Question
Prepare income statements under both variable and absorption costing for two consecutive years; compare and explain key differences . Adrena was in her first year
Prepare income statements under both variable and absorption costing for two consecutive years; compare and explain key differences.
Adrena was in her first year of work at an accounting services firm after earning her degree. She had become very comfortable preparing financial statements for many different companies that used standard costing within their absorption costing systems. Her supervisor came to her with a slightly different assignment today, though: One of their clients needed its standard, absorption costing income statements prepared, as usual, but the client also requested the same-period financial statements be presented under variable costing. Adrena's supervisor explained that it had something to do with a different benchmark from which they might award bonuses to their employees. Adrena was intrigued, because she didn't remember off the top of her head if these two income statement formats would generate the same income or not.
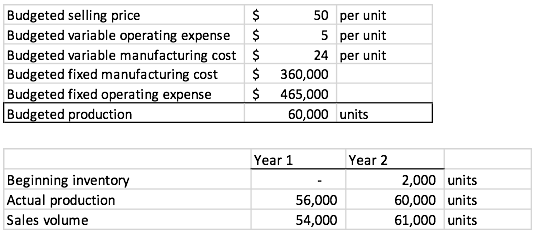
She gathered the following information in preparation for her work, noting there were no price, efficiency, or spending variances in either year. If there was a Fixed-MOH volume variance, company policy was to write it off directly to cost of goods sold:
Required:
a) Prepare income statements for both years under the client's original absorption costing method, in good form.
b) Prepare income statements for both years under the variable costing method, in good form.
c) For Year 1, determine any difference in income between the two methods, and explain any difference.
d) For Year 2, determine any difference in income between the two methods, and explain any difference.
e) As if you are Adrena, explain clearly the key difference(s) between these two methods so the client can decide which method to use for bonus distribution decisions.
Budgeted selling price $ 50 per unit Budgeted variable operating expense $ 5 per unit Budgeted variable manufacturing cost $ 24 per unit Budgeted fixed manufacturing cost $ 360,000 Budgeted fixed operating expense $ 465,000 Budgeted production 60,000 units Year 1 Beginning inventory Actual production Sales volume Year 2 2,000 units 60,000 units 61,000 units 56,000 54,000 Budgeted selling price $ 50 per unit Budgeted variable operating expense $ 5 per unit Budgeted variable manufacturing cost $ 24 per unit Budgeted fixed manufacturing cost $ 360,000 Budgeted fixed operating expense $ 465,000 Budgeted production 60,000 units Year 1 Beginning inventory Actual production Sales volume Year 2 2,000 units 60,000 units 61,000 units 56,000 54,000Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


