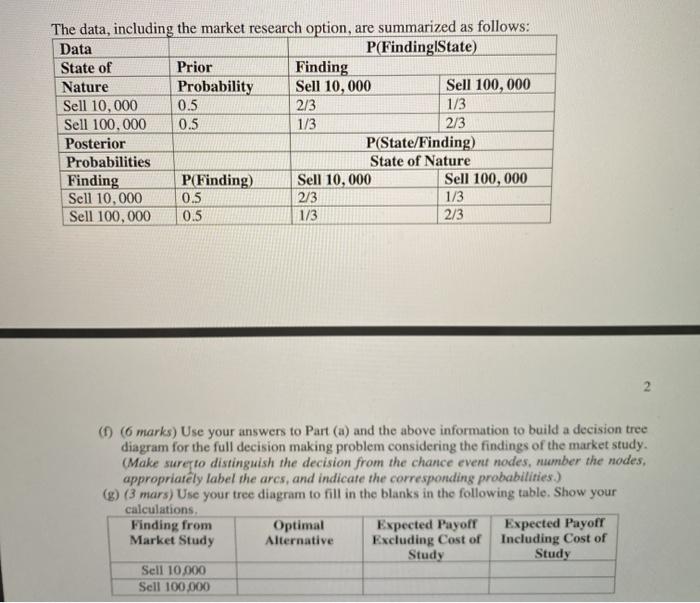
Problem 1. (28 Marks in total) A company has developed a new process that will enable it to begin producing and marketing a new product if it so desires. Alternatively, it can sell the rights to the new process for $15 million. If the company chooses to produce the new product, the profitability of the venture depends upon the company's ability to market the product during the first year. It has sufficient access to retail outlets that it can guarantee sales of 10,000 units. On the other hand, if this product catches on, the company can sell 100,000 units. For analysis purposes, these two levels of sales are taken to be the two possible outcomes of marketing the product, and are assumed to be equally likely (i.e. the prior probabilities of the two levels of sales are both 0.5). The cost of setting up the assembly line is $6 million. The difference between the selling price and the variable cost of each unit of product is $600. (a) (4 marks) Develop a decision analysis formulation of this problem by identifying the decision alternatives, the states of nature, and the payoff table. (b) (2 marks) What is the best alternative under the optimistic approach? (Show your calculations) (a) (2 marks) What is the best alternative under the conservative approach? (Show your calculations) (b) (3 marks) Use the minmax regret approach to find the best alternative. (Show your calculations) (c) (3 marks) What is the best alternative, if the expected value approach is used? (Show your steps) (d) (3 marks) Calculate the value of perfect information (EVPD). Management of the company now is considering doing a full-fledged market research at a cost of $1 million to predict which of the two levels of demand is likely to occur. Previous experience indicates that such market research is correct two thirds of the time (e) (2 marks) Based on your answer to Part (d), might it be worth doing the full-fledged market research? Please, explain your answer. The data, including the market research option, are summarized as follows: Data P(Finding State) State of Prior Finding Nature Probability Sell 10,000 Sell 100,000 Sell 10,000 0.5 2/3 1/3 Sell 100,000 0.5 2/3 Posterior P(State/Finding) Probabilities State of Nature Finding P(Finding) Sell 10,000 Sell 100,000 Sell 10.000 0.5 2/3 1/3 Sell 100,000 0.5 1/3 2/3 1/3 2 ( 6 marks) Use your answers to Part (a) and the above information to build a decision tree diagram for the full decision making problem considering the findings of the market study. (Make sure to distinguish the decision from the chance event nodes, number the nodes, appropriately label the ares, and indicate the corresponding probabilities.) (g) (3 mars) Use your tree diagram to fill in the blanks in the following table. Show your calculations Finding from Optimal Expected Payoff Expected Payoff Market Study Alternative Excluding Cost of Including Cost of Study Study Sell 10.000 Sell 100.000