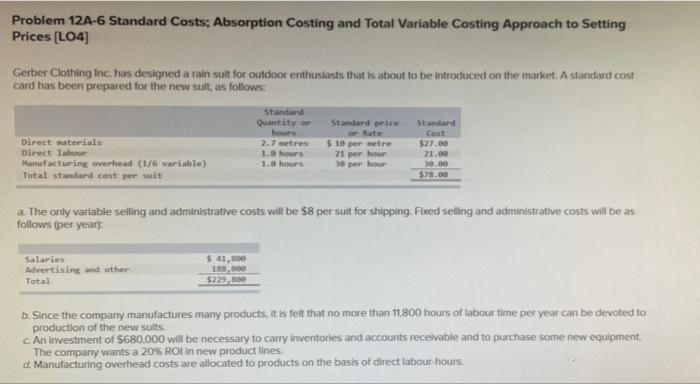
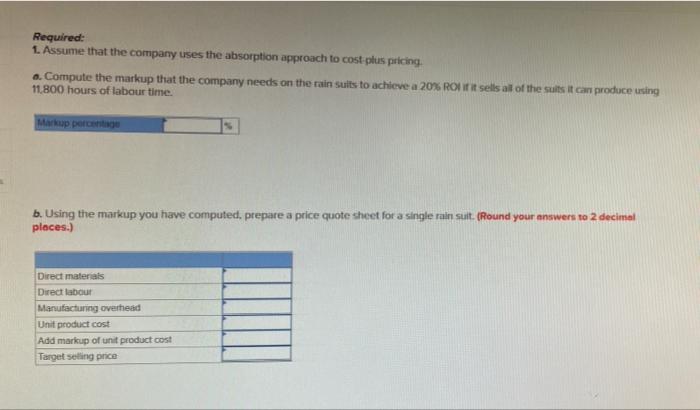
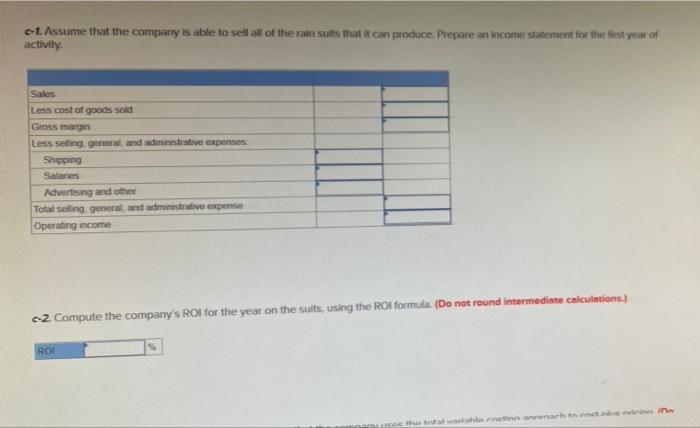
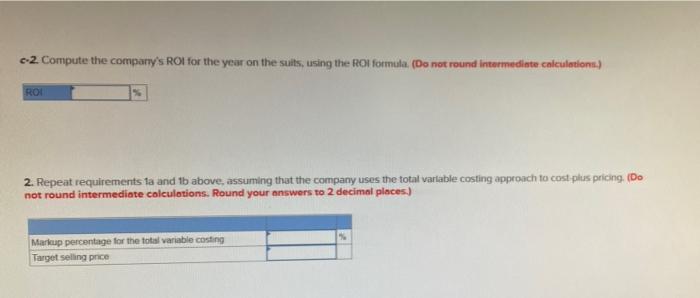
Problem 12A-6 Standard Costs: Absorption Costing and Total Variable Costing Approach to Setting Prices [LO4) Gerber Clothing Inc. has designed a rain sult for outdoor enthusiasts that is about to be introduced on the market. As standard cost card has been prepared for the new sult, as follows: Standard Quantity or Standard price Standard hours on Rate cost Direct materials 2.7 metres $10 per tre $27.00 Direct Labour 1.0 hours 21 per hour 21.00 Manufacturing overhead (1/6 variable) 1.0 hours 0 per hour Total standard cost per suit $7.00 30.00 a The only variable selling and administrative costs will be $8 per suit for shipping. Fixed selling and administrative costs will be as follows (per years: Salaries Advertising and other $ 41, 188,000 $229,500 Total b. Since the company manufactures many products. It is felt that no more than 11.800 hours of labour time per year can be devoted to production of the new suits An investment of S680.000 will be necessary to carry inventories and accounts receivable and to purchase some new equipment The company wants a 20% ROI in new product lines d. Manufacturing overhead costs are allocated to products on the basis of direct labour hours Required: 1. Assume that the company uses the absorption approach to cost plus pricing o. Compute the markup that the company needs on the rain suits to achieve a 20% Ronit sells all of the suits it can produce using 11,800 hours of labour time. Markup percentage b. Using the markup you have computed, prepare a price quote sheet for a single rain suit. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) Direct materials Direct labour Manufacturing overhead Unit product cost Add markup of unit product cost Target selling price c-L Assume that the company is able to sell all of the rain sults that it can produce. Prepare an income statement for the first year of activity Sales Eess cost of goods sold Gross margin Less selling general and administrative expenses Shipping Salanes Advertising and other Total selling general, and administrative expense Operating income c-2 Compute the company's ROI for the year on the suits, using the ROI formula. (Do not round intermediate calculations.) ROS that c-2. Compute the company's Rol for the year on the suits, using the Rol formula. (Do not round intermediate calculations.) ROS 2. Repeat requirements fa and 1b above, assuming that the company uses the total variable costing approach to cost.plus pricing. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) Markup percentage for the total variable costing Target selling price