Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a ubiquitous technique in molecular genetics that enables researchers to make a huge number of copies of a DNA sequence
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a ubiquitous technique in molecular genetics that enables researchers to make a huge number of copies of a
DNA sequence of interest. Because PCR is essentially in vitro DNA replication, each cycle of heating (denaturation) and cooling (annealing and
strand extension) leads, in theory, to a doubling of the number of target molecules present in the reaction mixture. In other words, as a PCR
proceeds, the number of target molecules present increases according to the equation i2^(mx) where "x' is the number of heating/cooling cycles the
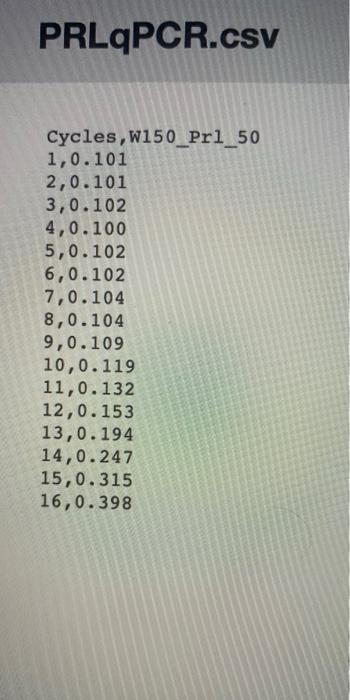
reaction mixture is subjected to and "i' is the initial number of target sequence copies present when the reaction is started. In the file
'PRLqPCR.cv' are data generated using a technology known as real-time PCR, which enables one to fluorescently tag target sequences as they
are synthesized and measure the change in fluorescence (i.e., copy number) as the PCR proceeds. Use 'nis' to fit the equation that I have given you above to these data, then provide the parameter estimate for "i'_____ its' standard error ______ the parameter estimate for 'm'______ , and its standard error
Please round all answer to three decimal places
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


