Question
(((Polynomial.cpp))) #include #include #include #include using namespace std; class poly{ private: int* coef; int length; public: poly(); poly(int* c, int l); ~poly(); poly operator=(const poly&


(((Polynomial.cpp)))
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class poly{
private:
int* coef;
int length;
public:
poly();
poly(int* c, int l);
~poly();
poly operator=(const poly& p);
poly(const poly& p);
friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, poly& p);
friend ostream& operator
poly operator*(poly p);
};
int main()
{
poly p1, p2;
cout
cin >> p1;
cout
cin >> p2;
cout
cout
cout
cout
poly p3 = p1 * p2; // MAKE THIS
cout
return 0;
}
poly::poly()
{
coef = new int[1];
coef[0] = 0;
length = 1;
}
poly::poly(int* c, int l)
{
length = l;
coef = new int[l];
for(int i=0; i
{
coef[i] = c[i];
}
}
poly poly::operator=(const poly& p)
{
length = p.length;
delete [] coef;
coef = new int[length];
for(int i=0; i
{
coef[i] = p.coef[i];
}
poly result(p.coef, p.length);
return result;
}
poly::poly(const poly& p)
{
coef = new int[p.length];
//*this = p; // this line was causing errors for some people
length = p.length;
for(int i=0; i
{
coef[i] = p.coef[i];
}
}
poly::~poly()
{
delete [] coef;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& in, poly& p)
{
string s;
getline(in, s);
int numberCount = 0;
bool onNumeric = false;
// first loop counts amount of numbers
for(int i=0; i (s.length()); i++)
{
if(isdigit(s[i]) && !onNumeric)
{
numberCount++;
onNumeric=true;
}
if(!isdigit(s[i]) && onNumeric)
{
onNumeric=false;
}
}
// delete old poly & replace with correct size
delete [] p.coef;
p.length = numberCount;
if(numberCount == 0) // case if nothing entered (don't want create 0 length array...)
{
p.coef = new int[1];
p.coef[0] = 0;
return in;
}
p.coef = new int[numberCount];
// loop through again to fill array (similar logic to last loop)
onNumeric = false;
int previousIndex = 0; // used to find negative signs
int lastIndex=0;
int coefIndex=0;
for(int i=0; i (s.length()); i++)
{
if(isdigit(s[i]) && !onNumeric)
{
previousIndex=lastIndex;
lastIndex=i;
onNumeric = true;
}
if(!isdigit(s[i]) && onNumeric)
{
string currentNumber = s.substr(lastIndex, i-lastIndex);
p.coef[coefIndex] = atoi(currentNumber.c_str());
string before = s.substr(previousIndex, lastIndex-previousIndex);
if(static_cast
{
p.coef[coefIndex] *= -1;
}
coefIndex++;
onNumeric = false;
}
}
// case if last character is part of the digit
if(onNumeric)
{
string currentNumber = s.substr(lastIndex);
p.coef[coefIndex] = atoi(currentNumber.c_str());
string before = s.substr(previousIndex, lastIndex-previousIndex);
if(static_cast
{
p.coef[coefIndex] *= -1;
}
}
return in;
}
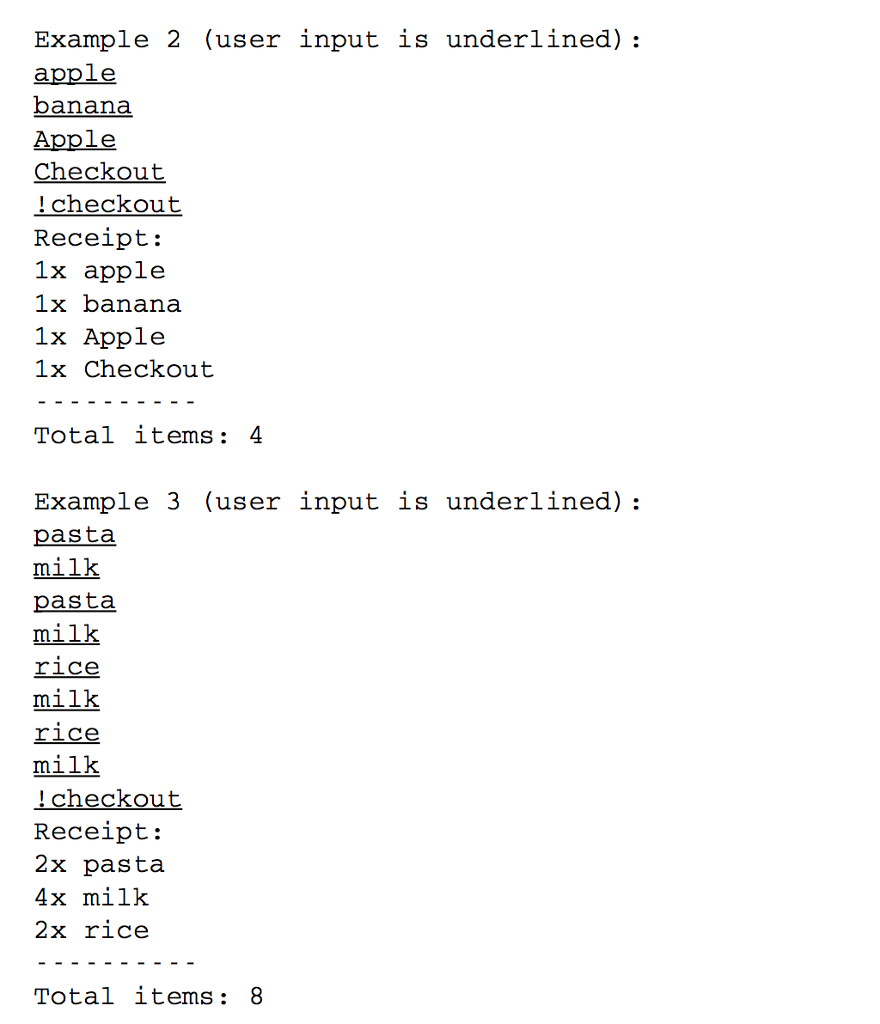
(((Checkout.cpp)))
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
string int2str(int x);
class GroceryList
{
// Make me!
};
int main()
{
GroceryList gl;
string item;
getline(cin, item);
while(item != "!checkout")
{
gl.add(item);
getline(cin, item);
}
int size;
string* receipt = gl.checkout(size); // this should initialize size
cout
int maxLen = 0;
for(int i=0; i
{
cout
if(static_cast
{
maxLen = receipt[i].length();
}
}
for(int i=0; i
{
cout
}
cout
cout
delete [] receipt;
return 0;
}
string int2str(int x)
{
string reverse = "";
int pos = abs(x);
while(pos > 0)
{
reverse += ('0'+pos%10);
pos/=10;
}
if(reverse.length() == 0)
{
return "0";
}
string result = "";
if(x
{
result += '-';
}
for(int i=0; i (reverse.length()); i++)
{
result += reverse[reverse.length()-1-i];
}
return result;
}
Problem A: Polynomial multiplication (20 points) Start with the polynomial.cpp file provided. This is a basic outline of the class, which reads the in the polynomial from the keyboard. You must overload the multiplication operator to multiply polynomials together (i.e., FOIL arbitrary dimension polynomials'). Also overload for cout and make sure you follow the formatting shown below exactly The program provided has no memory leaks, and your submission should not not leak memory as well. In other words, if you create dynamic memory you also need to delete it somewhere in the code. [Hint: What is the relationship to the index and the power of "x"?] Example 1 (user input is underlined): What are the coefficients of first polynomial lowest power first) What are the coefficients of second polynomial (lowest power first) 4 5 6 (1) (2) x A1 (3)x12 (4) (5) x A1 (6) x A2 (4) (13) xA1 (28) xA2 (27)xA3 (18) xA4 Example 2 (user input is underlined: What are the coefficients of first polynomial lowest power first) 1 2 1 What are the coefficients of second polynomial (lowest power first) (1) (-2) xA1 (1)x12 (-1) (-1) (2) A1 (-1) *A2 Problem A: Polynomial multiplication (20 points) Start with the polynomial.cpp file provided. This is a basic outline of the class, which reads the in the polynomial from the keyboard. You must overload the multiplication operator to multiply polynomials together (i.e., FOIL arbitrary dimension polynomials'). Also overload for cout and make sure you follow the formatting shown below exactly The program provided has no memory leaks, and your submission should not not leak memory as well. In other words, if you create dynamic memory you also need to delete it somewhere in the code. [Hint: What is the relationship to the index and the power of "x"?] Example 1 (user input is underlined): What are the coefficients of first polynomial lowest power first) What are the coefficients of second polynomial (lowest power first) 4 5 6 (1) (2) x A1 (3)x12 (4) (5) x A1 (6) x A2 (4) (13) xA1 (28) xA2 (27)xA3 (18) xA4 Example 2 (user input is underlined: What are the coefficients of first polynomial lowest power first) 1 2 1 What are the coefficients of second polynomial (lowest power first) (1) (-2) xA1 (1)x12 (-1) (-1) (2) A1 (-1) *A2Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


