
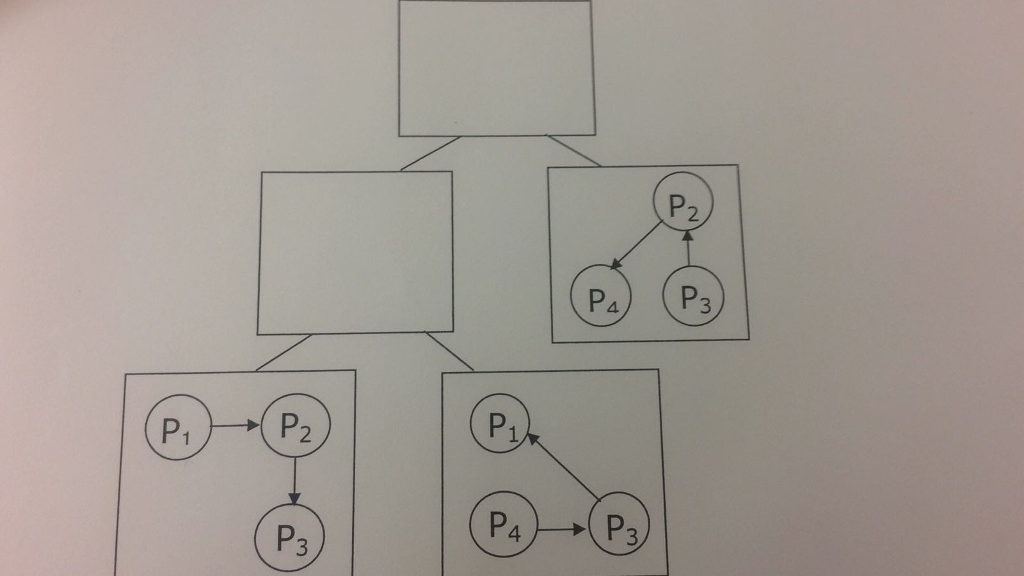
points) Consider the following hierarchical deadlock detection algorithm, in which the global wait for graph is distributed over a number of different controllers, which are organized in a tree. Each non-leaf controller maintains a wait-for graph that contains relevant information from the wait for graphs of the controllers in the subtree below it. particular, let Cbe such that C is the lowest common ancestor of A and B (c is unique because we are dealing with a tree). Suppose that node Pi appears in the local wait-for graph of A and B. Then Pi must also appear in the local wait-for graph of 1. Controller C. 2. Every controller in the path from A to C, and 3. Every controller in the path from B to C. In addition, if Pi and appear in the wait-for graph of controller D and there exists a path from Pi a to Pj in the wait-for graph of one of the children of D, hen an edge Pi Pi must be included in the wait-for graph of D. If a cycle exists in any of the wait-for graphs, then the system is deadlocked (1) (15 points) Complete the wait-for graphs shown below according to the above hierarchical deadlock detection algorithm, and justify your graphs by explaining the steps you followed. (2) (5 points) Is the system deadlocked? Why or why not? points) Consider the following hierarchical deadlock detection algorithm, in which the global wait for graph is distributed over a number of different controllers, which are organized in a tree. Each non-leaf controller maintains a wait-for graph that contains relevant information from the wait for graphs of the controllers in the subtree below it. particular, let Cbe such that C is the lowest common ancestor of A and B (c is unique because we are dealing with a tree). Suppose that node Pi appears in the local wait-for graph of A and B. Then Pi must also appear in the local wait-for graph of 1. Controller C. 2. Every controller in the path from A to C, and 3. Every controller in the path from B to C. In addition, if Pi and appear in the wait-for graph of controller D and there exists a path from Pi a to Pj in the wait-for graph of one of the children of D, hen an edge Pi Pi must be included in the wait-for graph of D. If a cycle exists in any of the wait-for graphs, then the system is deadlocked (1) (15 points) Complete the wait-for graphs shown below according to the above hierarchical deadlock detection algorithm, and justify your graphs by explaining the steps you followed. (2) (5 points) Is the system deadlocked? Why or why not








