depreciation of factory equipment $12,000, Depreciation of office equipment $20,000 and Sales Salaries $ 34,000. D. Indirect Materials used during March, $400; Indirect Labor, $17,700 E. By end of March 31, Jobs 30, 31,32 and 34 were completed. The rest of the jobs remained in process. F. Jobs sold and billed to customers: Job 30, 31 and 34, $41,350, $38,950, and $28,750 respectively. G. Actual inputs for work done in March were as follows DL Hours Machine Hours 220 DM Used (lbs) 1,778 Job # 155 Job 30 350 310 778 Job 31 90 252 252 Job 32 725 328 5,334 9,334 16,556 Job 33 115 526 Job 34 905 865 Job 35 Instructions: Calculate the following amounts: 1. Calculate the predetermined overhead rate. 2. The total cost of direct materials used in March. 3. The total factory overhead applied to production in March. 4. The total amount of actual Factory Overhead for March. 5. The total cost of jobs completed in March. 6. The Cost of Goods Sold for March. 7. The amount of Sales Revenue for jobs sold and billed to customers. 8. The ending balance in Materials Inventory on March 31. 9. The ending balance in Work in Process Inventory on March 31. 10. The factory overhead variance, also state "over" or "under" applied. Responses: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Poblem e P18-32A Preparing production cost report, second department with beginning WIP; journal entries Leaming Objectives 2, 3, 4 1. Cost per EUP DM $24.00 Claudia Carpet manufactures broadloom carpet in seven processes: spinning, dyeing, plying, spooling, tufting, latexing, and shearing. In the Dyeing Department, direct materials (dye) are added at the beginning of the process. Conversion costs are incurred evenly throughout the process. Information for November 2016 follows: UNITS Beginning Work-in-Process Inventory 55 rolls Transfered in from Spinning Department during November 560 rolls 490 rolls Completed during November Ending Work-in-Process Inventory (80 % complete for conversion work) 125 rolls COSTS Beginning Work-in-Process Inventory (transferred in costs $3,500; materials costs, $1,750; conversion costs, $5,420) $10,670 18,025 Transferred in from Spinning Department 13,010 Materials costs added during November Conversion costs added during November (manufacturing wages, $8,120; manufacturing overhead allocated, $45,460) 53,580 Requirements 1. Prepare the November production cost report for Claudia's Dyeing Department 2. Journalize all transactions affecting Claudia's Dyeing Department during November, including the entries that have already been posted. Poblem 3 ABC Practice Problem Indianapolis Auto Parts (IAP) has a Seat Assembly Department that uses activity-based costing. IAP's system has the following estimated activities for the year: Allocation Base #of Set-ups # of DM Ibs #of Boxes Total Cost $1,500,000 $7,953,000 $1,155,000 Activity Set-ups Assembling Shipping IAP makes two models of seats with the following information: Base Model 10,000 350 8 Luxary Model 49,500 150 9 30 $16 Number of Total Finished Seats Number of Total Machine Set-ups Number of DM lbs per seat Units per box Direct Materials Cost per seat Direct Labor Cost per seat 50 $7 $4 $6 Suppose an automobile manufacturer has asked LAP for a bid on 75,000 Base Model seats. To fill this order LAP would need 300 machine set-ups and 1,000 boxes. Calculate the activity rates for LAP. 2. 3. Calculate the Average Cost Per Seat for the order. 4. If LAP requires a 45 % mark -up on cost, what would the total price of the bid be? 5