Question
Problem 1 Maria's Knick Knacks is a boutique store that sells seasonal merchandise. For this Christmas season, Maria paid $50,000 for an order of figurines,
Problem 1
Maria's Knick Knacks is a boutique store that sells seasonal merchandise. For this Christmas season, Maria paid $50,000 for an order of figurines, tree ornaments, candles, and wreaths. Maria marks up each piece of merchandise by 80% to arrive at the selling price. Thus, if Maria pays $20 for a figurine, she will price it at $36.
Unfortunately, sales were well below expectations, and Maria's revenues were only $60,000 (far less than the $90,000, or $50,000 1.80, that she had hoped for). This presents a quandary for Maria, who is contemplating what to do with the unsold merchandise. She has identified five options.
Option 1: To store the unsold merchandise for the next 10 months and attempt to sell it the next Christmas season. Maria estimates that it would cost her $4,000 to properly pack, store, and then unpack all of the unsold merchandise. In addition, because the merchandise would be somewhat dated, Maria believes that she will only be able to sell 30% of the remaining merchandise the following year (at the current year's retail price). Any unsold items will have negligible resale value, and Maria plans to donate them to a local charity.
Option 2: Hold a January "85% off" after-Christmas sale. Maria believes that she can sell 100% of the unsold merchandise with 85% off sale.
Option 3: Hold a January "75% off" after-Christmas sale. Maria believes that she can sell 60% of the unsold merchandise with 75% off sale.
Option 4: Hold a January "65% off" after-Christmas sale. Maria believes that she can sell 50% of the unsold merchandise with 65% off sale.
Option 5: Hold a January "55% off" after-Christmas sale. Maria believes that she can sell 35% of the unsold merchandise with 55% off sale.
These are the only options Maria plans to consider.
Required:
a)What is the net cash flow associated with each of Maria's options?
b)Based on your answer to part (b), what is the opportunity cost associated with each option?
c)What would you recommend to Maria?
Problem 2
Ron Clark is considering the wisdom of reducing the number of suppliers his firm uses. Currently, Clark uses 30 suppliers to purchase goods worth $4,500,000 per year. To manage the orders and coordinate with suppliers, Ron employs one supervisor and two clerical staff. The manager earns $120,000 per year and each clerical staff person earns $60,000 per year. (As VP, Ron Clark earns $250,000 annually.) Reducing the number of suppliers from 30 to 10 would allow Clark to free up one of the clerical staff. While the supervisor would "supervise" fewer people, she also would interact more with each supplier; thus, her workload would not change appreciably.
Clark bargains aggressively with suppliers, and, with 30 suppliers, he was anticipating a 8% savings in purchase costs next year. With only 10 suppliers, however, each supplier would have greater bargaining power, eliminating Ron's ability to reduce the prices paid for goods. Finally, Clark believes that better coordination with fewer suppliers would increase service quality (e.g., a lower risk of stock outs and other problems), and he estimates the cost savings at $200,000 per year.
Required:
a.Classify the following costs as to their relevance and controllability for Clark's decision: (1) Cost of goods purchased; (2) Clerical staff salaries; (3) Supervisor's salary; (4) Service quality cost savings; and (5) Ron Clark's salary. (note the status quo for Clark is using 30 suppliers). You may use the following tabular format for convenience.
Cost/BenefitControllable?(Y/N) Relevant?(Y/N)Explain
Cost of goods
Clerical salary
Supervisor salary
Cost savings
Ron Clark's salary
b.Should Ron use 30 or 10 suppliers? What would be the net financial impact (only consider relevant costs and benefits)?
Problem 3
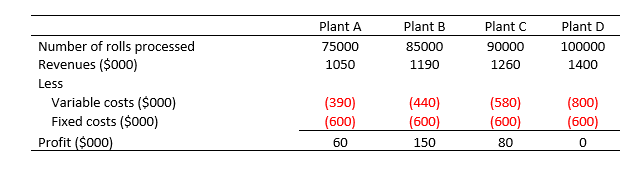
ABC Company operates four film developing plants in upstate Pennsylvania. The four plants are identical. They employ the same production technology, process the same mix, and buy raw materials from the same companies at the same prices. Wage rates are also the same at four plants. In reviewing the operating results for November, the newly hired assistant controller, Jason Bauer, became quite confused over the numbers.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


