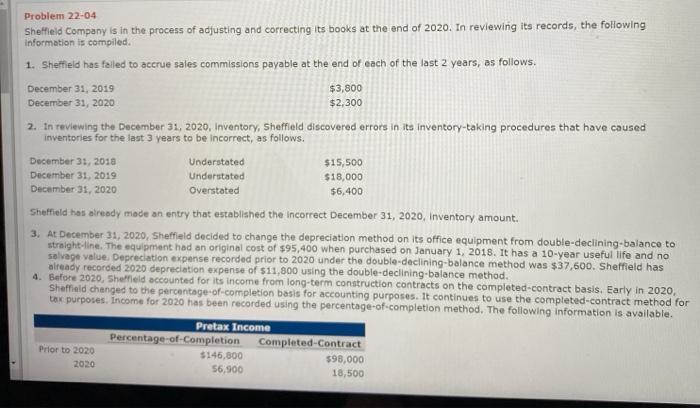
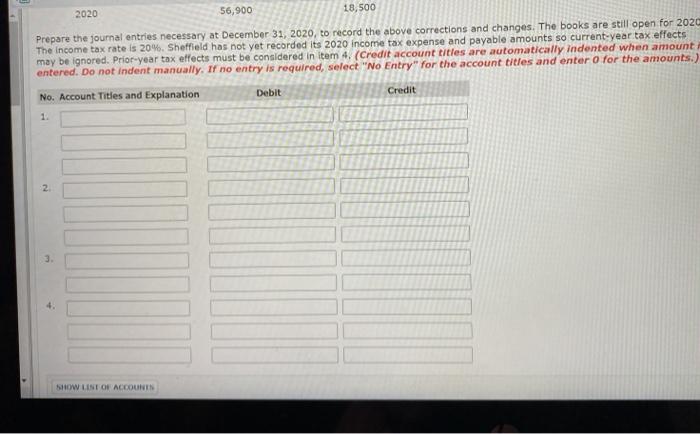
Problem 22-04 Sheffield Company is in the process of adjusting and correcting its books at the end of 2020. In reviewing its records, the following Information is compiled 1. Sheffield has failed to accrue sales commissions payable at the end of each of the last 2 years, as follows. December 31, 2019 $3,800 December 31, 2020 $2,300 2. In reviewing the December 31, 2020, Inventory, Sheffield discovered errors in its inventory-taking procedures that have caused inventories for the last 3 years to be incorrect, as follows. December 31, 2018 Understated $15,500 December 31, 2019 Understated $18,000 December 31, 2020 overstated $6,400 Sheffield has already made an entry that established the incorrect December 31, 2020, Inventory amount. 3. At December 31, 2020, Sheffield decided to change the depreciation method on its office equipment from double-declining-balance to straight-line. The equipment had an original cost of $95,400 when purchased on January 1, 2018. It has a 10-year useful life and no selvage value. Depreciation expense recorded prior to 2020 under the double-declining balance method was $37,600. Sheffield has already recorded 2020 depreciation expense of $11,800 using the double-declining-balance method. 4. Before 2020, Sheffield accounted for its income from long-term construction contracts on the completed-contract basis. Early in 2020, Sheffield changed to the percentage-of-completion basis for accounting purposes. It continues to use the completed-contract method for tax purposes. Income for 2020 has been recorded using the percentage-of-completion method. The following information is available. Pretax Income Percentage-of-Completion Completed-Contract Prior to 2020 $146.800 $98,000 2020 56,900 18,500 2020 56,900 18,500 Prepare the journal entries necessary at December 31, 2020, to record the above corrections and changes. The books are still open for 2020 The income tax rate is 20%. Sheffield has not yet recorded its 2020 income tax expense and payable amounts so current-year tax effects may be ignored. Prior-year tax effects must be considered in Item 4. (Credit account titles are automatically indented when amount entered. Do not indent manually. If no entry is required, select "No Entry" for the account titles and enter o for the amounts.) No. Account Titles and Explanation Debit Credit 1. 3 SHOW LINT OF ACCOUNT List Of Accounts Problem 22-04 Accounts Payable Accounts Receivable Accumulated Depreciation-Buildings Accumulated Depreciation Equipment Accumulated Depreciation-Machinery Advertising Expense Amortization Expense Allowance for Doubtful Accounts Bad Debt Expense Cash Compensation Expense Consignment Out Construction in Process Copyrights Cost of Goods Sold Deferred Gross Profit Deferred Tax Liability Depreciation Expense Dividend Revenue Due to Customer Discount on Bonds Payable Equipment Equity Investments Equity Investments (Available-for-Sale) Equity Investments (Equity Method) Fair Value Adjustment Finance Expense Gain on Disposal of Plant Assets Holding Gain or Loss-Investments Income Tax Receivable Insurance Expense Interest Expense Interest Payable Interest Receivable Interest Revenue Inventory Inventory on Consignment Fair Value Adjustment Finance Expense Gain on Disposal of Plant Assets Holding Gain or Loss-Investments Income Tax Receivable Insurance Expense Interest Expense Interest Payable Interest Receivable Interest Revenue Inventory Inventory on Consignment Investment Revenue Lawsuit Liability Lawsuit Loss Loss Due to Market Decline of Inventory Machinery Maintenance and Repairs Expense No Entry Prepaid Insurance Property, Plant and Equipment Purchases Rent Revenue Retained Earnings Revenue from Investment Salaries and Wages Expense Salaries and Wages Payable Sales Sales Commission Expense Sales Commission Payable Sales Revenue Sales Tax Expense Sales Tax Payable Share Capital Supplies Supplies Expenses Trademarks Unearned Rent Revenue Unrealized Holding Gain or Loss-Equity Unrealized Holding Gain or Loss-Income Warranty Expense Warranty Liability