

 Problem 2 is the only question needed. Provided code structure and expected output. Please help and use C, thank you!
Problem 2 is the only question needed. Provided code structure and expected output. Please help and use C, thank you!
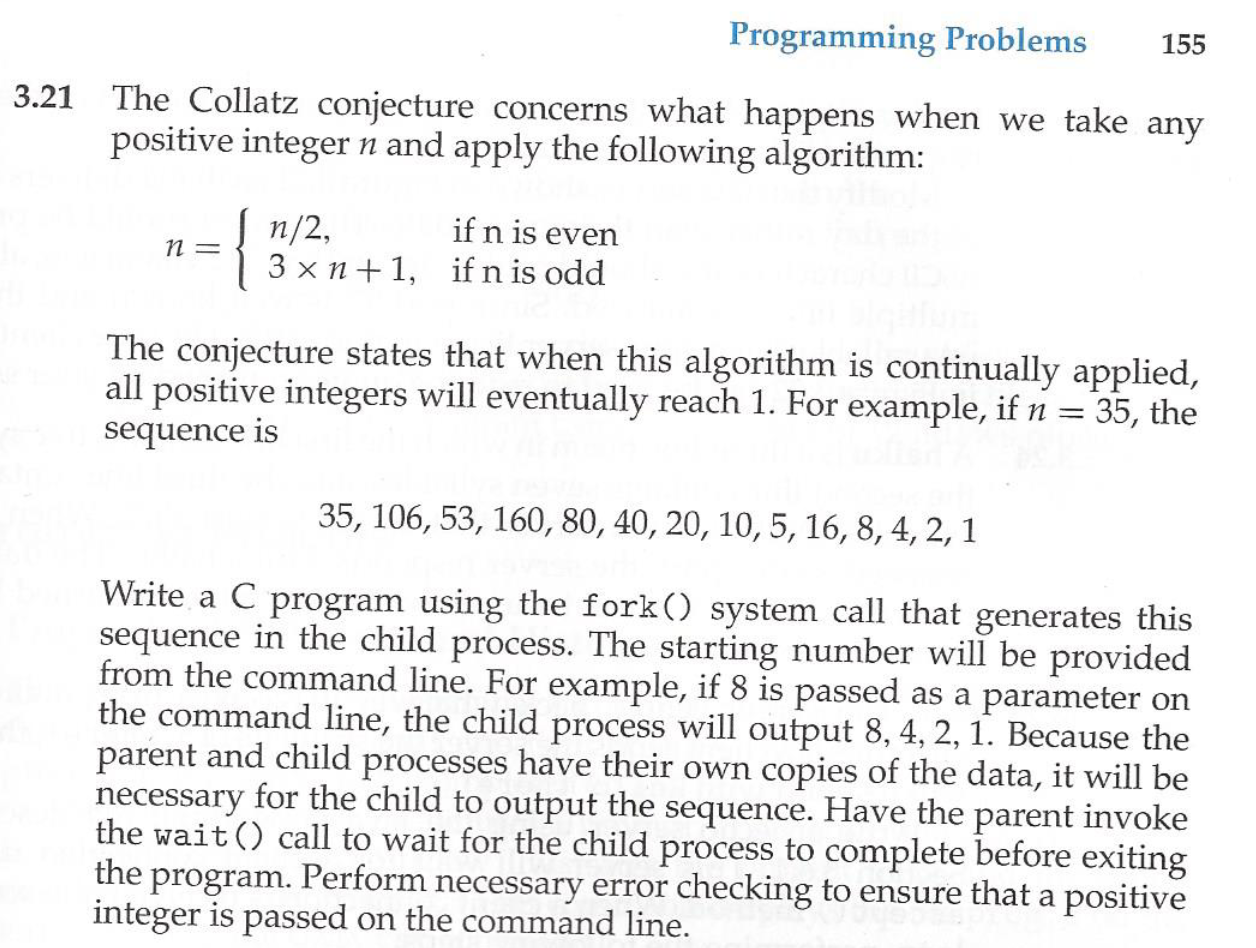
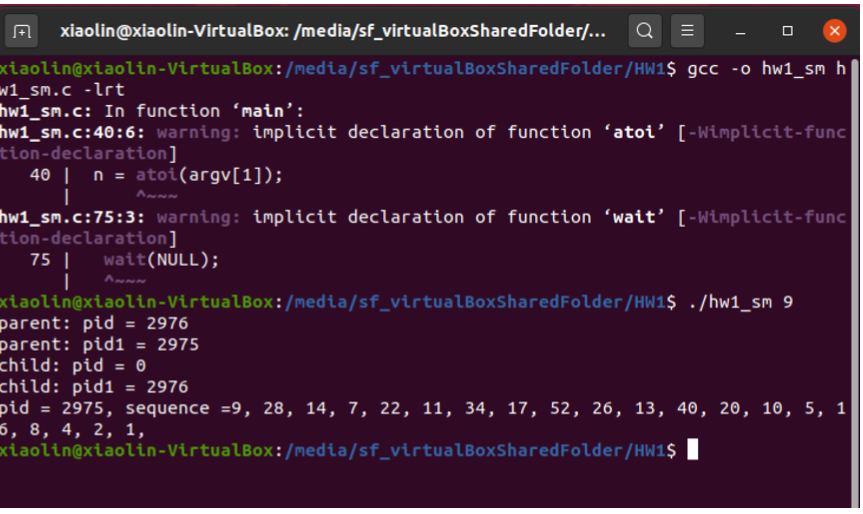
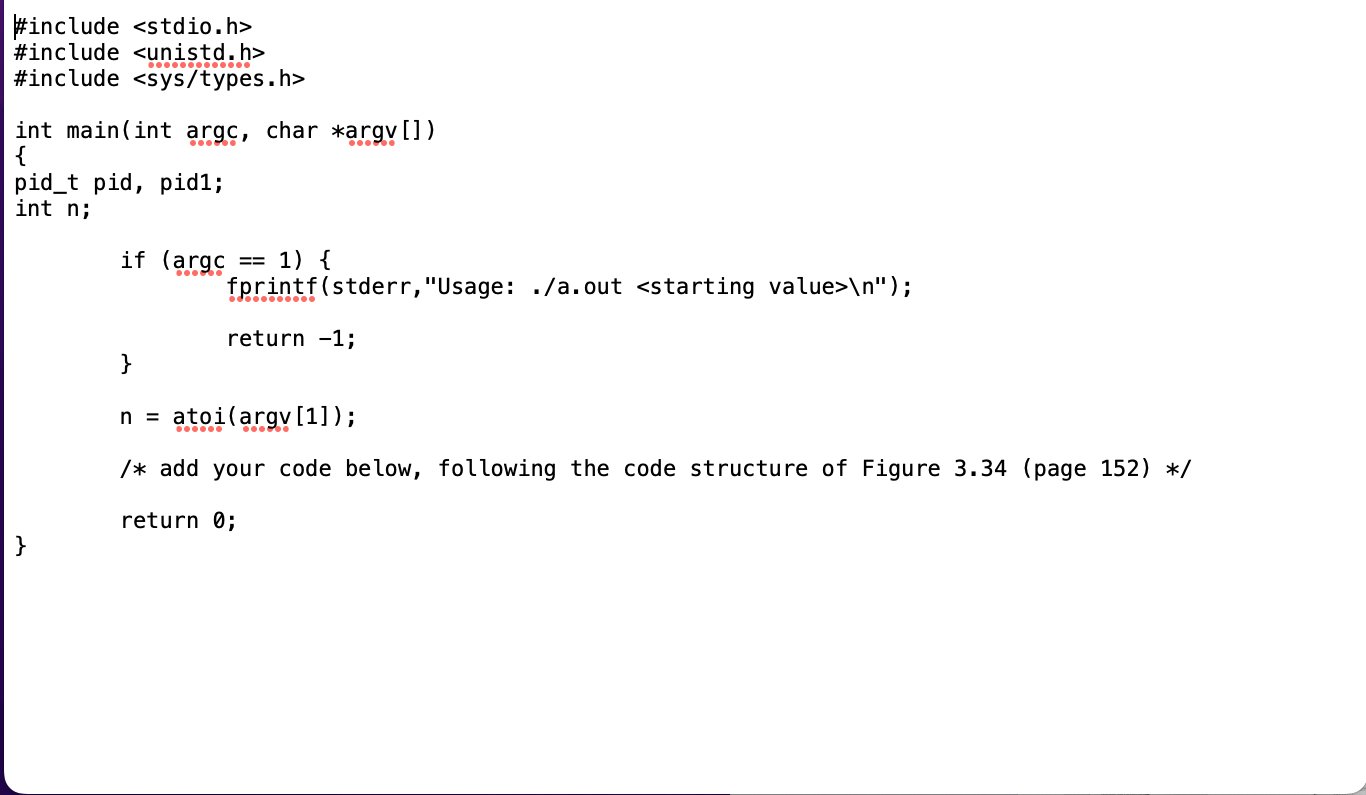
Programming problem 3.22 (page 155), with the following extra information/requirements: 1. This problem is an extension of the previous problem. So your code should have the same structure as the hw1.c, with the only difference being using shared memory to pass the sequence to the parent process as described in programming problem 3.22 (page 155). Name your solution as hw1 sm.c 2. Similar as the previous problem, your program should display the process IDs of both the parent and child processes. The parent and child processes print the IDs in their own processes in the same way as in the previous problem. 3. When the parent process prints the sequence (from the shared memory), it needs to add its own process ID before the sequence. This allows us to check if the sequence is indeed printed by the parent process. See the sample screenshot below. 4. When following the POSIX shared memory code described in Section 3.5.1, you need to include \#include in your .c file. Otherwise there will be compilation errors. Note: this is not described in the textbook. 5. When compiling, you need to add the -lrt option, e.g., gcc -o hw1_sm hw1_sm.c -lrt. See sample screenshot below. What to submit (submit through iCollege): Upload program file hw1 sm.c and include the following in the project report (named as "HW1.pdf" or "HW1.doc"): 1) a sample screenshot of the output; 2) the source code of hwl_sm.c. Sample compiling and output screenshot 22 In Exercise 3.21, the child process must output the sequence of numbers generated from the algorithm specified by the Collatz conjecture because the parent and child have their own copies of the data. Another approach to designing this program is to establish a shared-memory object between the parent and child processes. This technique allows the child to write the contents of the sequence to the shared-memory object. The parent can then output the sequence when the child completes. Because the memory is shared, any changes the child makes will be reflected in the parent process as well. This program will be structured using POSIX shared memory as described in Section 3.5.1. The parent process will progress through the following steps: a. Establish the shared-memory object (shm_open (), ftruncate(), and mmap()). b. Create the child process and wait for it to terminate. c. Output the contents of shared memory. d. Remove the shared-memory object. One area of concern with cooperating processes involves synchronization issues. In this exercise, the parent and child processes must be coordinated so that the parent does not output the sequence until the child finishes execution. These two processes will be synchronized using the wait () system call: the parent process will invoke wait(), which will suspend it until the child process exits. 1 The Collatz conjecture concerns what happens when we take any positive integer n and apply the following algorithm: n={n/2,3n+1,ifnisevenifnisodd The conjecture states that when this algorithm is continually applied, all positive integers will eventually reach 1 . For example, if n=35, the sequence is 35,106,53,160,80,40,20,10,5,16,8,4,2,1 Write a C program using the fork () system call that generates this sequence in the child process. The starting number will be provided from the command line. For example, if 8 is passed as a parameter on the command line, the child process will output 8,4,2,1. Because the parent and child processes have their own copies of the data, it will be necessary for the child to output the sequence. Have the parent invoke the wait () call to wait for the child process to complete before exiting the program. Perform necessary error checking to ensure that a positive integer is passed on the command line. xiaolin@xiaolin-VirtualBox: /media/sf_virtualBoxSharedFolder/




 Problem 2 is the only question needed. Provided code structure and expected output. Please help and use C, thank you!
Problem 2 is the only question needed. Provided code structure and expected output. Please help and use C, thank you!





